Похожие презентации:
Dialog+ SW 9.xx Hydraulics. Service Training Documentation
1. Folie 1
Dialog+ SW 9.xxHydraulics
Technical Support International
Enter
Service Training Documentation – no update service. This document may not be copied, partly or whole, or
made be accessible to third parties without our permission and remains the property of B. Braun Avitum AG
with all rights.
DialogP SW9.xx_std_Hydraulics Rev 1.02 2011-12-08
2. Folie 2
Dialog+Dialog+ Overview
Welcome to the Dialog+ Component Overview. Here you will have the opportunity to look
at different components in the machine. You will find out what there functions are, and
how they work together with other components.
Internal Hydraulics
Hydraulics Test
3. Folie 3
StartDialog+
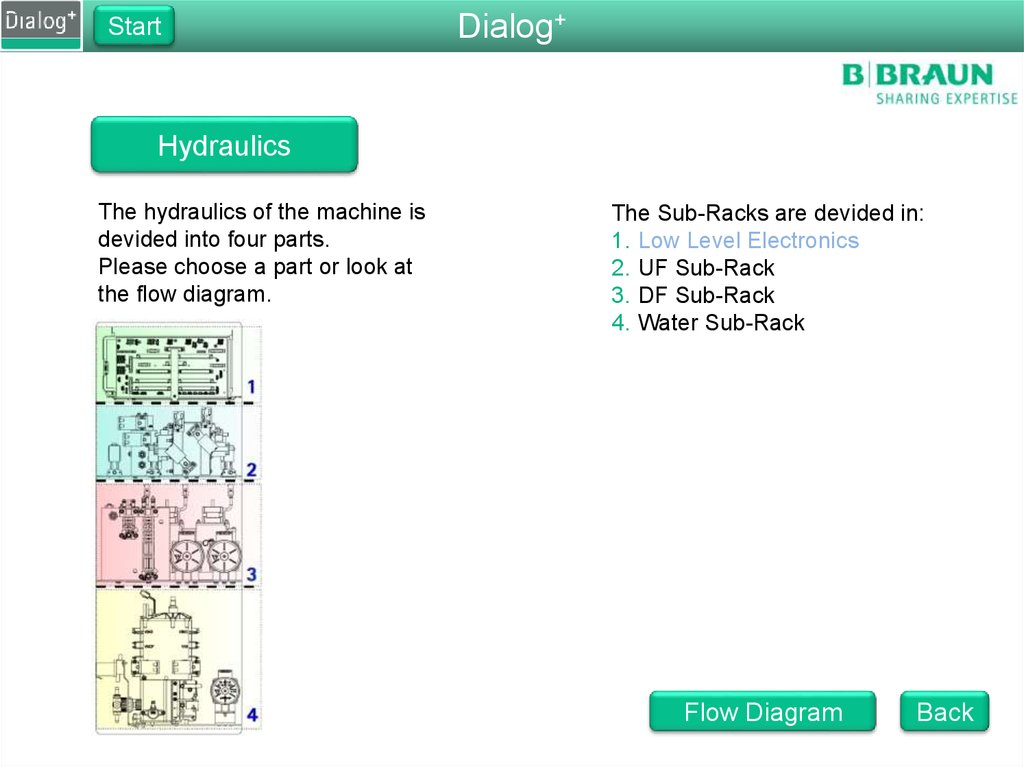
Hydraulics
The hydraulics of the machine is
devided into four parts.
Please choose a part or look at
the flow diagram.
The Sub-Racks are devided in:
1. Low Level Electronics
2. UF Sub-Rack
3. DF Sub-Rack
4. Water Sub-Rack
Flow Diagram
Back
4. Folie 4
StartDialog+
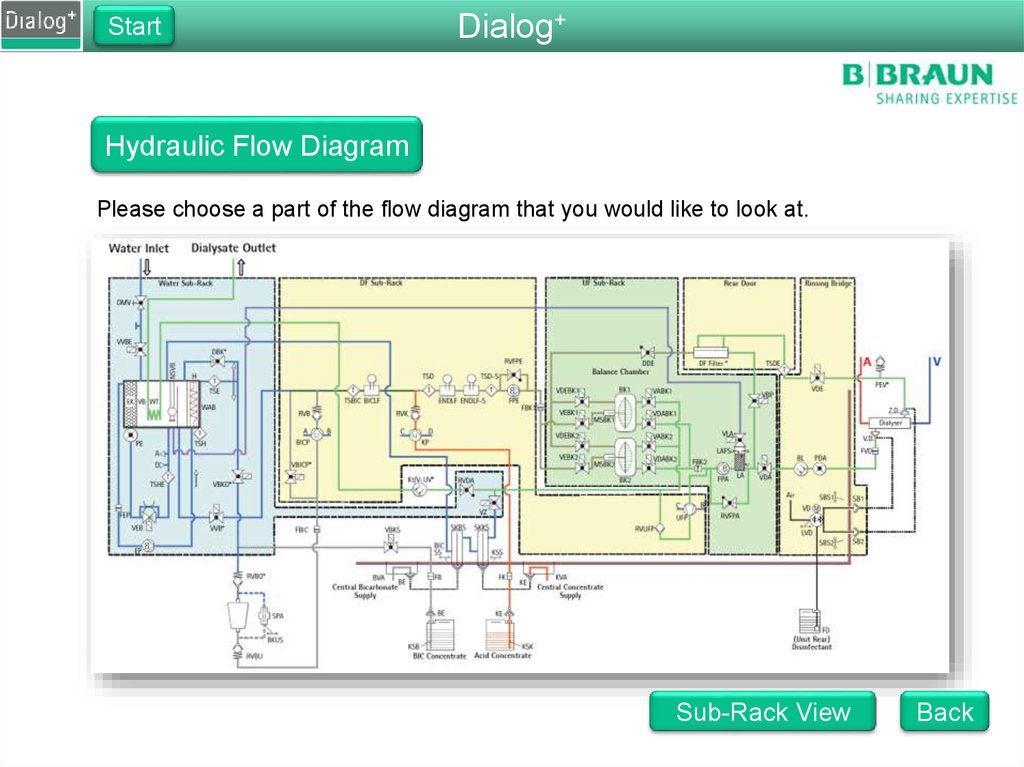
Hydraulic Flow Diagram
Please choose a part of the flow diagram that you would like to look at.
Sub-Rack View
Back
5. Folie 5
StartDialog+
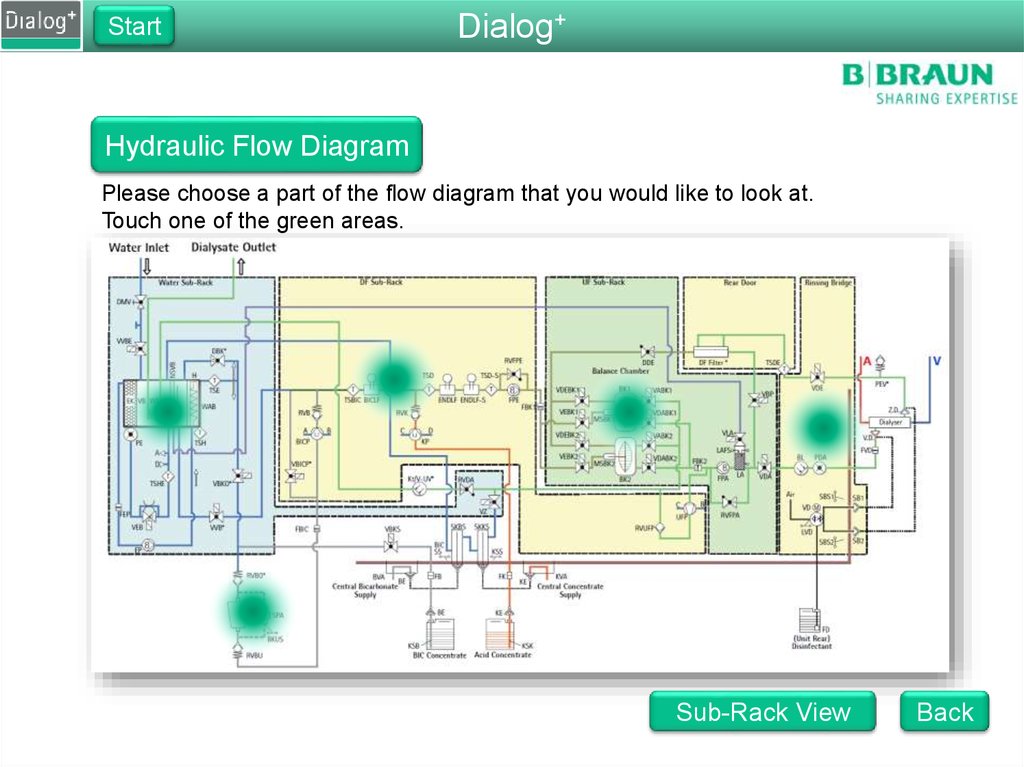
Hydraulic Flow Diagram
Please choose a part of the flow diagram that you would like to look at.
Touch one of the green areas.
Sub-Rack View
Back
6. Folie 6
Water Sub-RackStart
Water Sub-Rack
Functions of the Water Sub-Rack
Controls incoming water amount
Degasses the water
Heats the water
Contains bicarbonate valves
Degassing Circuit
Heating Regulation
Water Inlet
Water Block
Degassing Pump
Back
7. Folie 7
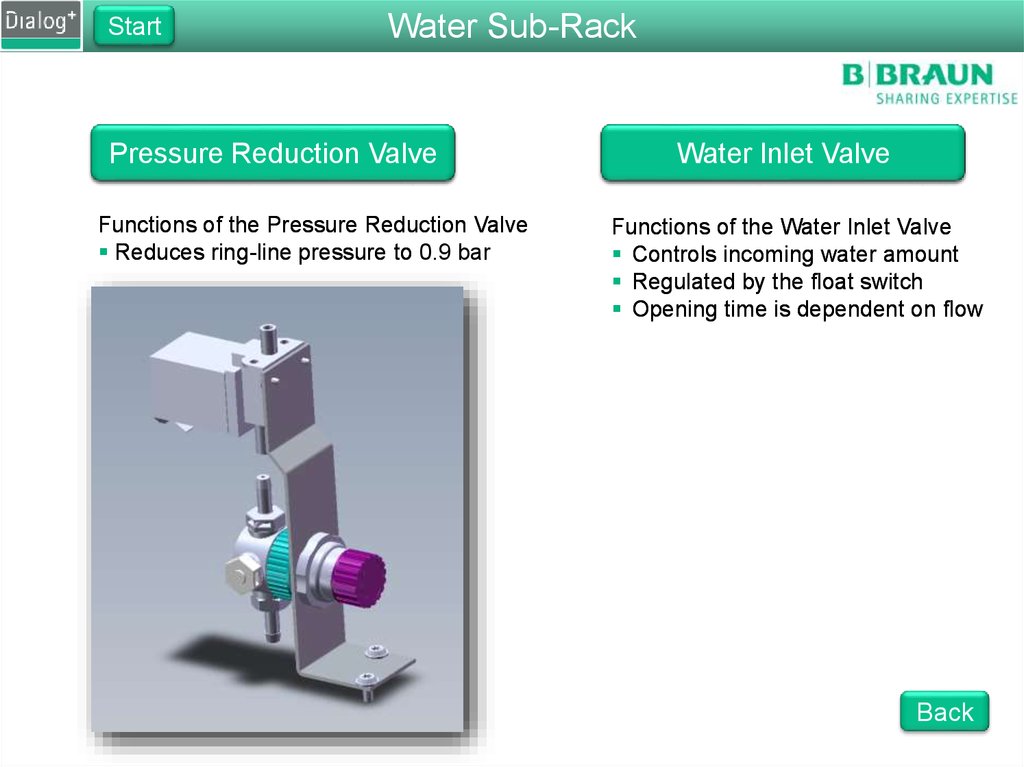
StartWater Sub-Rack
Pressure Reduction Valve
Functions of the Pressure Reduction Valve
Reduces ring-line pressure to 0.9 bar0.9
bar
bar
Water Inlet Valve
Functions of the Water Inlet Valve
Controls incoming water amount
Regulated by the float switch
Opening time is dependent on flow
Back
8. Folie 8
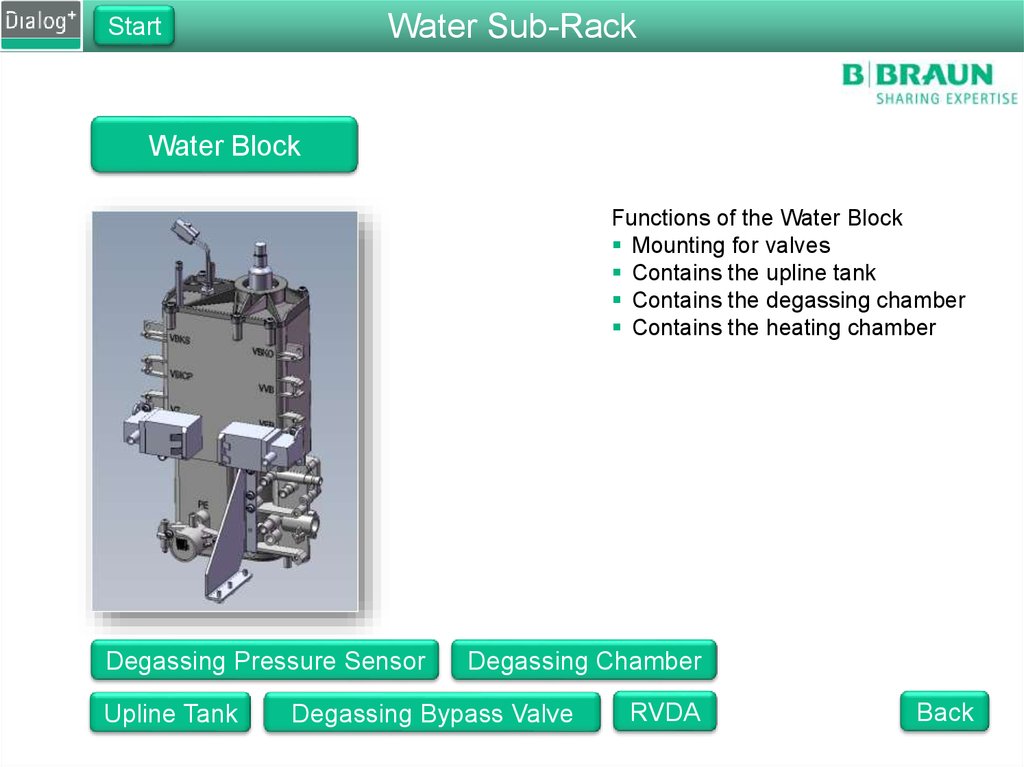
Water Sub-RackStart
Water Block
Functions of the Water Block
Mounting for valves
Contains the upline tank
Contains the degassing chamber
Contains the heating chamber
Degassing Pressure Sensor
Upline Tank
Degassing Chamber
Degassing Bypass Valve
RVDA
Back
9. Folie 9
StartWater Sub-Rack
Upline Tank
Components in the Upline Tank
Heat exchanger
Float Switch
Heater rod
Heat Exchanger
Float Switch
Heater Rod
Back
10. Folie 10
StartWater Sub-Rack
Degassing Valve VEB
Functions of the Degassing Valve
Creates a restriction in the water flow
The restriction creates a negative
pressure
If the valve is open there is no
restiction in the flow
If the valve is closed there is a fixed
gap for the water to pass
The valve will always be open during
disinfections
Back
11. Folie 11
StartWater Sub-Rack
Heater Rod
Functions of the Heater Rod
Heats up incoming water
Properties of the Heater Rod
It consists of 2 heating elements with
900 W each
The heater rod has a thermal fuse
that burns out at 120 oC
The thermal fuse is not resettable
Back
12. Folie 12
StartWater Sub-Rack
Float Switch
Functions of the Float Switch
Regulates the water level in the
upline tank
Turns off the heater and stops all
pumps when the tank is empty
Back
13. Folie 13
StartWater Sub-Rack
Heat Exchanger
Function of the Heat Exchanger
Pre-heats the incoming water to
increase energy efficiency
The tube is made of stainless steel
It is shaped in a spiral form to
increase the contect surface area
Back
14. Folie 14
StartWater Sub-Rack
Degassing Chamber
Functions of the Degassing Chamber
Allows water to degas
Slow flow of water
Contains granulate to allow bubbles
to form
Back
15. Folie 15
StartWater Sub-Rack
Degassing Pressure Sensor
Functions of the Degassing Pressure Sensor
Measure the degassing pressure
Feedback for the degassing pump speed
Protects the heater rod during disinfection
by monitoring the pressure. If the pressure
is too low, the heater is turned off.
