Похожие презентации:
Random variables (lecture VI)
1.
LECTURE 6DISCRETE RANDOM VARIABLES &
PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS
2.
RANDOM VARIABLESA random variable is a variable that takes on numerical values
determined by the outcome of a random experiment.
3.
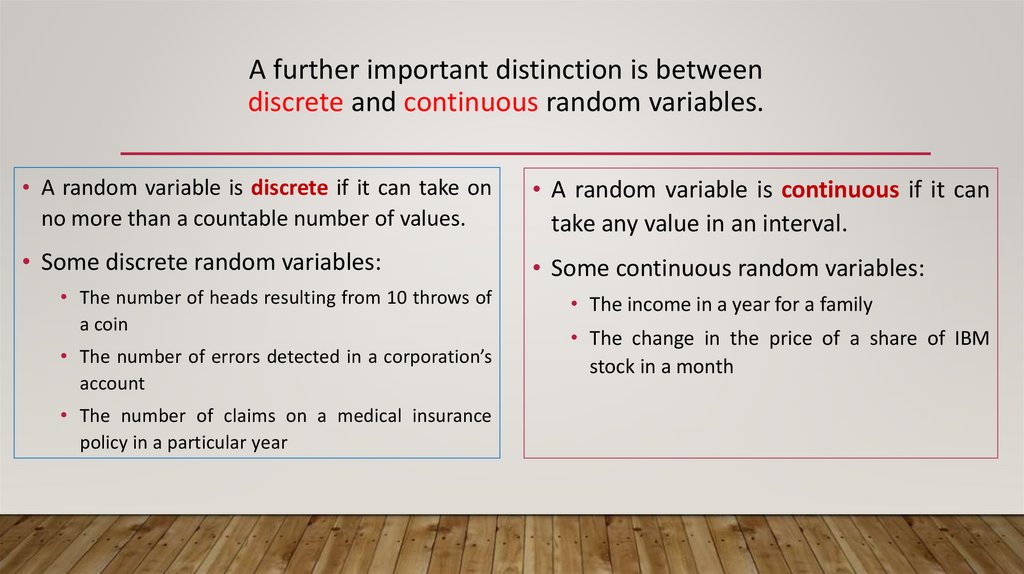
A further important distinction is betweendiscrete and continuous random variables.
• A random variable is discrete if it can take on
no more than a countable number of values.
• A random variable is continuous if it can
take any value in an interval.
• Some discrete random variables:
• Some continuous random variables:
• The number of heads resulting from 10 throws of
a coin
• The number of errors detected in a corporation’s
account
• The number of claims on a medical insurance
policy in a particular year
• The income in a year for a family
• The change in the price of a share of IBM
stock in a month
4.
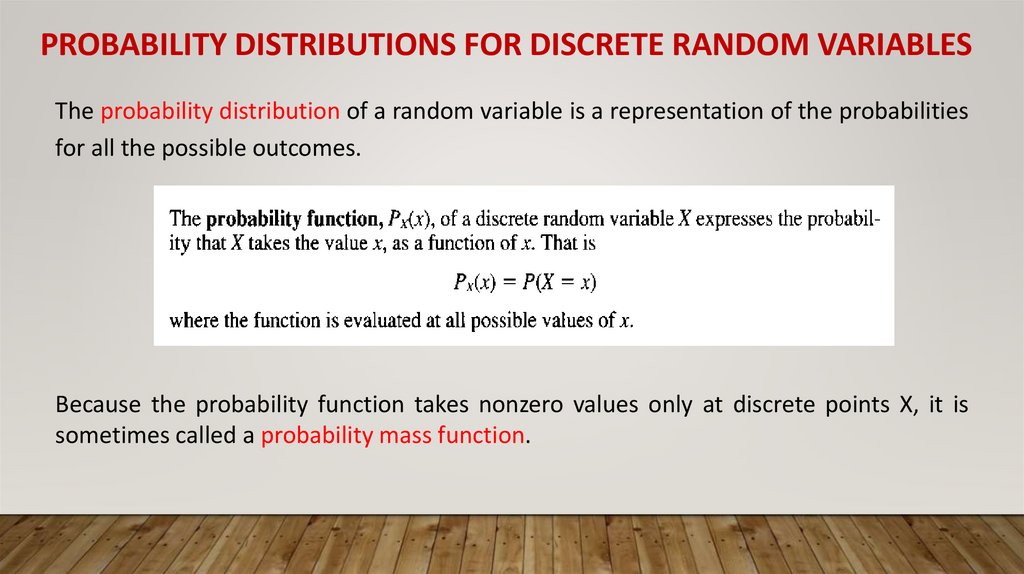
PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS FOR DISCRETE RANDOM VARIABLESThe probability distribution of a random variable is a representation of the probabilities
for all the possible outcomes.
Because the probability function takes nonzero values only at discrete points X, it is
sometimes called a probability mass function.
5.
PROPERTIES OF PROBABILITY FUNCTIONS OF DISCRETE RANDOMVARIABLES
6.
CUMULATIVE PROBABILITY FUNCTION7.
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN PROBABILITY FUNCTION ANDCUMULATIVE PROBABILITY FUNCTION
8.
PROPERTIES OF CUMULATIVE PROBABILITY FUNCTIONS FORDISCRETE RANDOM VARIABLES
9.
EXPECTATIONS FOR DISCRETE RANDOM VARIABLES10.
EXPECTATIONS FOR DISCRETE RANDOM VARIABLES11.
Ex: The probability function for the number of errors, X, on pages from an economics textbook is:Px(0) = 0.81
Px(1) = 0.17
Px(2) = 0.02
Find the mean number of errors per page.
12.
EXPECTATIONS FOR DISCRETE RANDOM VARIABLES13.
EXPECTATIONS FOR DISCRETE RANDOM VARIABLES14.
EXPECTATIONS FOR DISCRETE RANDOM VARIABLES15.
Ex: A coin has been thrown three times. What’s the expected value of the number of tails?16.
Ex: A businessman made an investment. He will get 100 billion TL profit with 60% probability, 200 billion TLprofit with 25% probability; and 600 billion TL loss with 15% probability. Calculate the expected value for this
investment.
17.
Ex: In a lottery conducted to benefit the local fire company, 8000 tickets are to be sold at $5. The prize is$12,000. If you purchase two tickets, what is your expected gain?
18.
Ex: A contracter is interested in the total cost of a project on which he intends to bid. He estimates thatmaterials will cost $25,000 and the labor costs will be $900 per day. If the project takes X days to complete,
the total labor costs will be 900X and the total cost of the project (in dollars) will be: C= 25,000 + 900X
The contracter forms subjective probability assestments of likely compeltion times for the project, as
indicated in the table:
Completion time X days
10
11
12
13
14
Probability
0.1
0.3
0.3
0.2
0.1
Estimate the mean and variance of the expected cost for this project.
19.
Ex: A corporation produces packages of paper clips. The number of clips per package varies as indicated in the table below:Number of Clips
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
Proportion of
Packages
0.04
0.13
0.21
0.29
0.20
0.10
0.03
a) Find the mean and standard deviation of the number of paper clips per package.
b) The cost (in cents) of producing a package of clips is 16 + 2X, where X is the number of clips in the package. The revenue
from selling the package, however many clips it contains, is $1.5. If profit is defined as “the difference between revenue
and cost”, find the mean and standard deviation of profit per package.

















 Математика
Математика