The same type of sensor is used for PDA
Back
16. Folie 16
Water Sub-RackStart
Degassing Circuit
E
K
WT
The Flow Path of the Water
Water is taken from the upline tank
If VEB is closed, a restriction in the
flow causes a negative pressure
A negative pressure is measured at PE
The degassing chamber allows
bubbles to form
The FEP protects the degassing pump
from particles that might damage the
pump
The EP generates the negative
pressure by pumping water to the
heater rod
Back
17. Folie 17
StartWater Sub-Rack
Degassing Pump, Micropump Vers. 2
Functions of the Degassing Pump
Degasses the water
Creates a negative pressure
Adapter Block
Gear Pump
Motor
Cover
Back
18. Folie 18
StartWater Sub-Rack
Degassing Pump
Functions of the Degassing Pump
Creates a negative degassing
pressure
Pumps fluid with two interlocked
gears
The gears are driven by a magnet
The pump can only pump water
If the pump speed is too low the
heater is turned off
Degassing pressure should be
between -500 mmHg to -550 mmHg
Normal speed is around 2100 rpm
Back
19. Folie 19
StartWater Sub-Rack
Degassing Motor
Functions of the Degassing Motor
Drives the degassing pump
Onboard driving circuits
Is regulated by the degassing pressure
Back
20. Folie 20
StartWater Sub-Rack
Degassing Motor Cover
Functions of the Degassing Motor Cover
Protects the moving parts of the motor
Protects the electronics of the motor
Back
21. Folie 21
StartWater Sub-Rack
Degassing Adapter Block
Function of the Adapter Block
Mounting of the degassing pump
O-rings to seal the connection with
the motor
Four clips to hold the pump head
Back
22. Folie 22
StartWater Sub-Rack
Degassing Pump Foot Piece
Functions of the Foot Piece
Holds the degassing pump module
Absorbs vibrations from the pump
Reduces the sound volume
Back
23. Folie 23
Water Sub-RackStart
RVDA
Functions of the RVDA
Ensures a minimum pressure of
400 mmHg on the balance
chamber
Must be set to 500 mmHg for
HDF-Online machines
Back
24. Folie 24
Water Sub-RackStart
RVDA
Rear view of the RVDA
Pay attention to the assembly direction
Back
25. Folie 25
UF Sub-RackStart
DF Sub-Rack
Functions of the DF Sub-Rack
Contains the pumps that push
water in and out of the balance
chamber
Responsible for mixing the
dialysate fluid
Contains the piston pumps
Concentrate pump
Bicarbonate pump
UF pump
Flow Pump Inlet
DF Block
Flow Pump Outlet
Concentrate Pumps
UF Pump
Back
26. Folie 26
DF Sub-RackStart
Inlet Flow Pump
Functions of the FPE
Pumps fresh dialysate into
the balance chamber
Pumps used dialysate to the
drain
Creates a high positive
pressure for the DFS
pressure test
RVFPE
Adapter Block
Gear Pump
Motor
Cover
Back
27. Folie 27
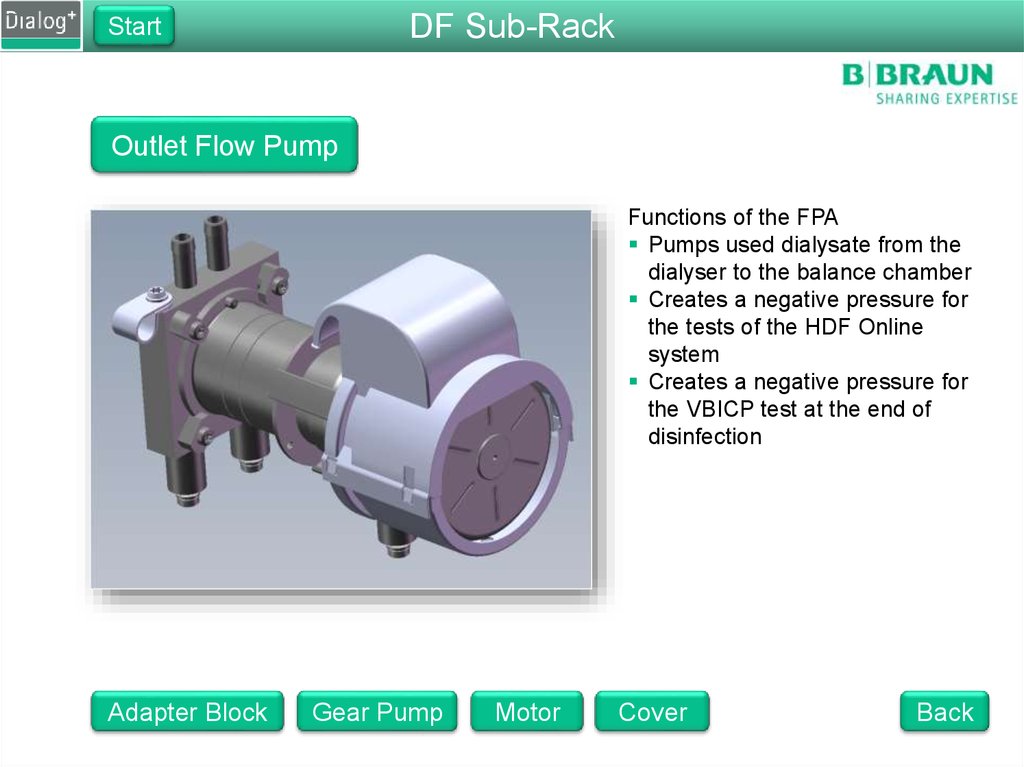
DF Sub-RackStart
Outlet Flow Pump
Functions of the FPA
Pumps used dialysate from the
dialyser to the balance chamber
Creates a negative pressure for
the tests of the HDF Online
system
Creates a negative pressure for
the VBICP test at the end of
disinfection
Adapter Block
Gear Pump
Motor
Cover
Back
28. Folie 28
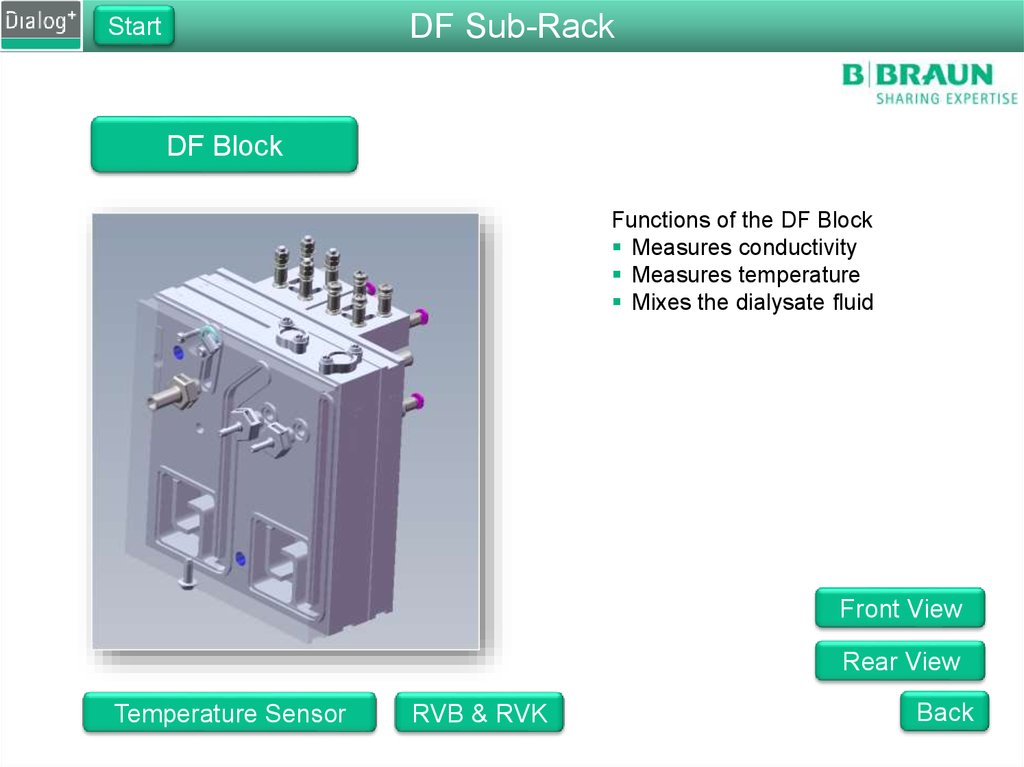
DF Sub-RackStart
DF Block
Functions of the DF Block
Measures conductivity
Measures temperature
Mixes the dialysate fluid
Inner View
Rear View
Temperature Sensor
RVK & RVB
Back
29. Folie 29
DF Sub-RackStart
DF Block
Functions of the DF Block
Measures conductivity
Measures temperature
Mixes the dialysate fluid
Front View
Rear View
Temperature Sensor
RVB & RVK
Back
30. Folie 30
DF Sub-RackStart
DF Block
Functions of the DF Block
Measures conductivity
Measures temperature
Mixes the dialysate fluid
Inner View
Front View
Temperature Sensor
RVB & RVK
Conductivity Sensors
Back
31. Folie 31
StartDF Sub-Rack
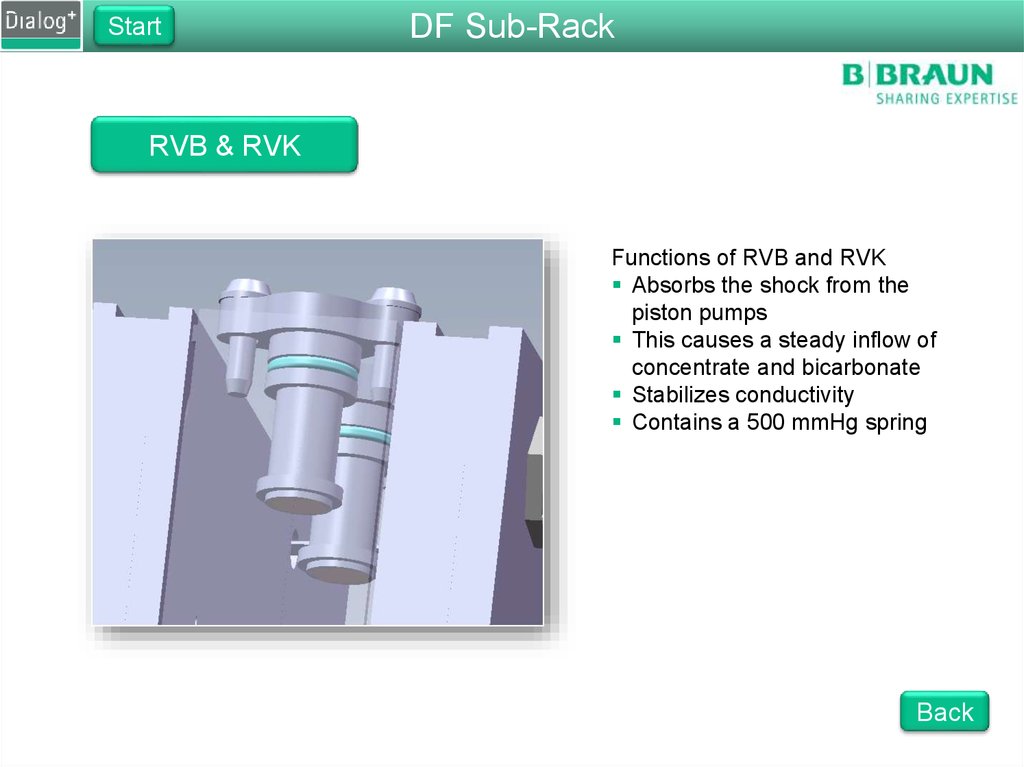
RVB & RVK
Functions of RVB and RVK
Absorbs the shock from the
piston pumps
This causes a steady inflow of
concentrate and bicarbonate
Stabilizes conductivity
Contains a 500 mmHg spring
Back
32. Folie 32
StartDF Sub-Rack
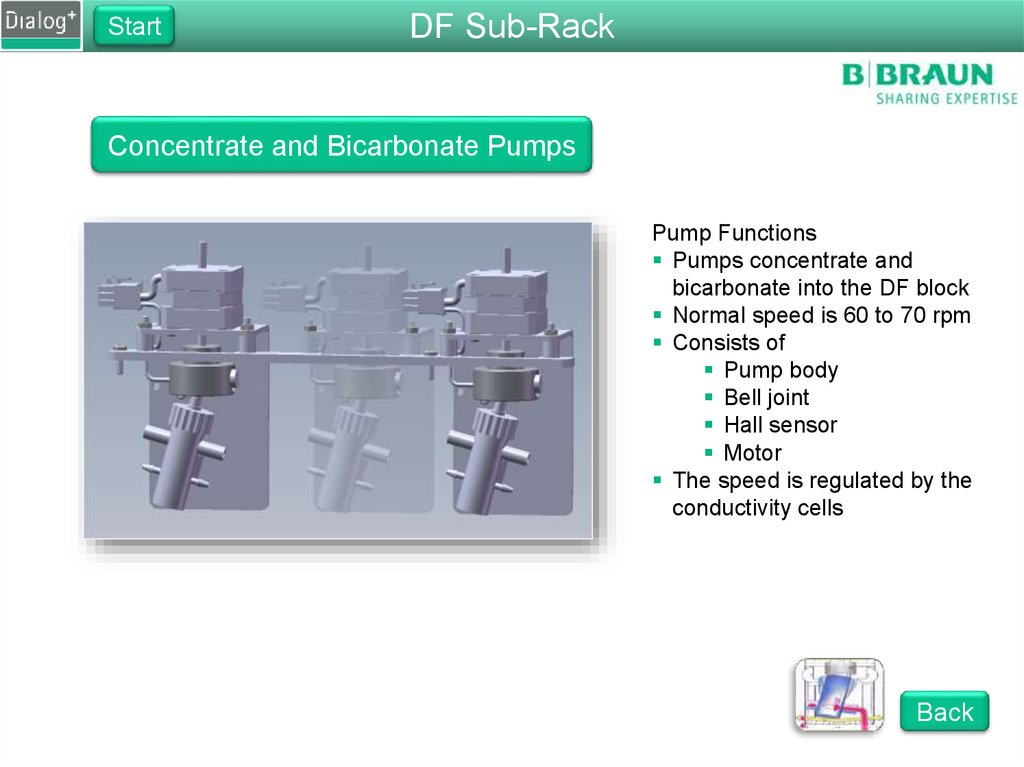
Concentrate and Bicarbonate Pumps
Pump Functions
Pumps concentrate and
bicarbonate into the DF block
Normal speed is 60 to 70 rpm
Consists of
Pump body
Bell joint
Hall sensor
Motor
The speed is regulated by the
conductivity cells
Back
33. Folie 33
StartDF Sub-Rack
Working concept of the Piston Pump
Fluid is sucked in on the one
side of the pump.
By rotating the shaft fluid is
pushed out the other side of
the pump.
The volume for each stroke is
the same.
Back
34. Folie 34
DF Sub-RackStart
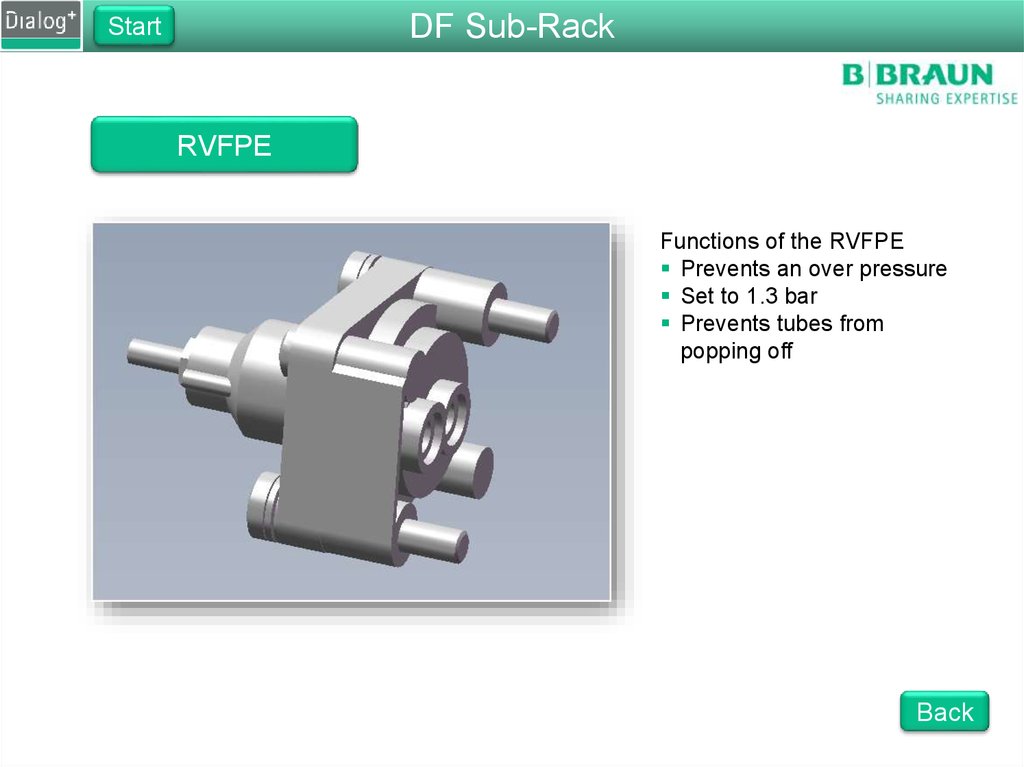
RVFPE
Functions of the RVFPE
Prevents an over pressure
Set to 1.3 bar
Prevents tubes from
popping off
Back
35. Folie 35
StartDF Sub-Rack
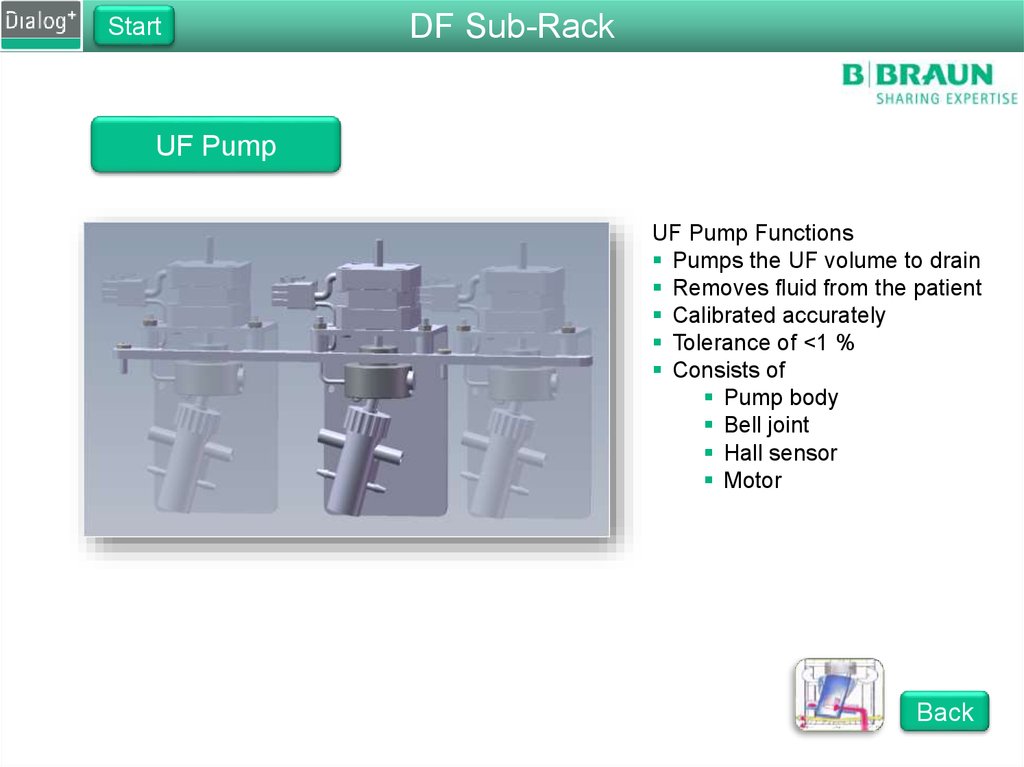
UF Pump
UF Pump Functions
Pumps the UF volume to drain
Removes fluid from the patient
Calibrated accurately
Tolerance of <1 %
Consists of
Pump body
Bell joint
Hall sensor
Motor
Back
36. Folie 36
DF Sub-RackStart
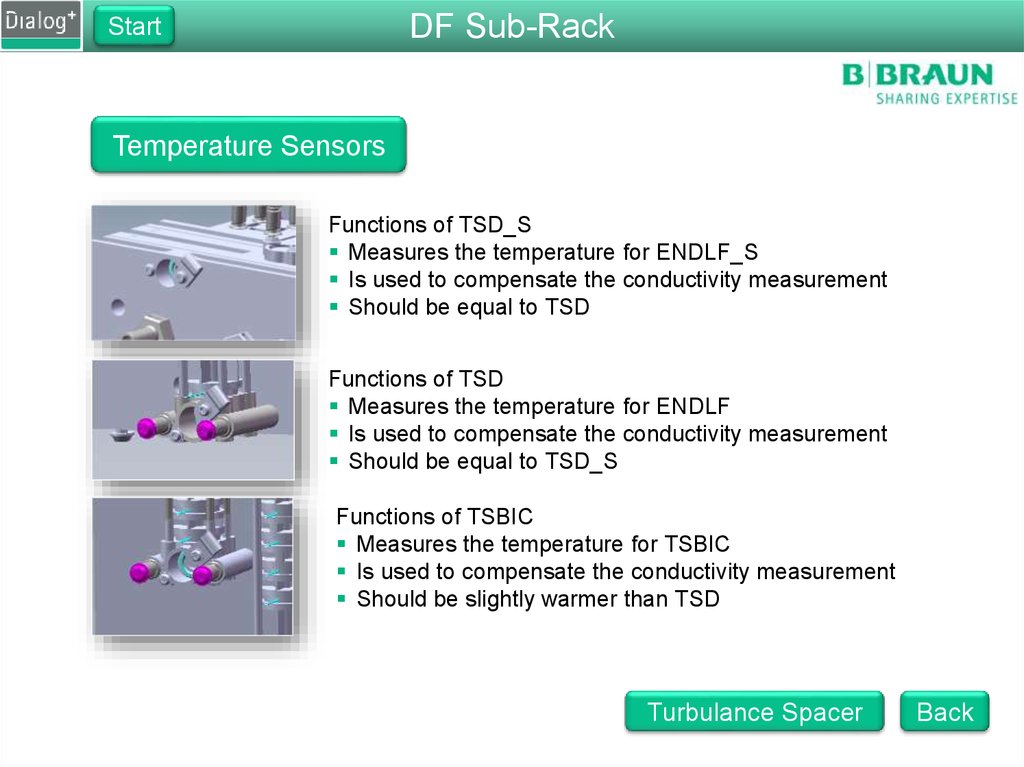
Temperature Sensors
Functions of TSD_S
Measures the temperature for ENDLF_S
Is used to compensate the conductivity measurement
Should be equal to TSD
Functions of TSD
Measures the temperature for ENDLF
Is used to compensate the conductivity measurement
Should be equal to TSD_S
Functions of TSBIC
Measures the temperature for TSBIC
Is used to compensate the conductivity measurement
Should be slightly warmer than TSD
Turbulance Spacer
Back
37. Folie 37
StartDF Sub-Rack
Turbulance Spacer
Functions of the Turbulance Spacer
Creates turbulance on the
temperature sensor
Removes dead spaces from the
sensor
Back
38. Folie 38
DF Sub-RackStart
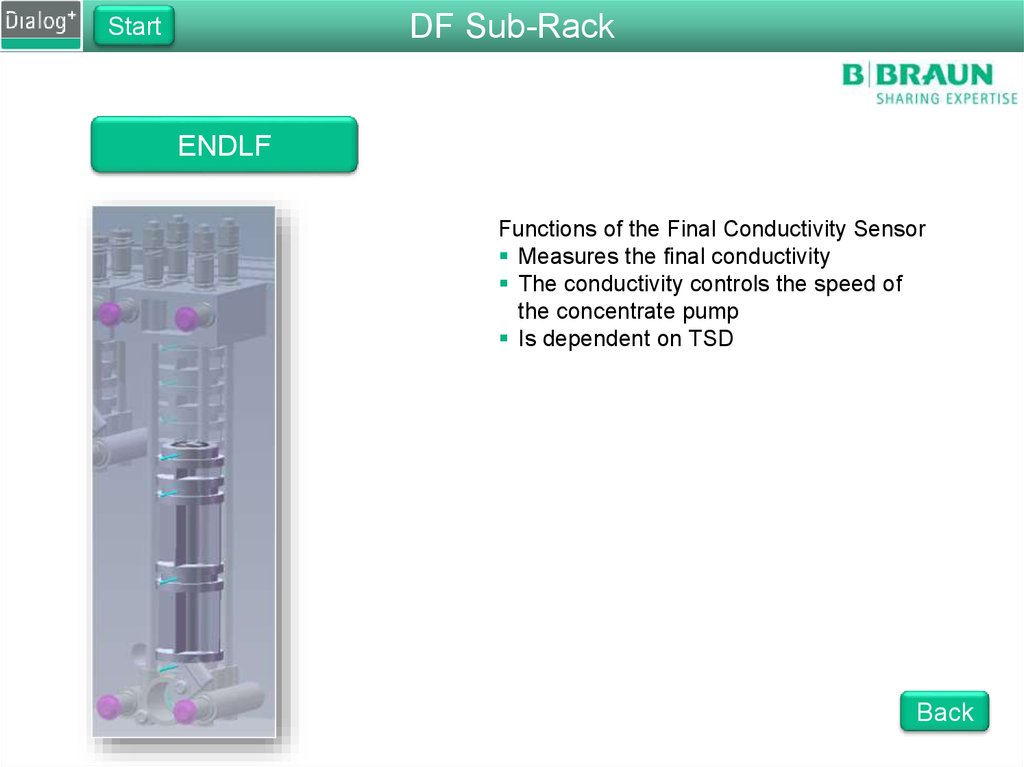
ENDLF
Functions of the Final Conductivity Sensor
Measures the final conductivity
The conductivity controls the speed of
the concentrate pump
Is dependent on TSD
Back
39. Folie 39
StartDF Sub-Rack
ENDLF_S
Functions of the Final Conductivity Sensor
for the Supervisor
Measures the final conductivity
Is dependent on TSD_S
Back
40. Folie 40
DF Sub-RackStart
BICLF
Functions of the Bicarbonate Conductivity Sensor
Measures bicarbonate conductivity
The conductivity controls the speed of the
bicarbonate pump
Is dependent on TSBIC
Back
41. Folie 41
DF Sub-RackStart
Conductivity Sensors
Functions of the conductivity cells
ENDLF measures the final
conductivity
ENDLF_S supervises the ENDLF
BICLF measures the bicarbonate
conductivity
Conductivity is dependent on
temperature
Conductivity Regulation
BICLF
ENDLF
ENDLF-S
Temperature Sensors
Back
42. Folie 42
StartRinsing Bridge
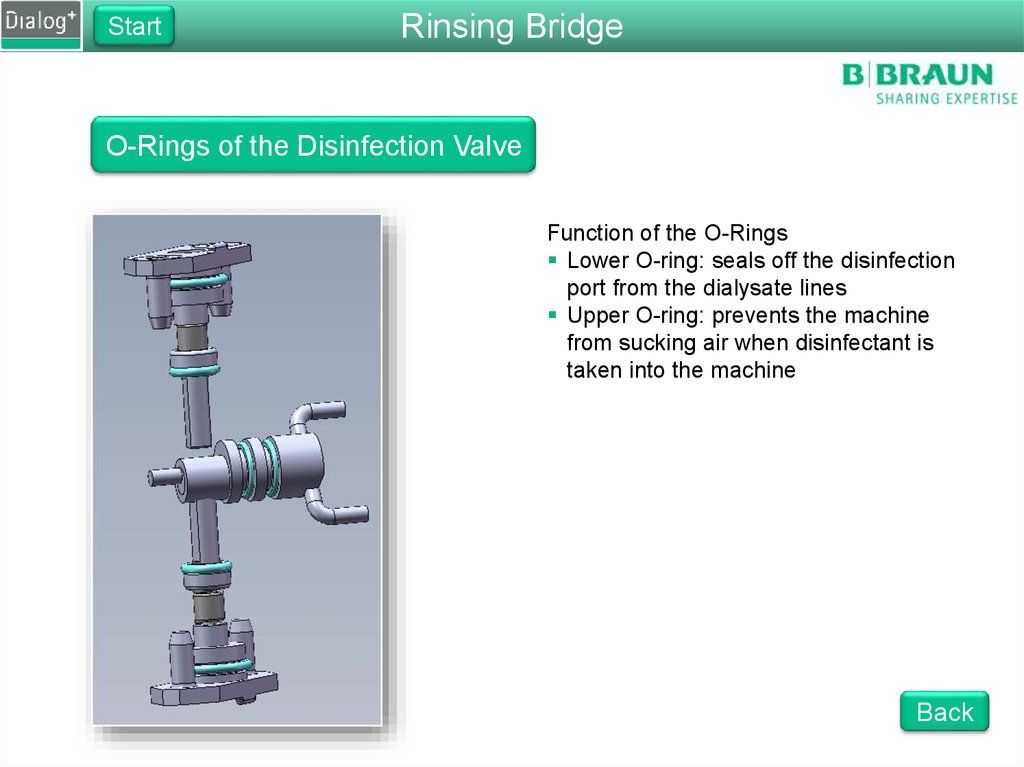
O-Rings of the Disinfection Valve
Function of the O-Rings
Lower O-ring: seals off the disinfection
port from the dialysate lines
Upper O-ring: prevents the machine
from sucking air when disinfectant is
taken into the machine
Back
43. Folie 43
StartRinsing Bridge
Disinfection Valve
Functions of the Disinfection Valve
Opens when the machine needs
to suck in disinfectant
Closes to allow air back into the
disinfection tube
Is controlled by a servo motor
Disinfection Procedure
Disinfection Valve
Light Barrier
Servo Motor
Back
44. Folie 44
StartSub-Rack
FPA Adapter Block
Functions of the FPA Adapter Block
Mounts the FPA
Absorbs vibrations for noise reduction
Back
45. Folie 45
StartRinsing Bridge
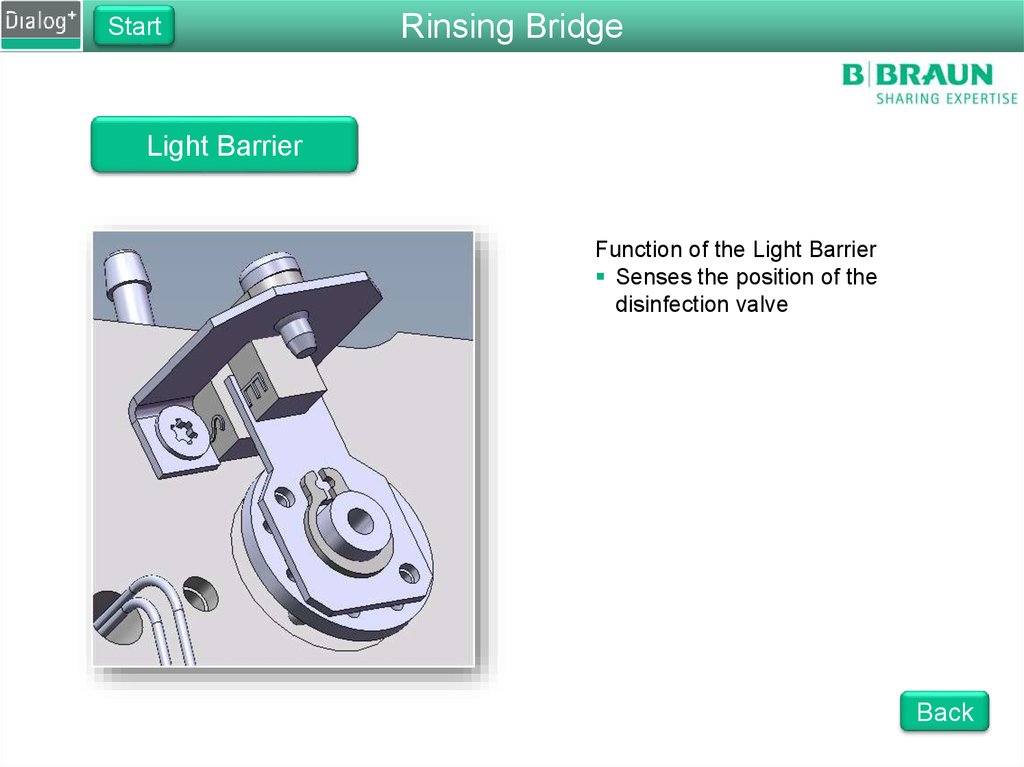
Light Barrier
Function of the Light Barrier
Senses the position of the
disinfection valve
Back
46. Folie 46
StartRinsing Bridge
Pressure Sensor Dialysate
Functions of PDA
Measures the dialysate pressure
This is used to calculate TMP
Used as testing device during
the DFS Pressure Test
Large working range
The same type of sensor as PE
Back
47. Folie 47
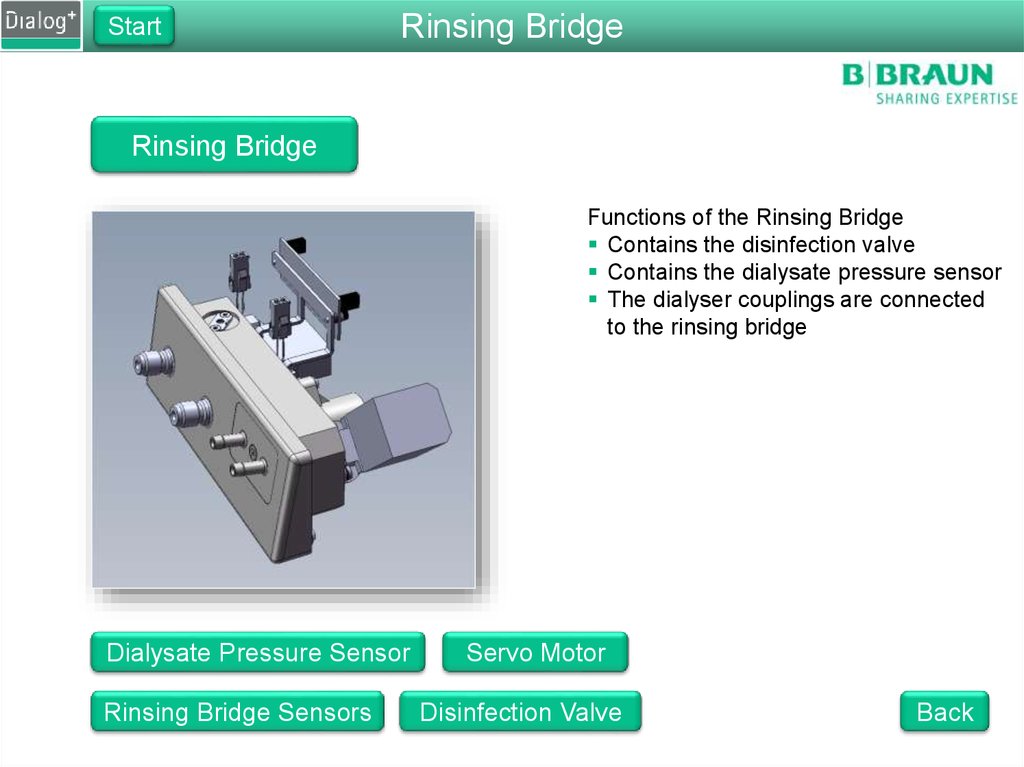
StartRinsing Bridge
Rinsing Bridge
Functions of the Rinsing Bridge
Contains the disinfection valve
Contains the dialysate pressure sensor
The dialyser couplings are connected
to the rinsing bridge
Dialysate Pressure Sensor
Rinsing Bridge Sensors
Servo Motor
Disinfection Valve
Back
48. Folie 48
StartRinsing Bridge
Rinsing Bridge Sensors
Function of the Sensors
Detects whether the dialyser
couplings are connected to the
rinsing bridge
Back
49. Folie 49
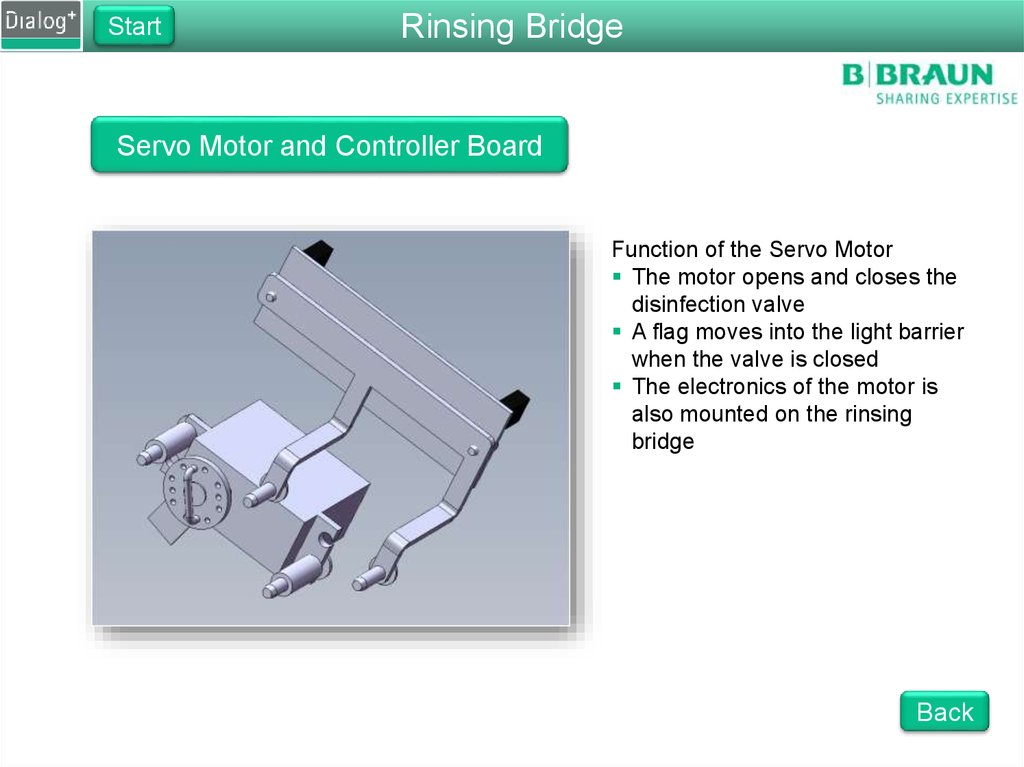
StartRinsing Bridge
Servo Motor and Controller Board
Function of the Servo Motor
The motor opens and closes the
disinfection valve
A flag moves into the light barrier
when the valve is closed
The electronics of the motor is
also mounted on the rinsing
bridge
Back
50. Folie 50
StartDF Sub-Rack
FPE Motor Cover
Functions of the FPE Motor Cover
Protects the moving parts of the motor
Protects the electronics of the motor
Back
51. Folie 51
StartDF Sub-Rack
FPE Motor
Functions of the FPE Motor
Drives the Flow Pump Inlet pump
Onboard driving circuits
Is regulated by the movement
of the membranes
Back
52. Folie 52
StartDF Sub-Rack
FPA Motor
Functions of the FPA Motor
Drives the outlet pump
Onboard driving circuits
Is regulated by the movement of the
membranes
Back
53. Folie 53
StartDF Sub-Rack
FPA Motor Cover
Functions of the FPA Motor Cover
Protects the moving parts of the motor
Protects the electronics of the motor
Back
54. Folie 54
StartDF Sub-Rack
FPE Adapter Block
Functions of the FPE Adapter Block
Mounts the FPE
Absorbs vibrations for noise reduction
Back
55. Folie 55
StartDF Sub-Rack
FPE, Micropump Vers. 1
Functions of the FPE Pump
Creates a positive pressure to
refill the balance chamber
Pumps fluid with two interlocked
gears
The gears are driven by a magnet
The pump can only pump fluid
A normal speed during treatment
is about 1000 rpm if the dialysate
flow is set to 500 ml / min.
Back
56. Folie 56
StartDF Sub-Rack
FPA, Micropump Vers. 1
Functions of the FPA Pump
Creates a positive pressure to fill
the balance chamber used
dialysate
Pumps fluid with two interlocked
gears
The gears are driven by a magnet
The pump can only pump fluid
A normal speed during treatment
is about 1000 rpm if the dialysate
flow is set to 500 ml / min.
Back
57. Folie 57
StartUF Sub-Rack
UF Sub-Rack
Functions of the UF Sub-Rack
Contains the balance
chamber
Is responsible for controlling
the UF during dialysis
Contains the air separator
Air Separator
Balance Chamber
Back
58. Folie 58
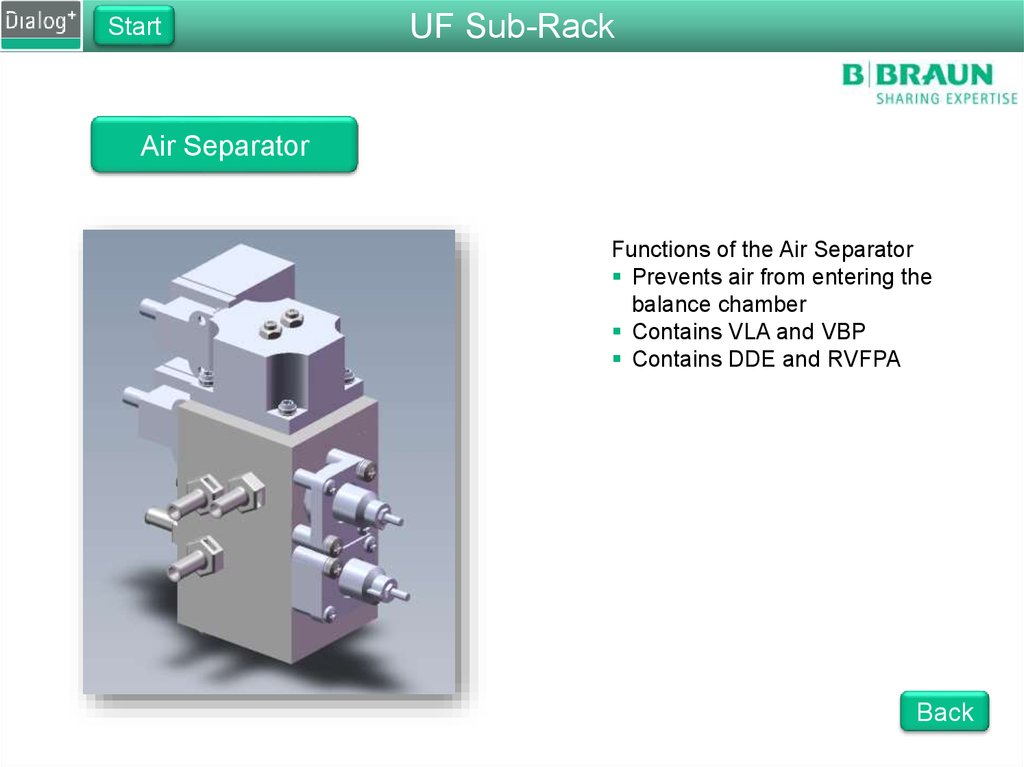
StartUF Sub-Rack
Air Separator
Functions of the Air Separator
Prevents air from entering the
balance chamber
Contains VLA and VBP
Contains DDE and RVFPA
Front View
Level Sensors
Back
59. Folie 59
StartUF Sub-Rack
Air Separator
Functions of the Air Separator
Prevents air from entering the
balance chamber
Contains VLA and VBP
Contains DDE and RVFPA
Back
60. Folie 60
StartUF Sub-Rack
Air Separator
Functions of the Air Separator
There are 2 pins that sense the
level of fluid in the air separator
VLA is opened when air is
detected on both sensors
VLA is closed when the top
sensor detects fluid
The sensors do not work on
pure RO Water
Back
61. Folie 61
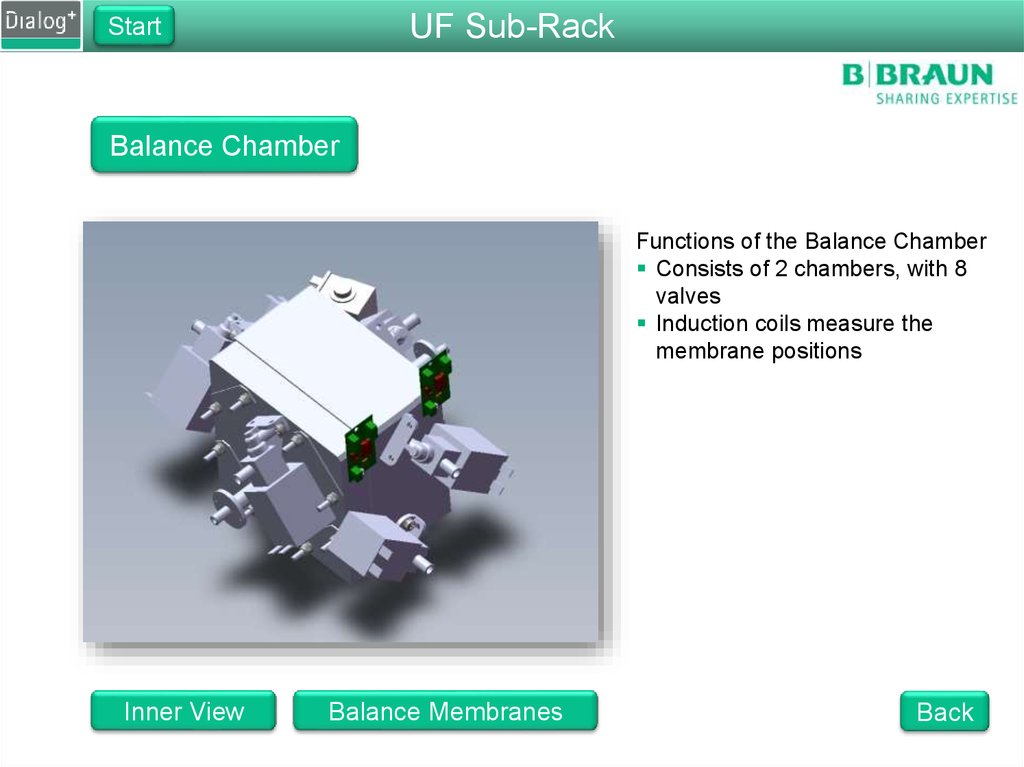
UF Sub-RackStart
Balance Chamber
Functions of the Balance Chamber
Consists of 2 chambers, with 8
valves
Induction coils measure the
membrane positions
Inner View
Balance Membranes
Back
62. Folie 62
StartUF Sub-Rack
Balance Chamber Membrane
Functions of the Balance Chamber
Membrane
Separates fresh and used
dialysate
Controls incoming and outgoing
fluid volume
The position of the membrane is
measured with MSBK
Balance Membranes
Back
63. Folie 63
StartUF Sub-Rack
Membrane Position Sensor
Functions of the membrane
position sensor
Measures the position of the
membrane
Uses induction to sense the
position of a metal pin inside the
membrane
The pin moves in and out of the
coil in the sensor
The result is shown in µs.
Back
64. Folie 64
StartBicarbonate Cartridge Holder
Bicarbonate Cartridge Holder
Please select a part of the catridge
holder that you want to look at.
Functions of the cartridge holder
Holds the bicarbonate cartridge
Supplies the machine with fresh
bicarbonate
Filling the Cartridge
Mounting
Swivel Arm
Check Valve
Back
65. Folie 65
StartBicarbonate Cartridge Holder
Mounting
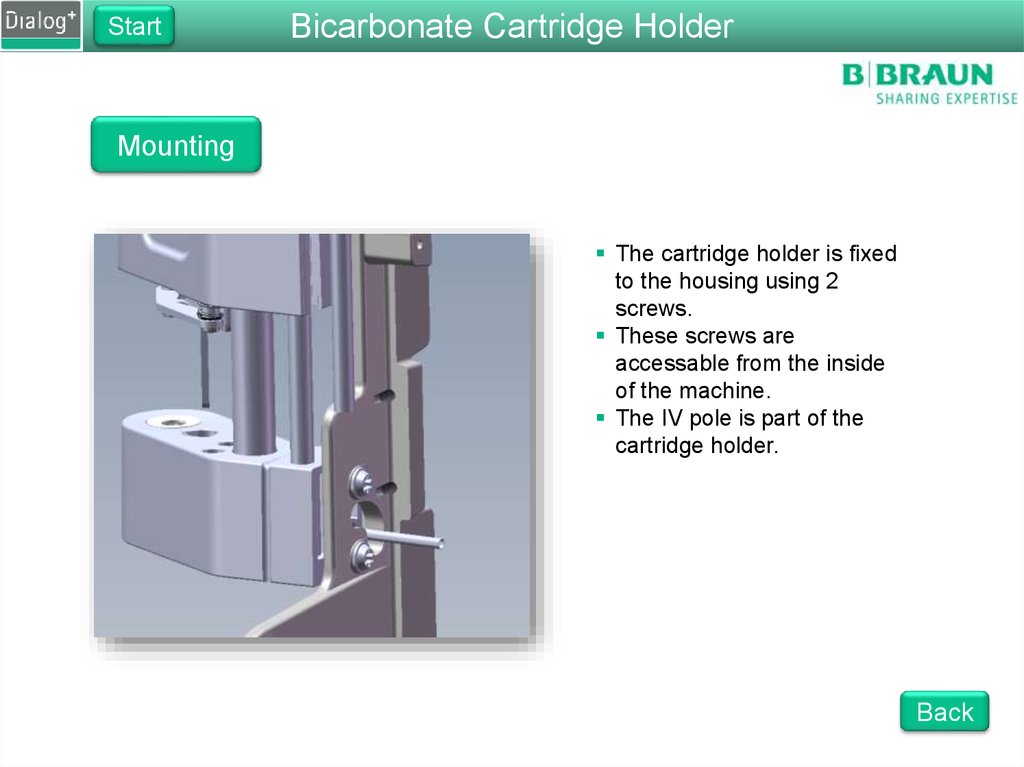
The cartridge holder is fixed
to the housing using 2
screws.
These screws are
accessable from the inside
of the machine.
The IV pole is part of the
cartridge holder.
Back
66. Folie 66
StartBicarbonate Cartridge Holder
Swivel Arm
Functions of the swivel arm
Closes the bicarbonate
circuit when no cartride is
inserted
Opens the check valves
The swivel arm must be
adjusted if it is not in the
center position
Back
67. Folie 67
StartBicarbonate Cartridge Holder
Check Valve
The check valve is opened
when a cartridge or the
swivel arm is inserted.
There is a O-ring to seal the
connection
A clear silicone O-ring can
also be used
Back
68. Folie 68
StartTemperature Regulation
The temperature regulation is done by the following components
TSE
TSHE
TSD
TSDE
Next
Back
69. Folie 69
StartTemperature Regulation
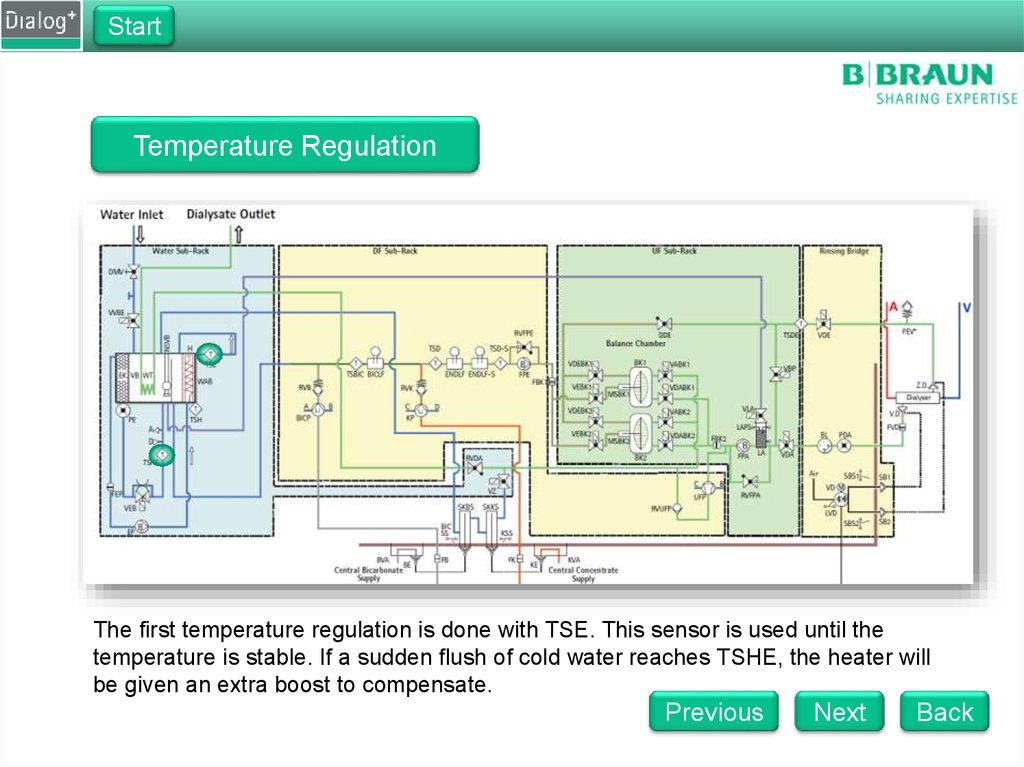
The first temperature regulation is done with TSE. This sensor is used until the
temperature is stable. If a sudden flush of cold water reaches TSHE, the heater will
be given an extra boost to compensate.
Previous
Next
Back
70. Folie 70
StartTemperature Regulation
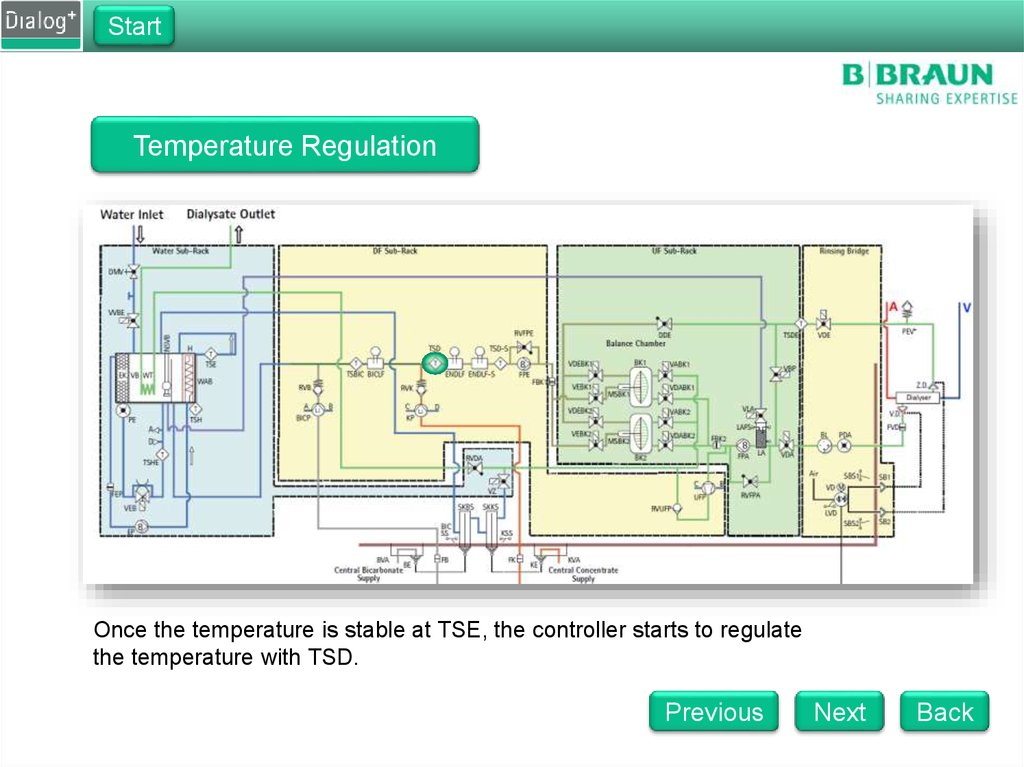
Once the temperature is stable at TSE, the controller starts to regulate
the temperature with TSD.
Previous
Next
Back
71. Folie 71
StartTemperature Regulation
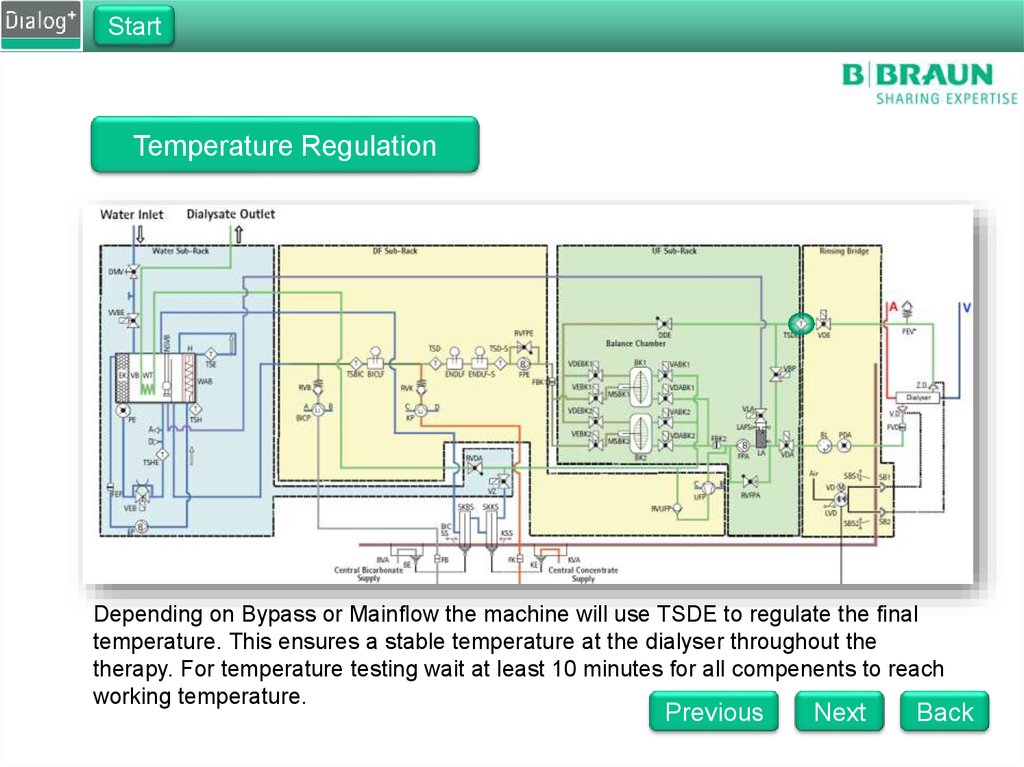
Depending on Bypass or Mainflow the machine will use TSDE to regulate the final
temperature. This ensures a stable temperature at the dialyser throughout the
therapy. For temperature testing wait at least 10 minutes for all compenents to reach
working temperature.
Previous
Next
Back
72. Folie 72
StartTemperature Regulation
If the machine is switched to bypass, TSD will take over regulation of the temperature,
because there is no flow through TSDE. Regulation by TSDE is restored once the
temperature is stable again at TSD.
Previous
Next
Back
73. Folie 73
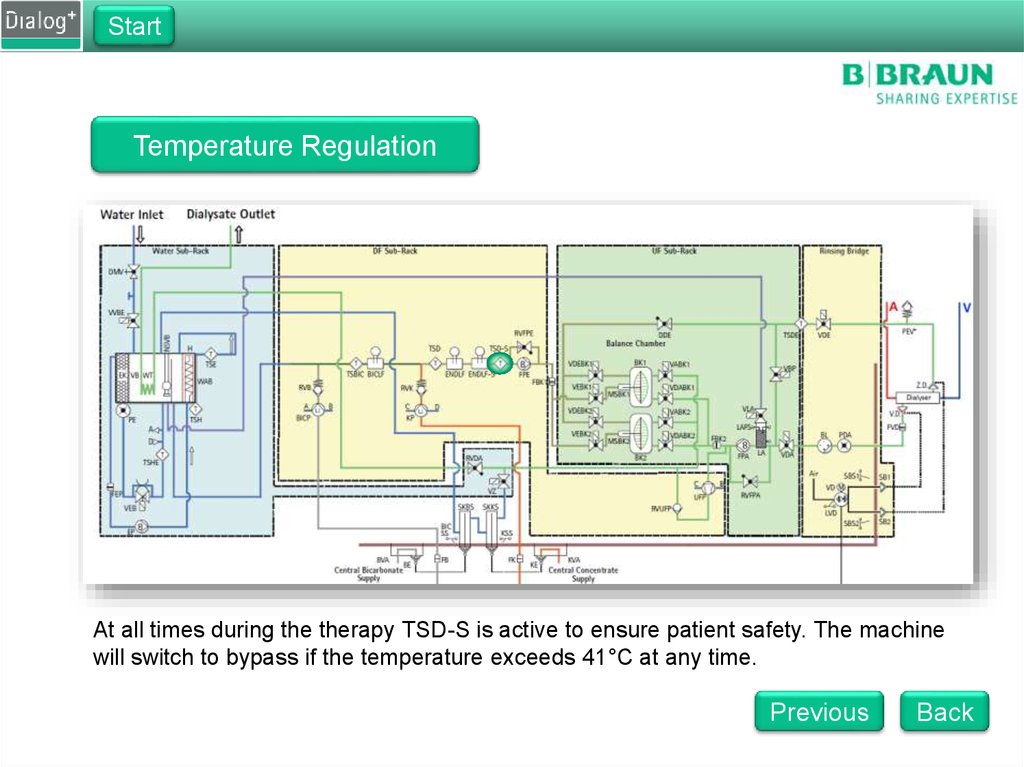
StartTemperature Regulation
At all times during the therapy TSD-S is active to ensure patient safety. The machine
will switch to bypass if the temperature exceeds 41°C at any time.
Previous
Back
74. Folie 74
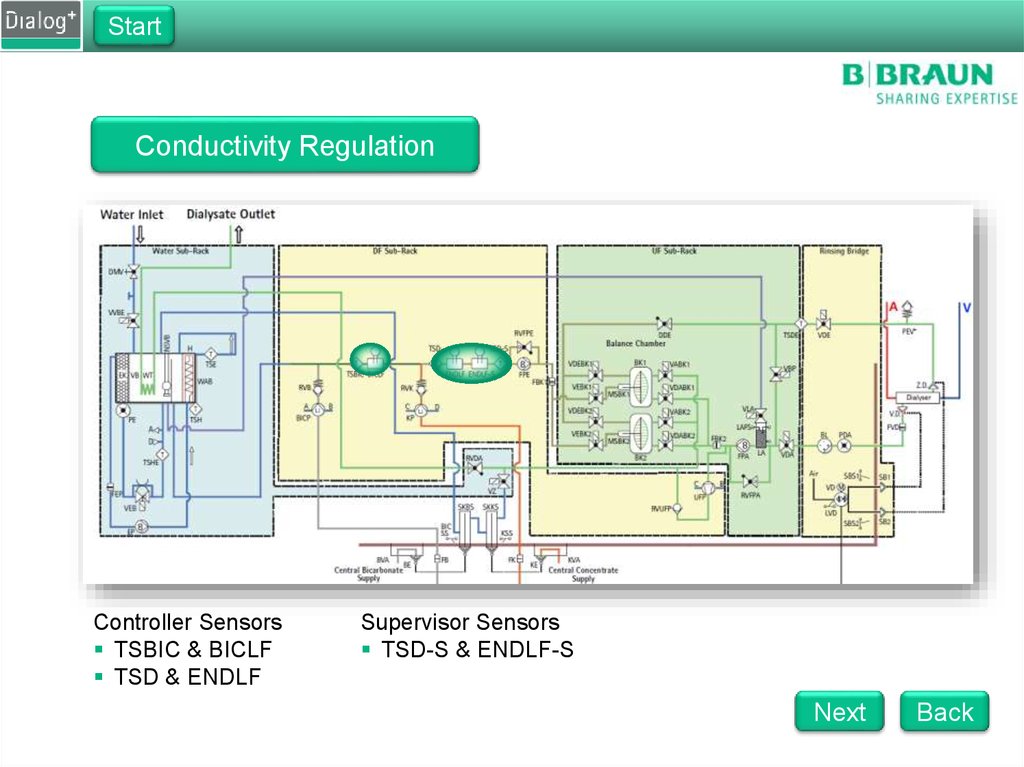
StartConductivity Regulation
Controller Sensors
TSBIC & BICLF
TSD & ENDLF
Supervisor Sensors
TSD-S & ENDLF-S
Next
Back
75. Folie 75
StartDF Sub-Rack
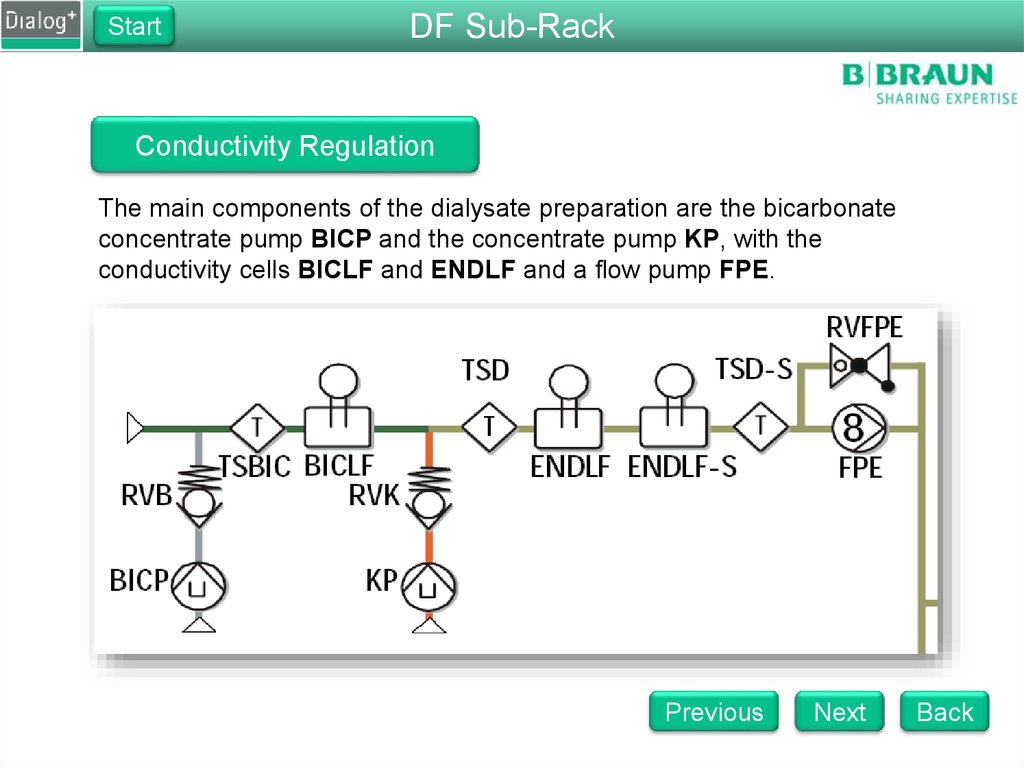
Conductivity Regulation
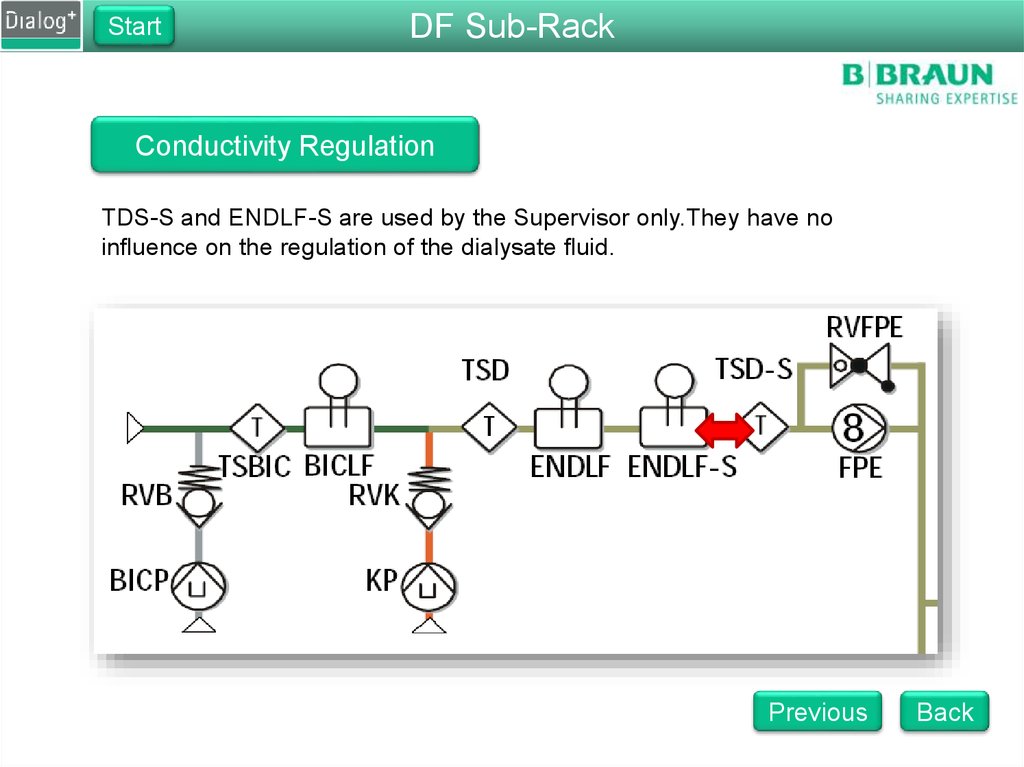
The main components of the dialysate preparation are the bicarbonate
concentrate pump BICP and the concentrate pump KP, with the
conductivity cells BICLF and ENDLF and a flow pump FPE.
Previous
Next
Back
76. Folie 76
StartDF Sub-Rack
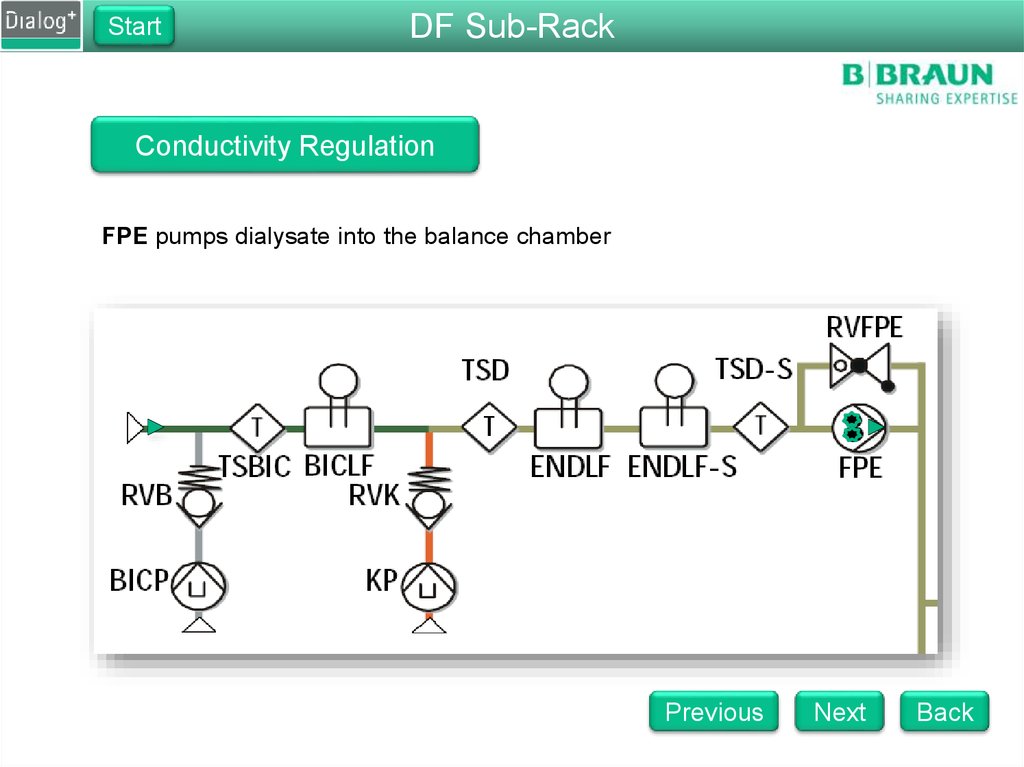
Conductivity Regulation
FPE pumps dialysate into the balance chamber
Previous
Next
Back
77. Folie 77
StartDF Sub-Rack
Conductivity Regulation
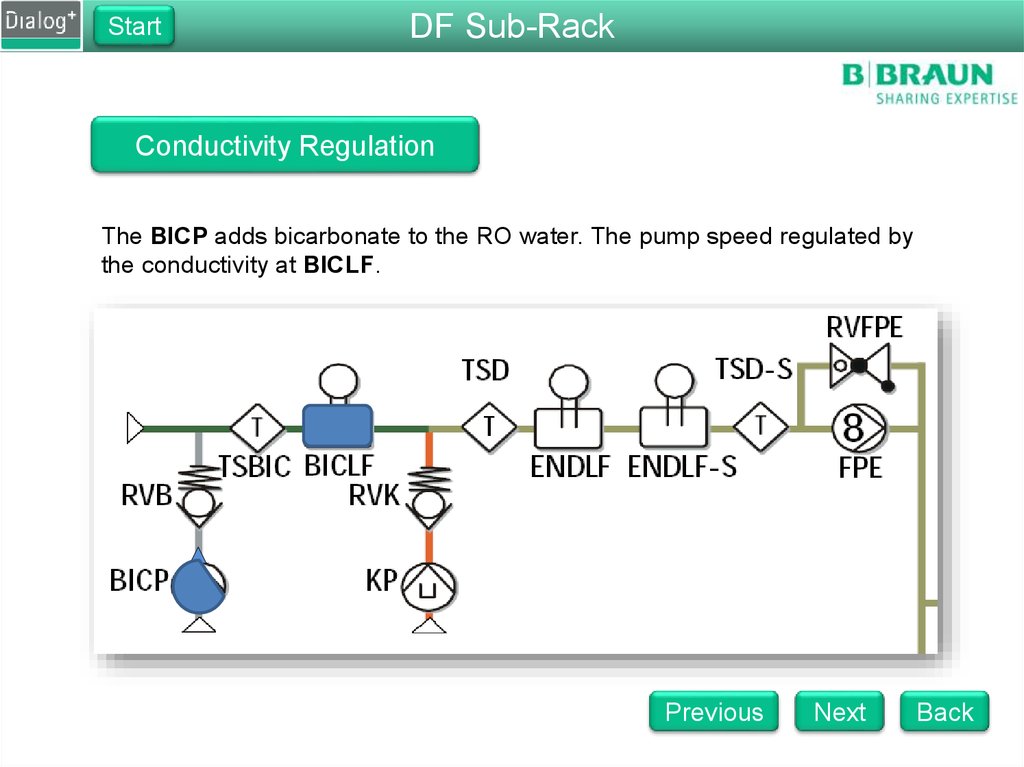
The BICP adds bicarbonate to the RO water. The pump speed regulated by
the conductivity at BICLF.
Previous
Next
Back
78. Folie 78
StartDF Sub-Rack
Conductivity Regulation
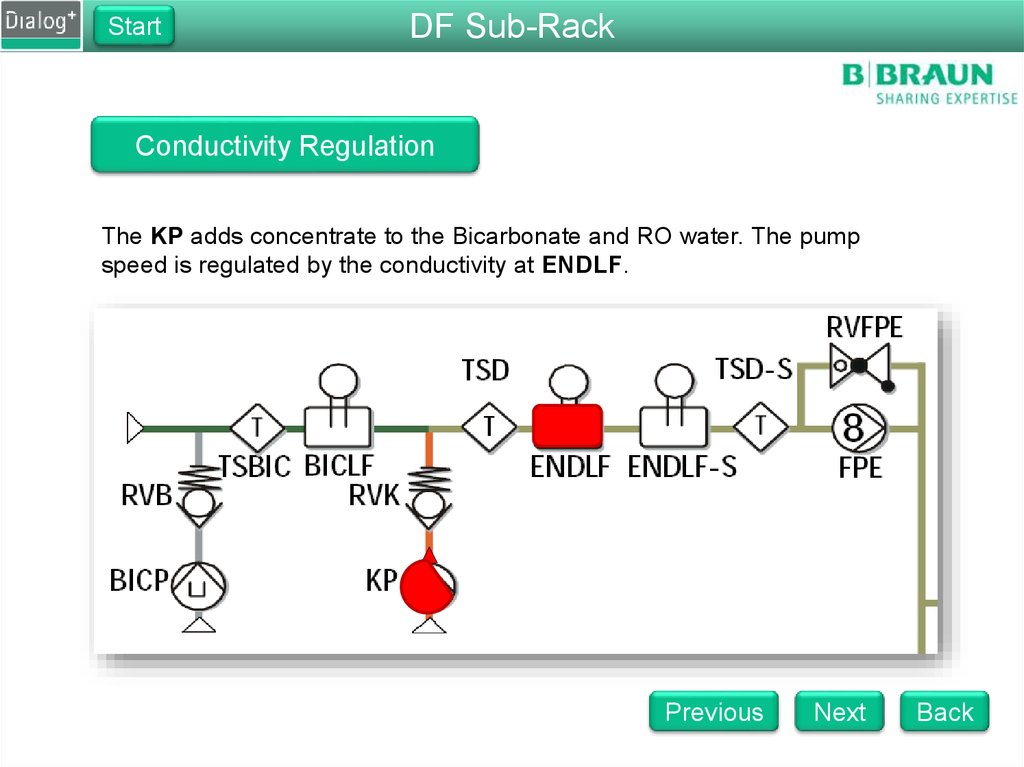
The KP adds concentrate to the Bicarbonate and RO water. The pump
speed is regulated by the conductivity at ENDLF.
Previous
Next
Back
79. Folie 79
StartDF Sub-Rack
Conductivity Regulation
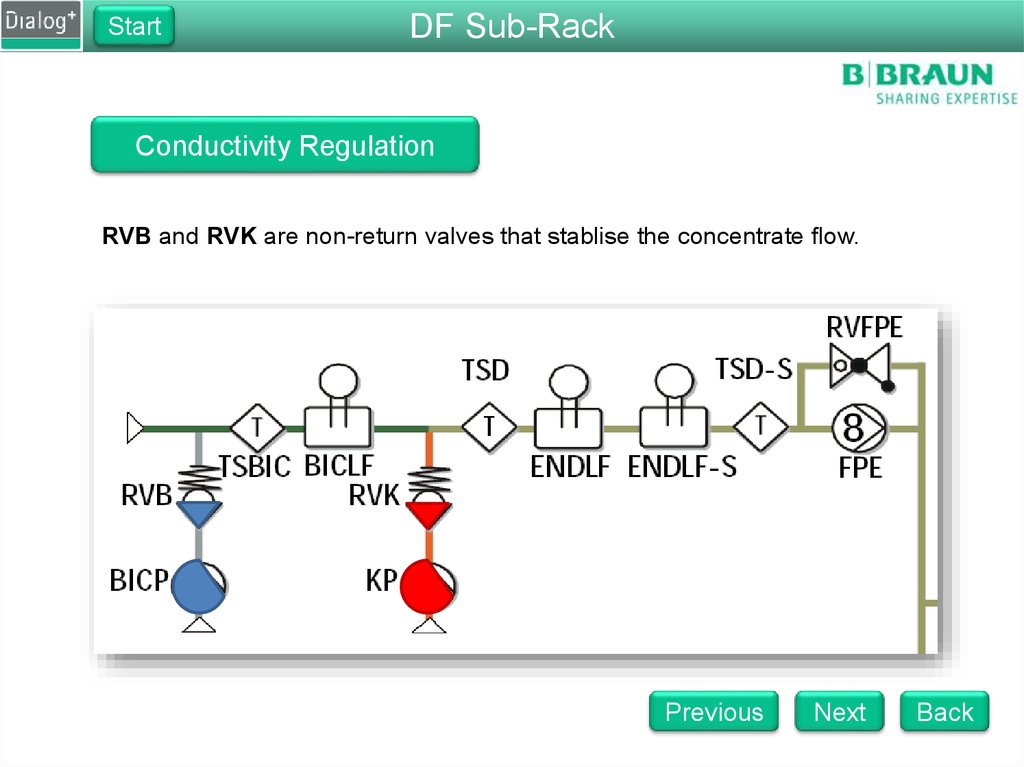
RVB and RVK are non-return valves that stablise the concentrate flow.
Previous
Next
Back
80. Folie 80
StartDF Sub-Rack
Conductivity Regulation
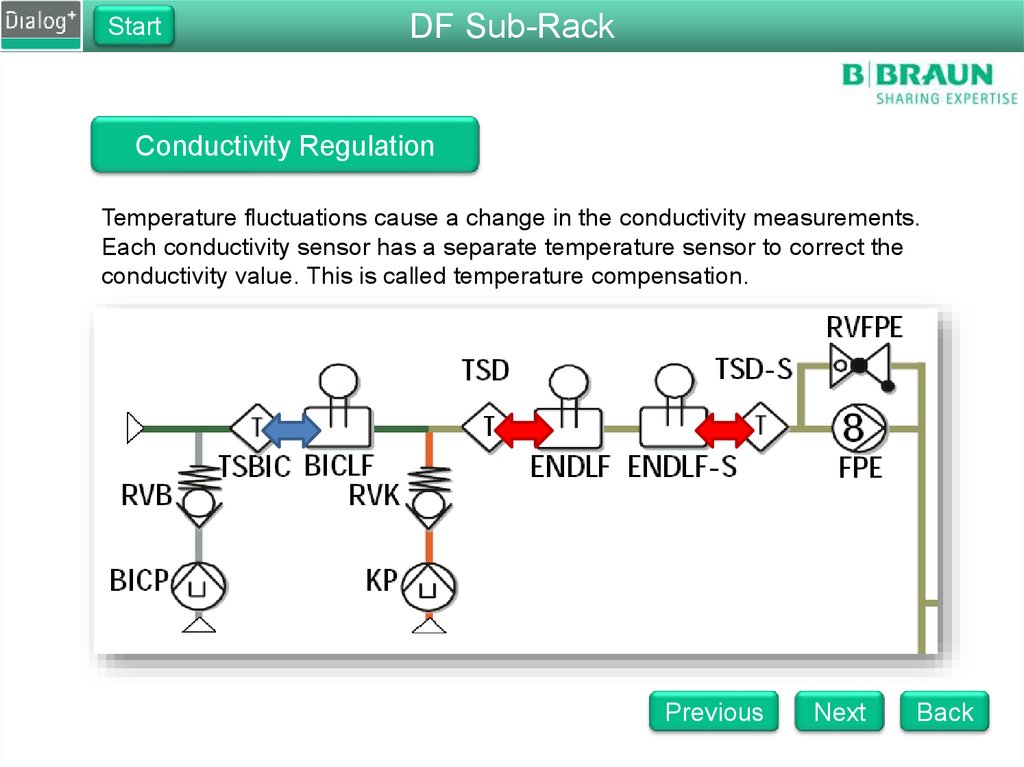
Temperature fluctuations cause a change in the conductivity measurements.
Each conductivity sensor has a separate temperature sensor to correct the
conductivity value. This is called temperature compensation.
Previous
Next
Back
81. Folie 81
StartDF Sub-Rack
Conductivity Regulation
TDS-S and ENDLF-S are used by the Supervisor only.They have no
influence on the regulation of the dialysate fluid.
Previous
Back
82. Folie 82
StartDialysate Preparation with BIC Cartridge Option
Next
Back
83. Folie 83
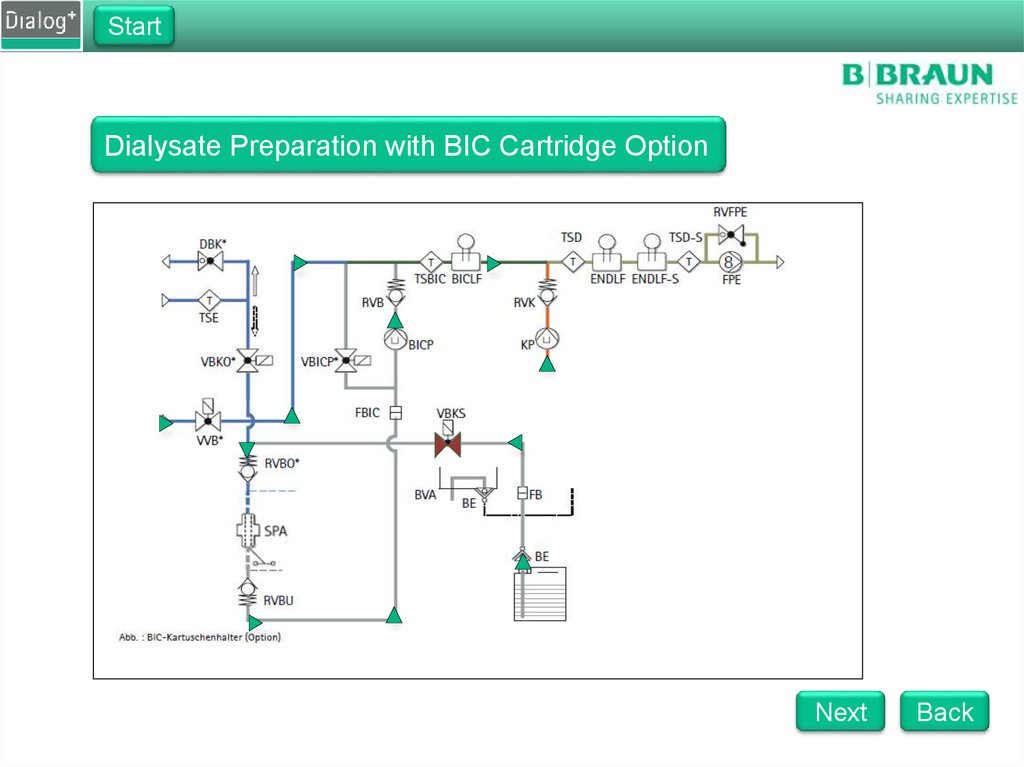
StartDF Sub-Rack
Dialysate Preparation with BIC Cartridge
Next
Back
84. Folie 84
StartDF Sub-Rack
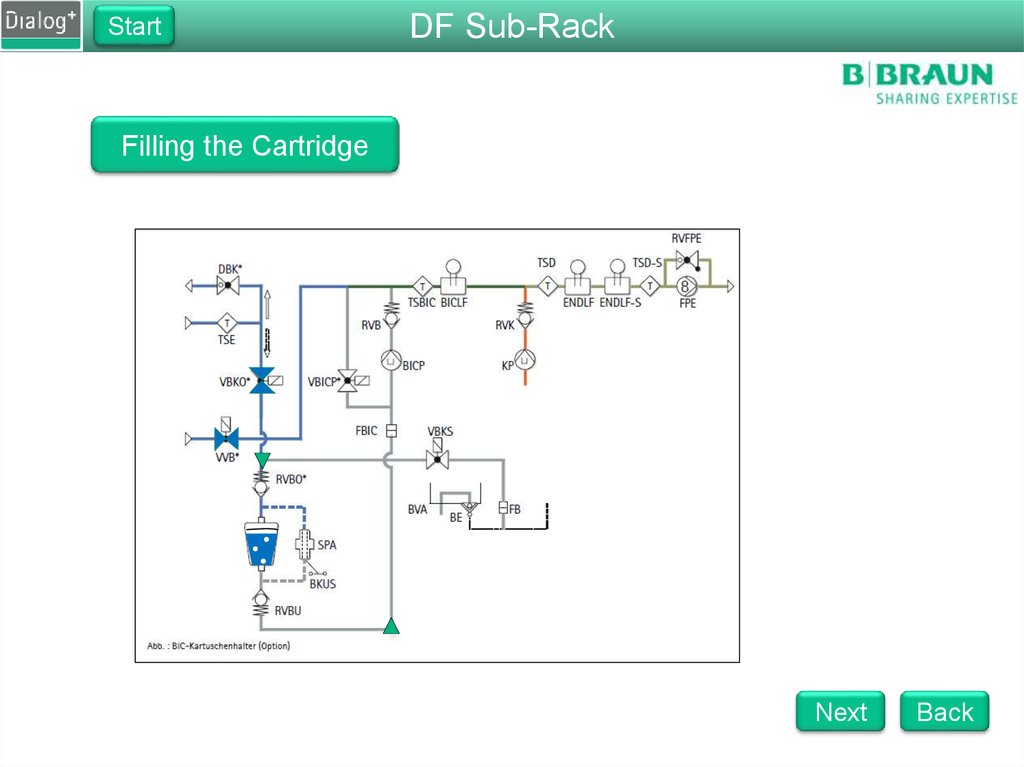
Filling the Cartridge
Next
Back
85. Folie 85
StartDF Sub-Rack
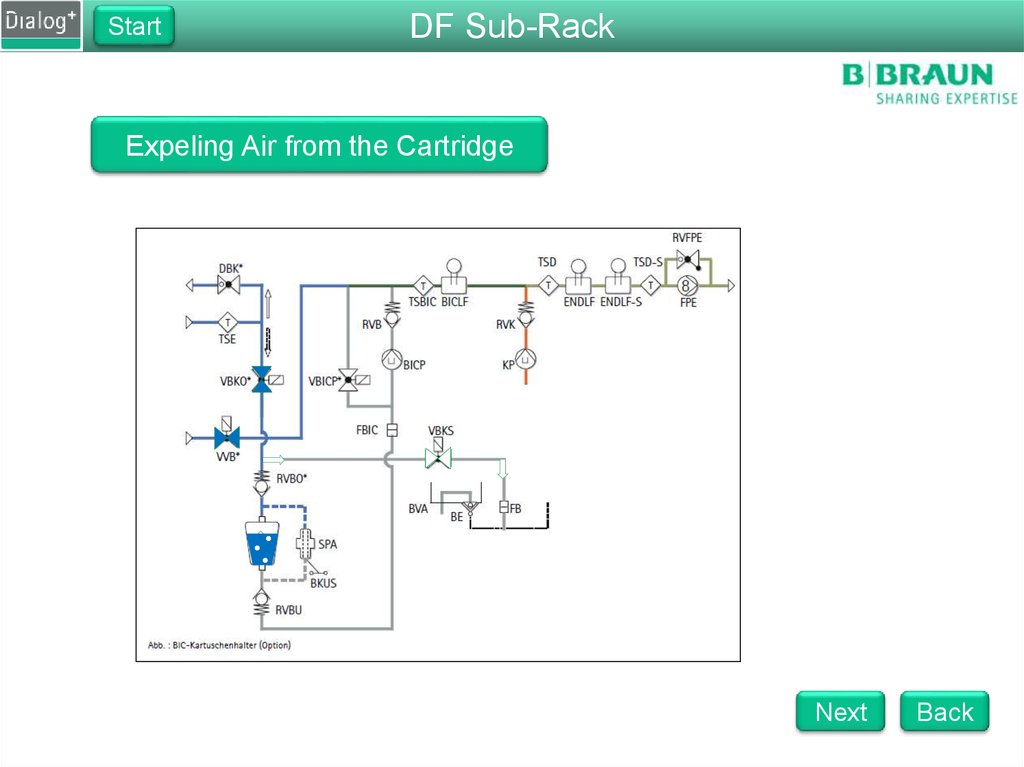
Expeling Air from the Cartridge
Next
Back
86. Folie 86
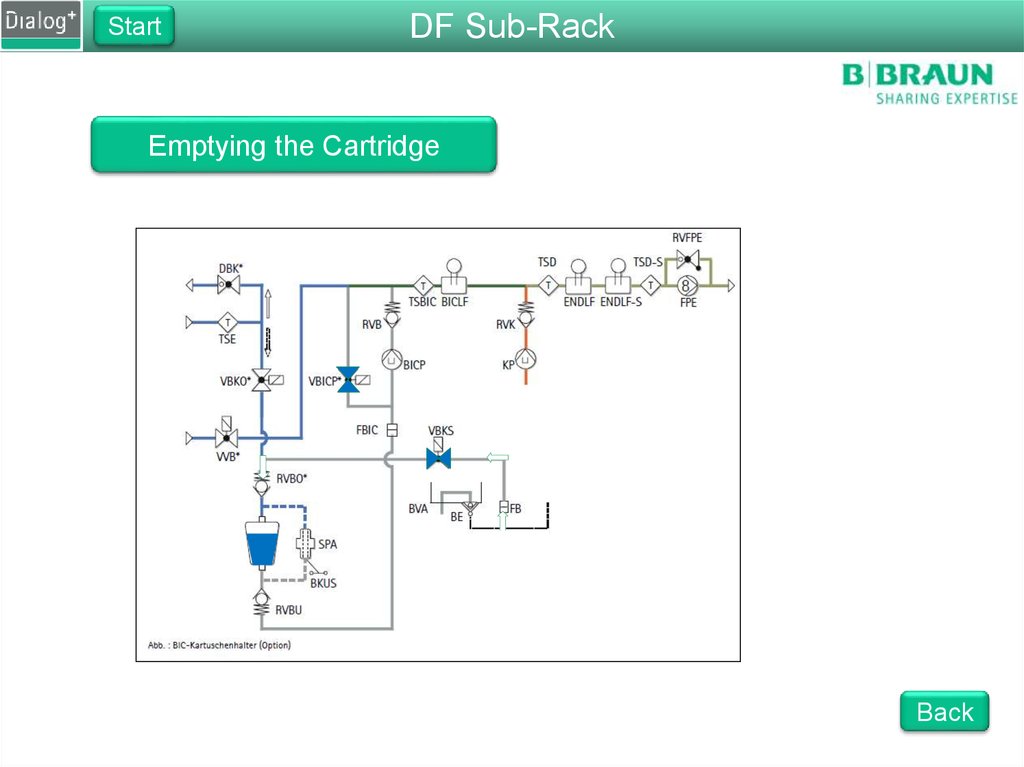
StartDF Sub-Rack
Emptying the Cartridge
Back
87. Folie 87
Dialog+Dialog+ Hydraulic Test
Welcome to the Dialog+ Component Overview. Here you will have the opportunity to look
at different components in Question
the machine.
1 You will find out what there functions are, and
how they work together with other components.
What compenent is not part of the water sub-rack?
A
The Disinfection Valve
B
The Degassing Valve
C
The Degassing Temperature Sensor
D
The Water Inlet Valve
Next
88. Folie 88
Dialog+Dialog+ Hydraulic Test
Question 2
How many temperature sensors are in the machine?
A
4
B
5
C
6
D
7
Next
89. Folie 89
Dialog+Dialog+ Hydraulic Test
Question 3
What is the status of the degassing valve during disinfection?
A
Closed
B
Open
C
Switches between open and closed
D
Only open for short times
Next
90. Folie 90
Dialog+Dialog+ Hydraulic Test
Question 4
Which pump is responsible for pumping fresh dialysate fluid
into the balance chamber?
A
Flow Pump Inlet
B
Flow Pump Outlet
C
Flow Pump Inlet and Flow Pump Outlet
D
Degassing Pump
Next
91. Folie 91
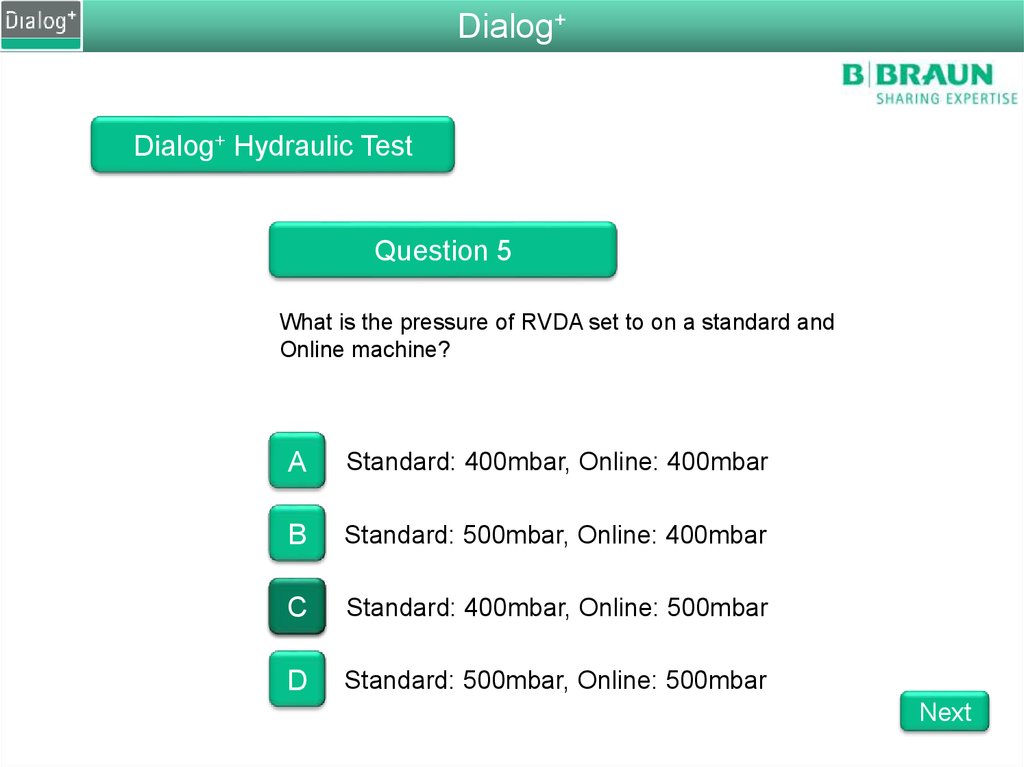
Dialog+Dialog+ Hydraulic Test
Question 5
What is the pressure of RVDA set to on a standard and
Online machine?
A
Standard: 400mbar, Online: 400mbar
B
Standard: 500mbar, Online: 400mbar
C
Standard: 400mbar, Online: 500mbar
D
Standard: 500mbar, Online: 500mbar
Next
92. Folie 92
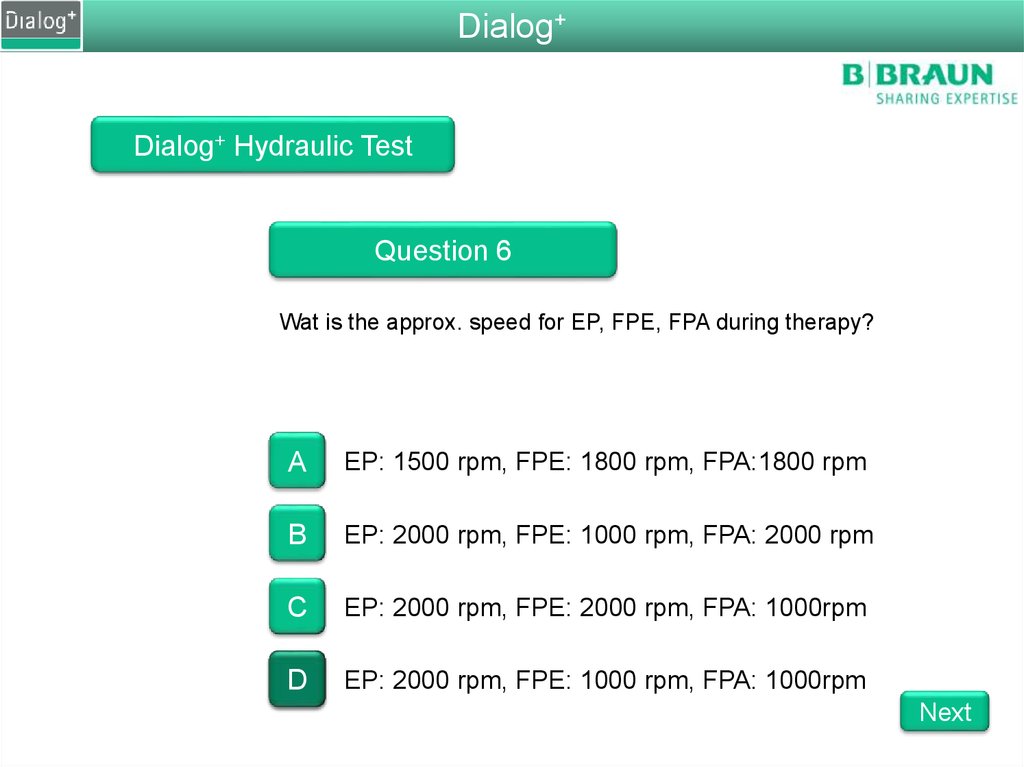
Dialog+Dialog+ Hydraulic Test
Question 6
Wat is the approx. speed for EP, FPE, FPA during therapy?
A
EP: 1500 rpm, FPE: 1800 rpm, FPA:1800 rpm
B
EP: 2000 rpm, FPE: 1000 rpm, FPA: 2000 rpm
C
EP: 2000 rpm, FPE: 2000 rpm, FPA: 1000rpm
D
EP: 2000 rpm, FPE: 1000 rpm, FPA: 1000rpm
Next
93. Folie 93
Dialog+Dialog+ Hydraulic Test
Test Completed
All the letters that have turned dark green were
answered correctly. Please Restart the test to see
how it went.
Restart Test
Back
94. Folie 94
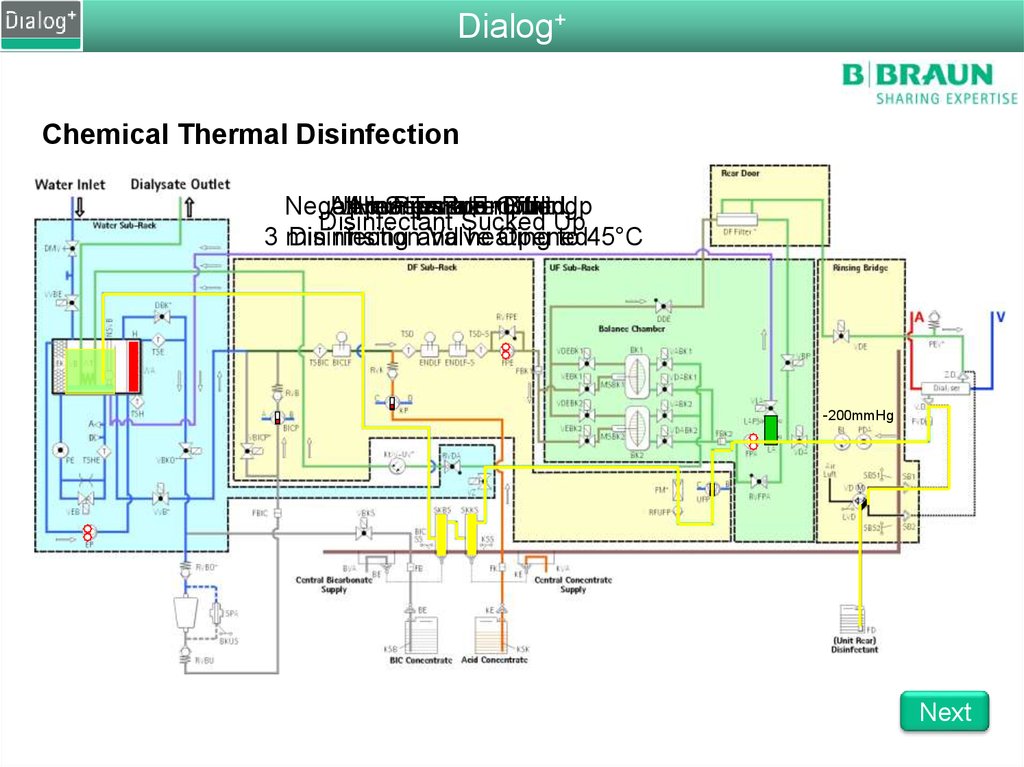
Dialog+Chemical Thermal Disinfection
Negative
All
Upline
Air
Heater
pumps
Separator
Pressure
Tank
Rod
are
Emptied
running
Off
Built
FilledUp
Disinfectant Sucked Up
3 min
Disinfection
rinsing and
Valve
heating
Opened
to 45°C
-200mmHg
Next
95. Folie 95
Dialog+Chemical Thermal Disinfection
All pumps are running
Minimum disinfection time, above minimum Temp
Next
96. Folie 96
Dialog+Chemical Thermal Disinfection
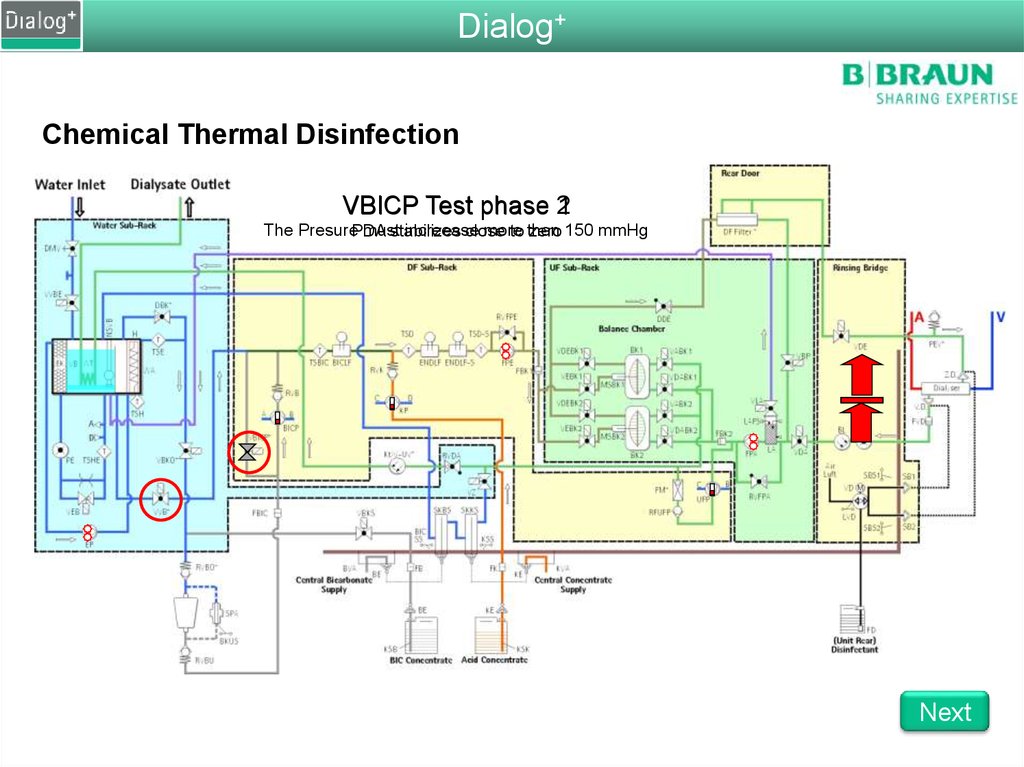
VBICP Test phase 2
1
The PresurePDA
must
increease
more
stabilizes
close
to then
zero 150 mmHg
Next
97. Folie 97
Dialog+Chemical Thermal Disinfection
Rinsing out of disinfectant
Back
98. Folie 98
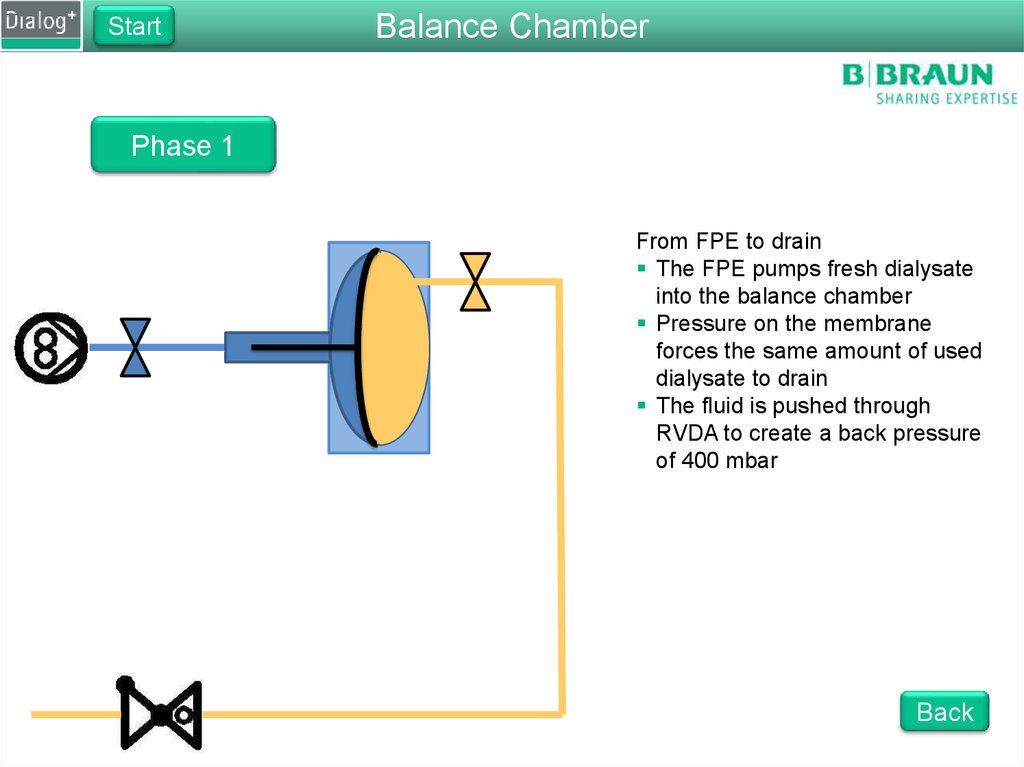
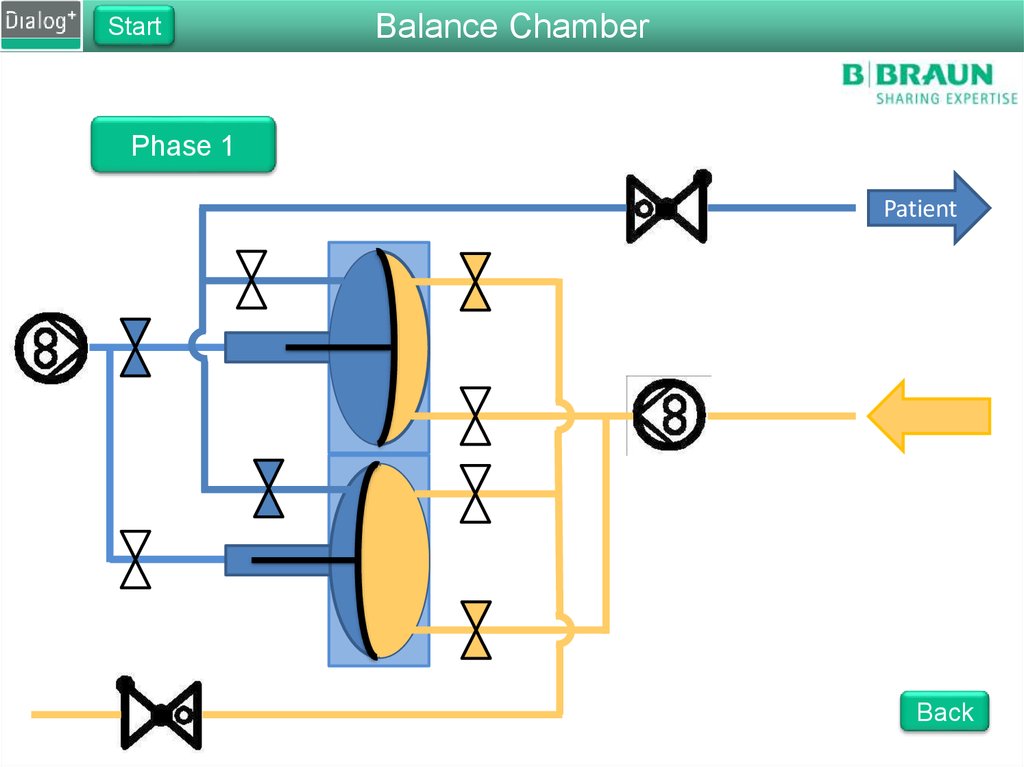
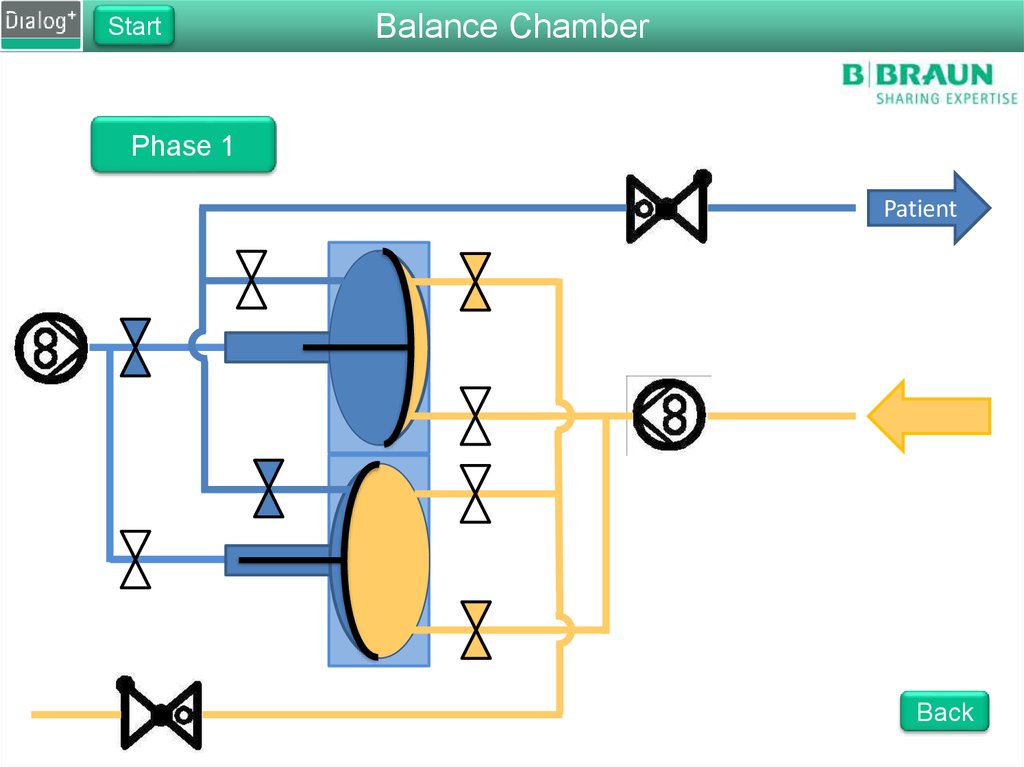
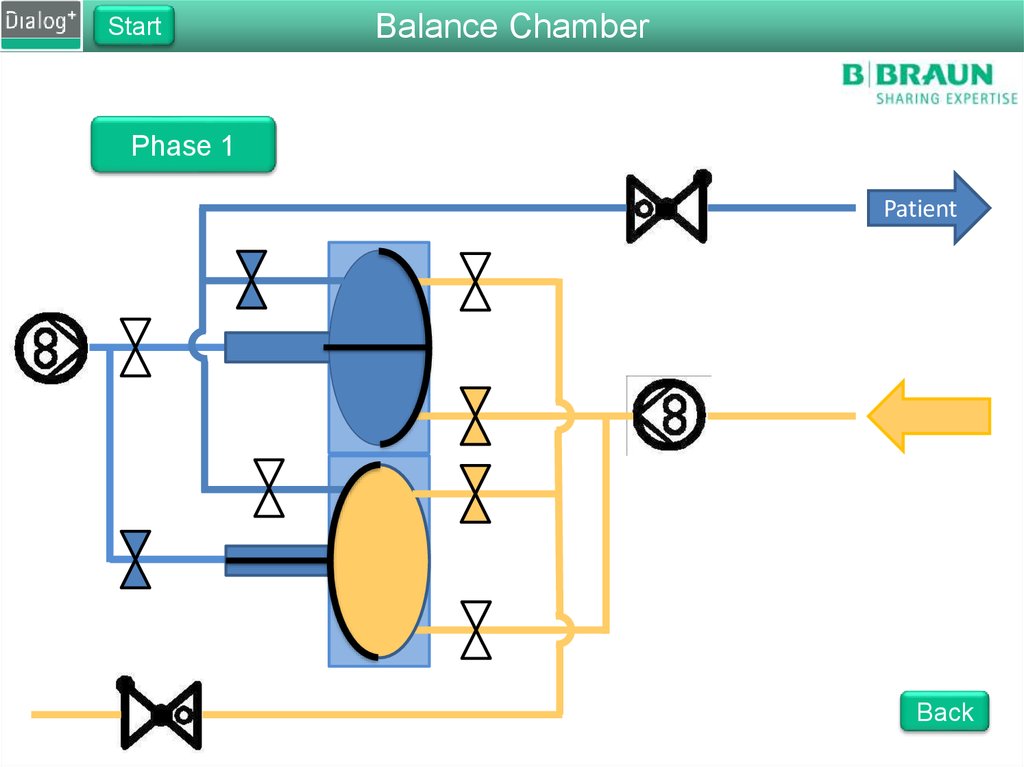
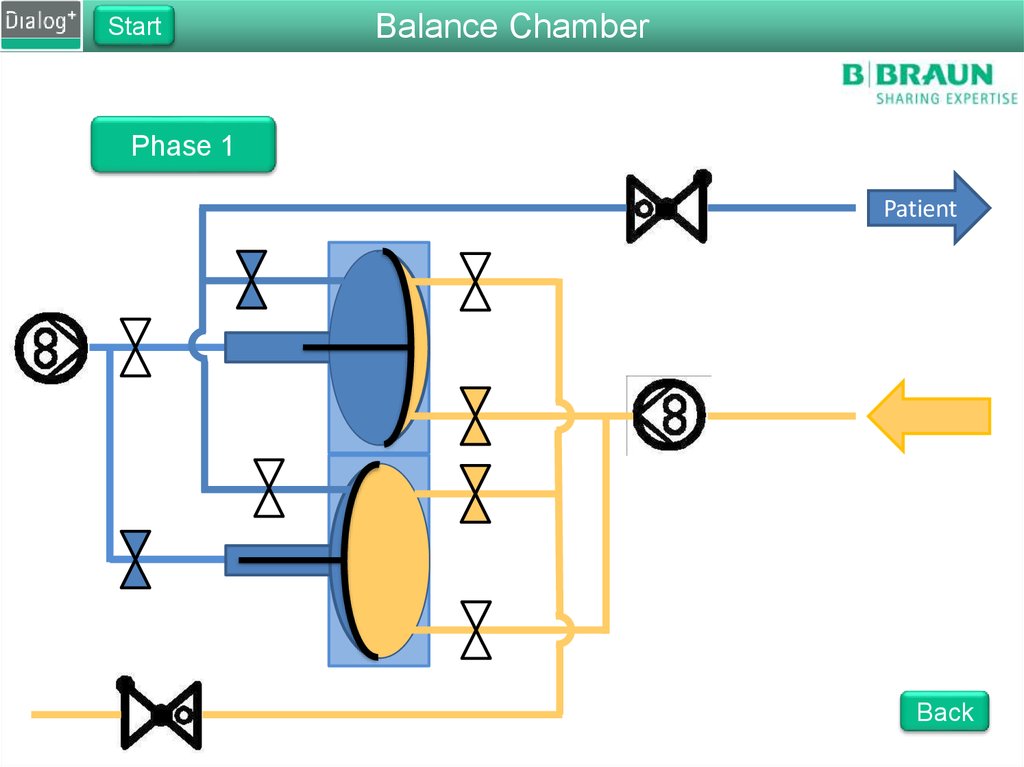
StartBalance Chamber
Phase 1
From FPE to drain
The FPE pumps fresh dialysate
into the balance chamber
Pressure on the membrane
forces the same amount of used
dialysate to drain
The fluid is pushed through
RVDA to create a back pressure
of 400 mbar
Back
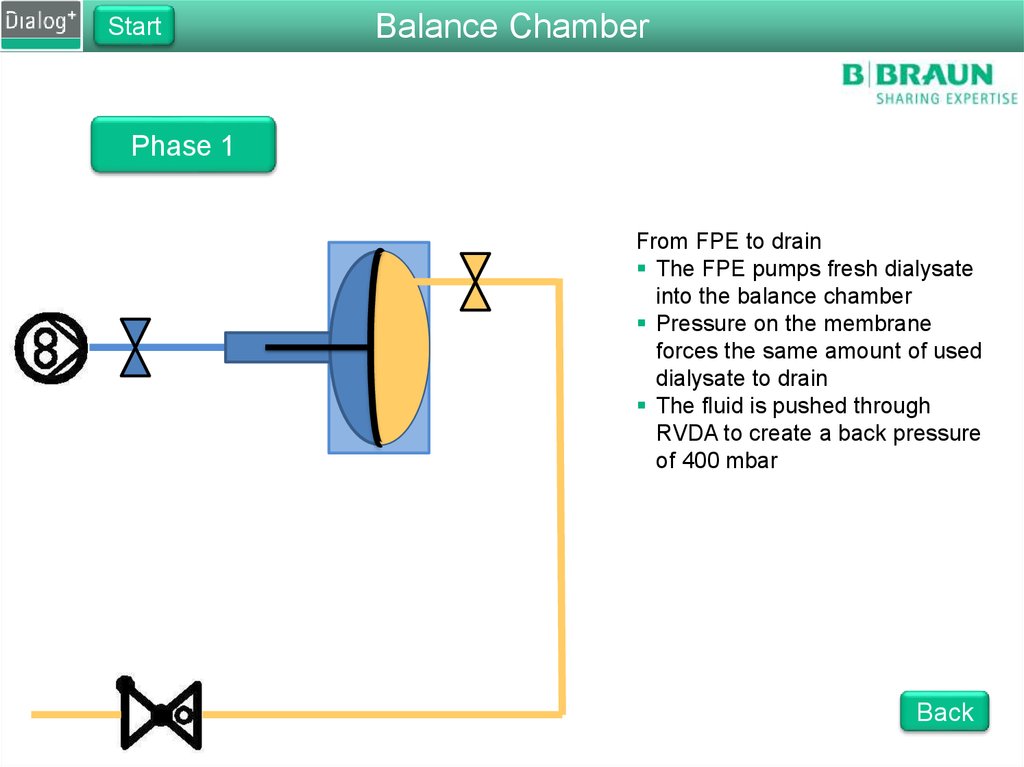
99. Folie 99
StartBalance Chamber
Phase 1
From FPE to drain
The FPE pumps fresh dialysate
into the balance chamber
Pressure on the membrane
forces the same amount of used
dialysate to drain
The fluid is pushed through
RVDA to create a back pressure
of 400 mbar
Back
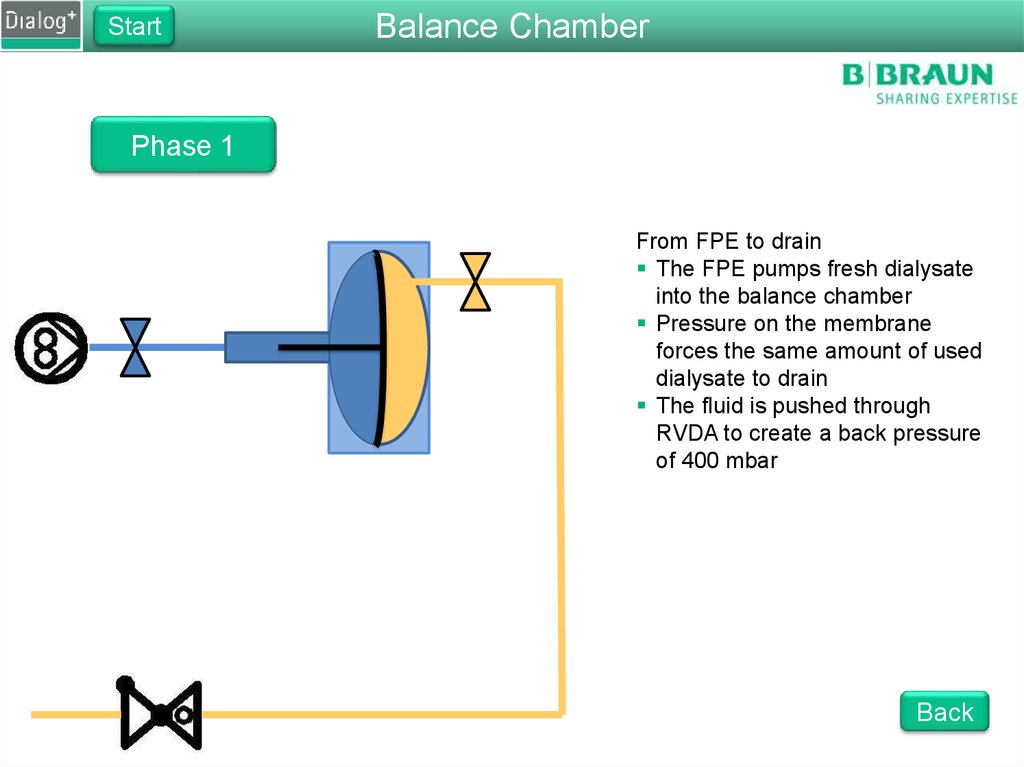
100. Folie 100
StartBalance Chamber
Phase 1
From FPE to drain
The FPE pumps fresh dialysate
into the balance chamber
Pressure on the membrane
forces the same amount of used
dialysate to drain
The fluid is pushed through
RVDA to create a back pressure
of 400 mbar
Back
101. Folie 101
StartBalance Chamber
Phase 1
From FPE to drain
The FPE pumps fresh dialysate
into the balance chamber
Pressure on the membrane
forces the same amount of used
dialysate to drain
The fluid is pushed through
RVDA to create a back pressure
of 400 mbar
Back
102. Folie 102
StartBalance Chamber
Phase 1
From FPE to drain
The FPE pumps fresh dialysate
into the balance chamber
Pressure on the membrane
forces the same amount of used
dialysate to drain
The fluid is pushed through
RVDA to create a back pressure
of 400 mbar
Back
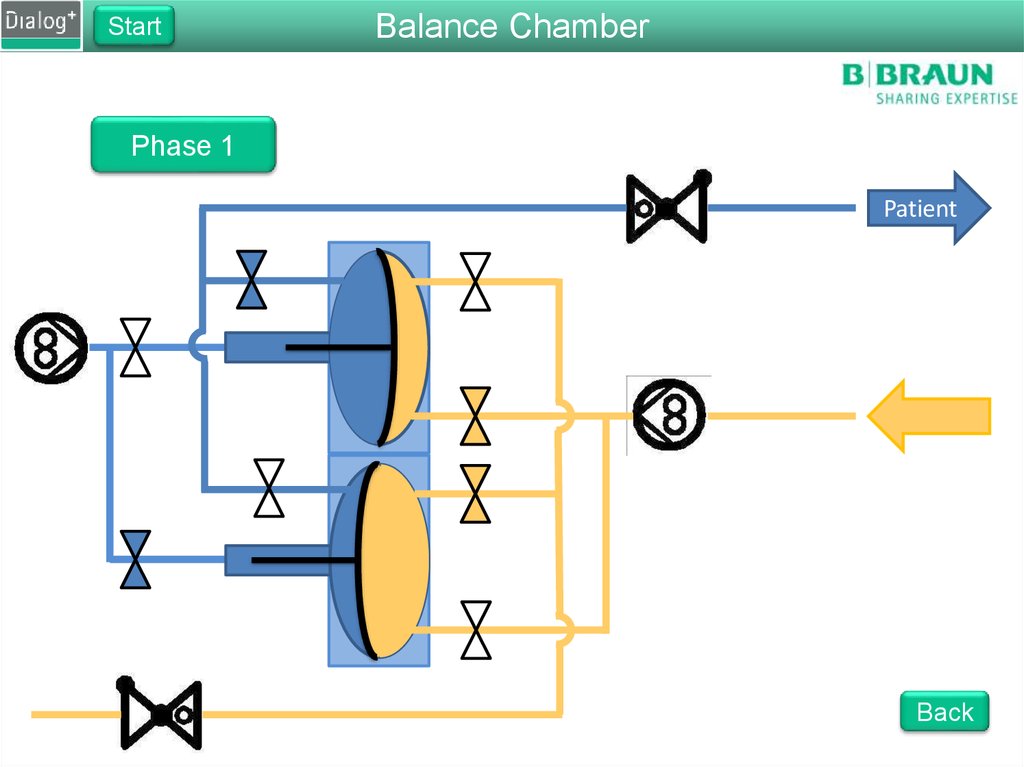
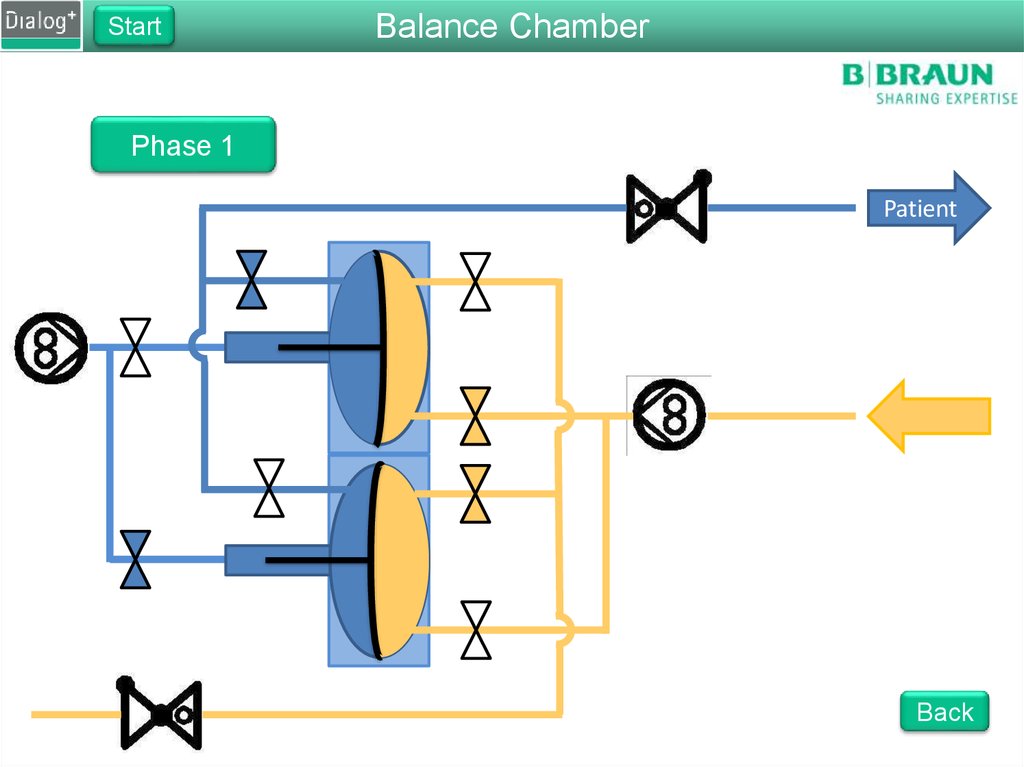
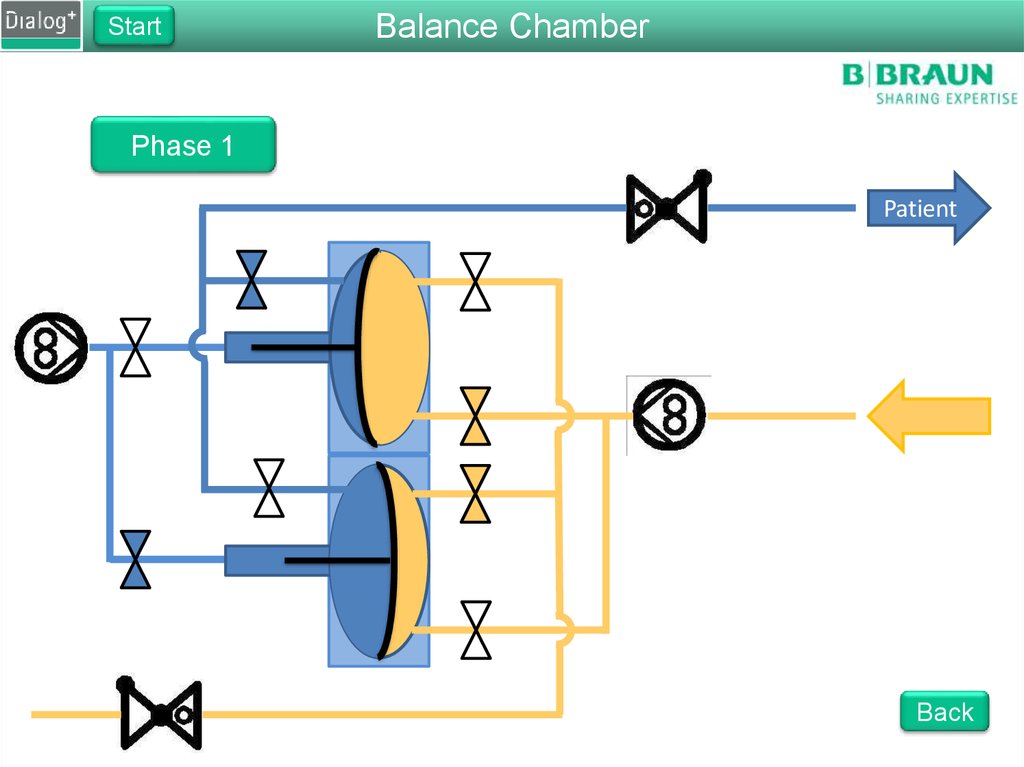
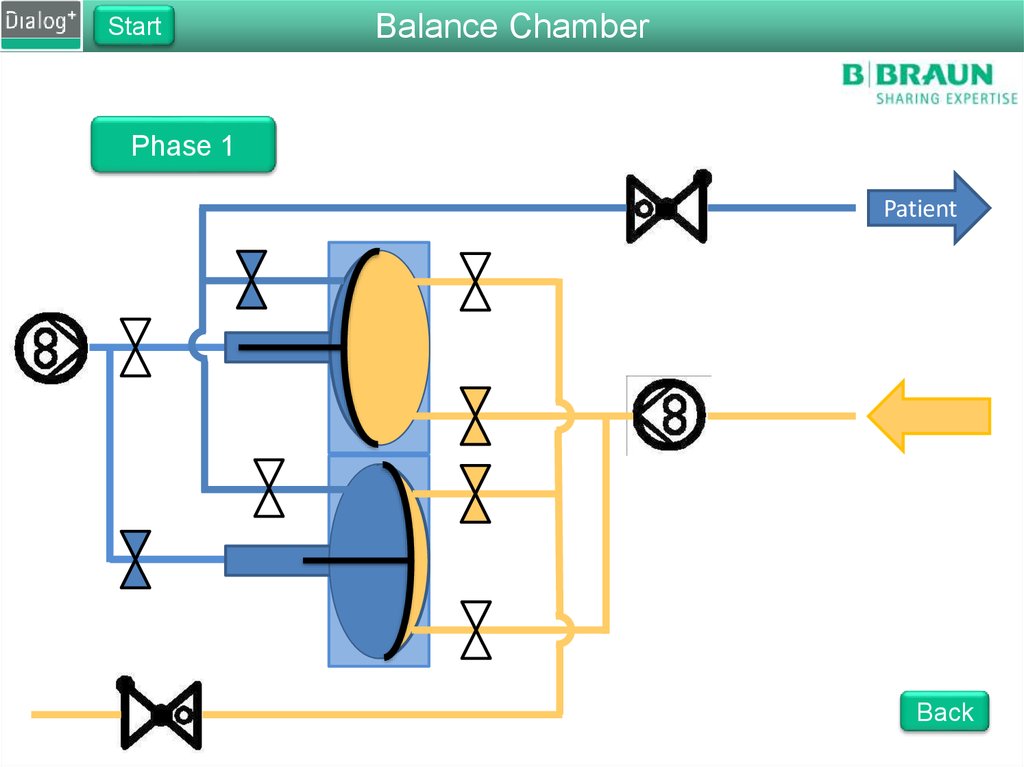
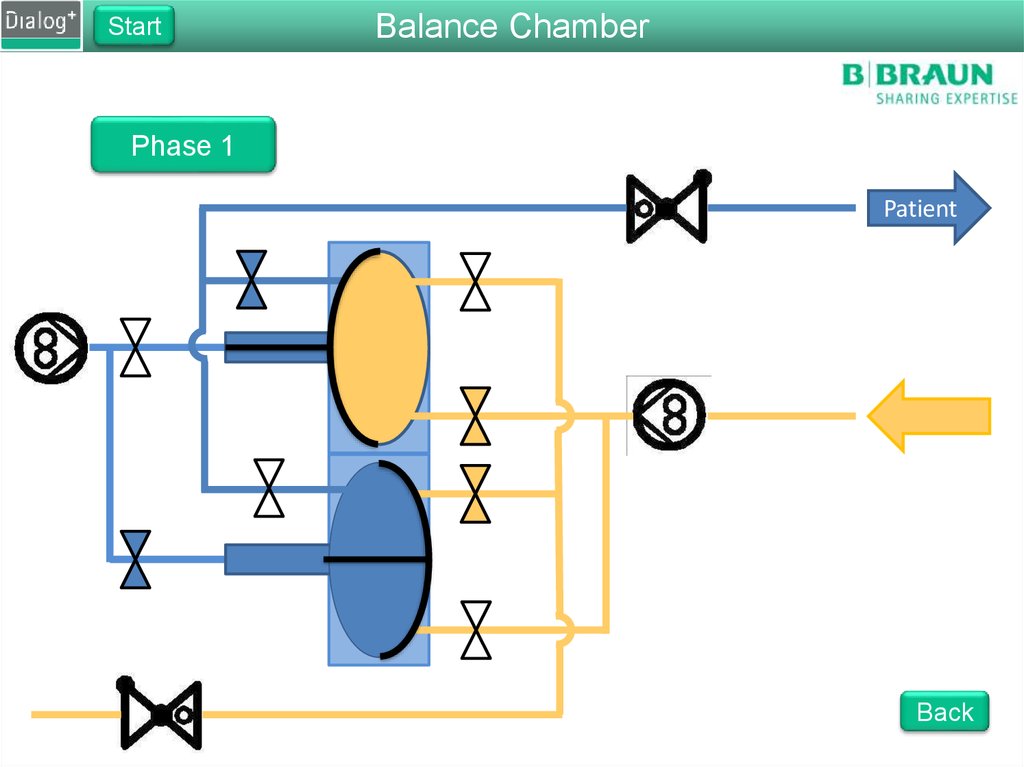
103. Folie 103
StartBalance Chamber
Phase 1
From FPE to drain
The FPE pumps fresh dialysate
into the balance chamber
Pressure on the membrane
forces the same amount of used
dialysate to drain
The fluid is pushed through
RVDA to create a back pressure
of 400 mbar
Back
104. Folie 104
StartBalance Chamber
Phase 1
From FPE to drain
The FPE pumps fresh dialysate
into the balance chamber
Pressure on the membrane
forces the same amount of used
dialysate to drain
The fluid is pushed through
RVDA to create a back pressure
of 400 mbar
Back
105. Folie 105
StartBalance Chamber
Phase 1
From FPE to drain
The FPE pumps fresh dialysate
into the balance chamber
Pressure on the membrane
forces the same amount of used
dialysate to drain
The fluid is pushed through
RVDA to create a back pressure
of 400 mbar
Repeat
Next
Back
106. Folie 106
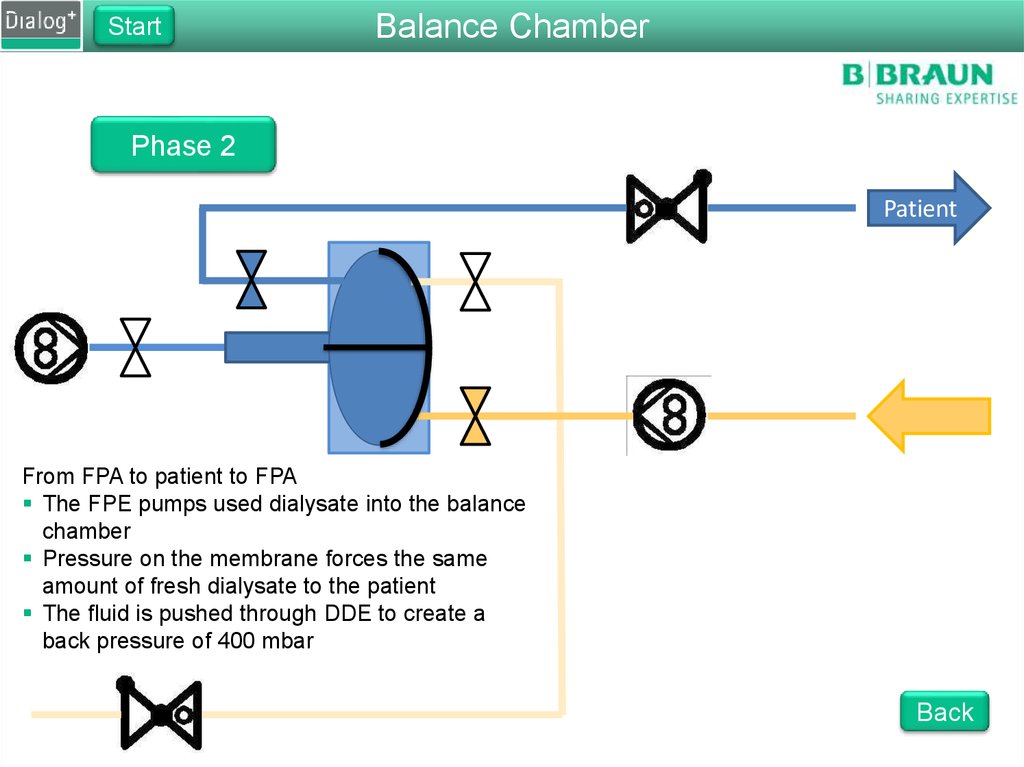
StartBalance Chamber
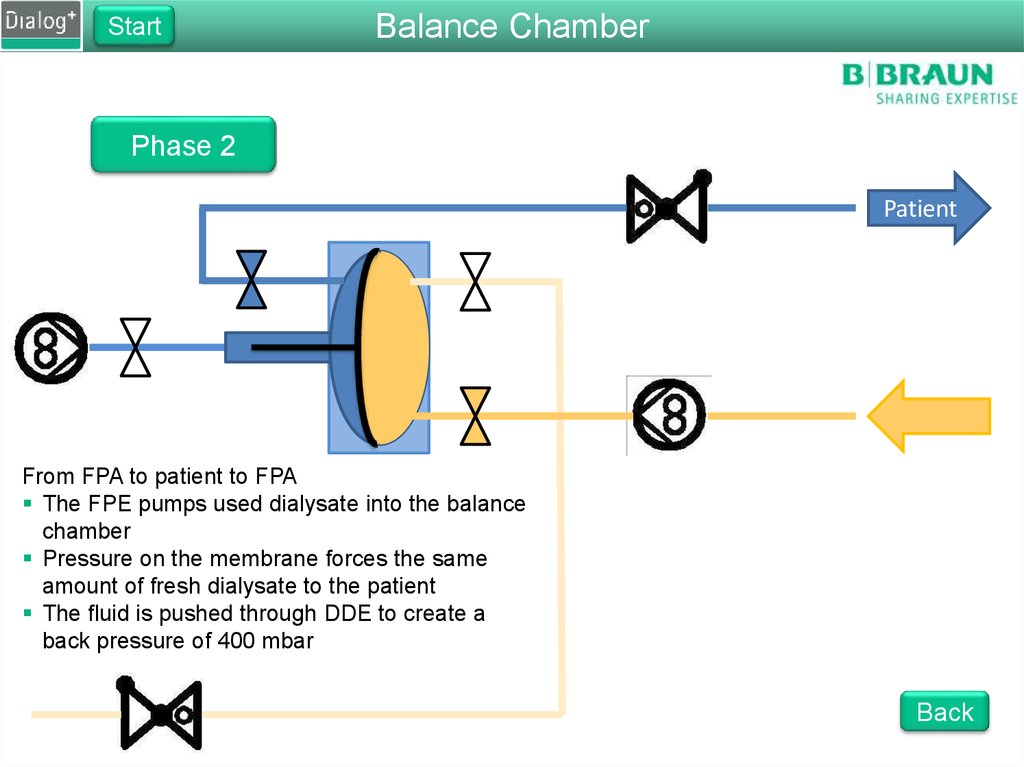
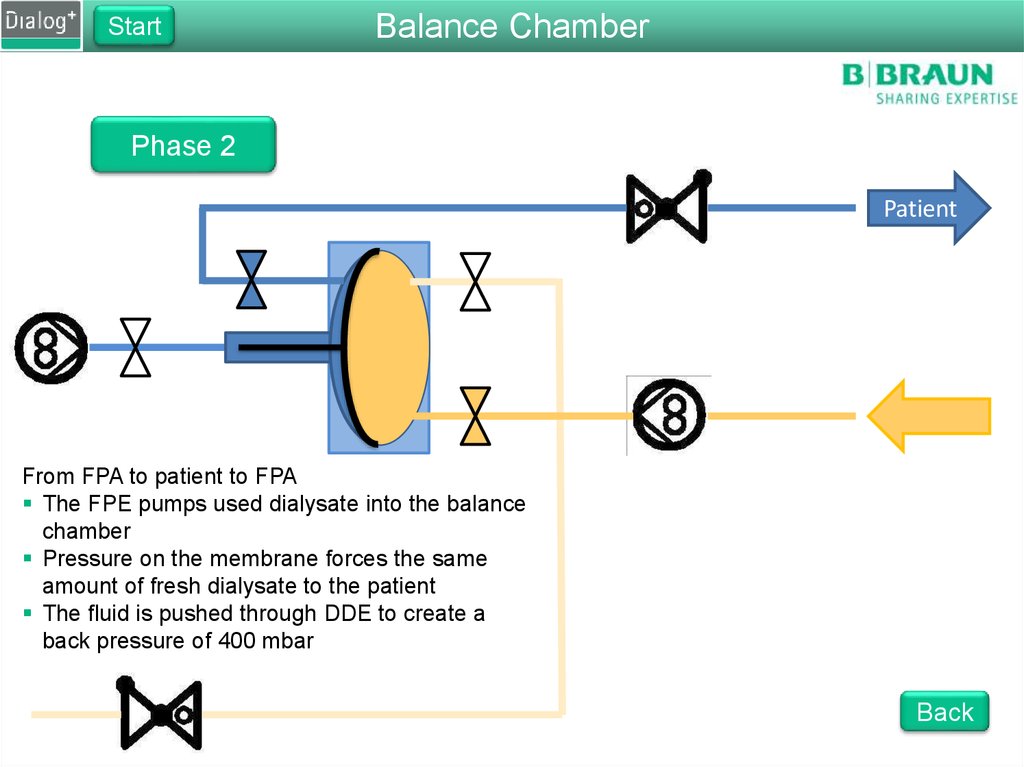
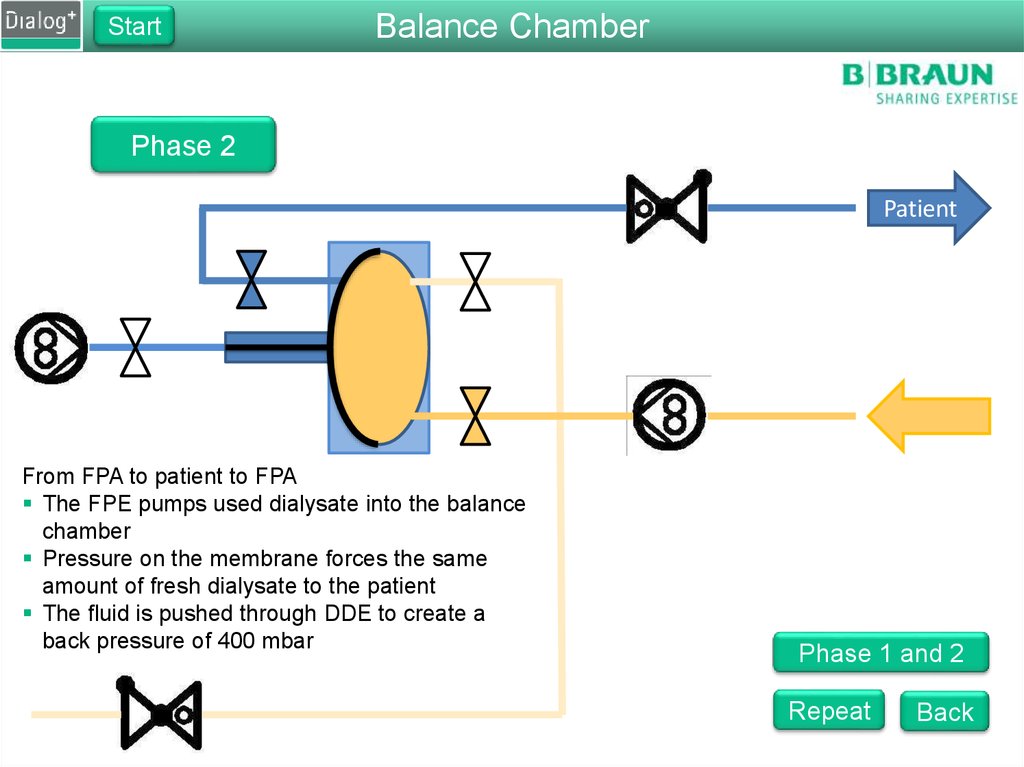
Phase 2
Patient
From FPA to patient to FPA
The FPE pumps used dialysate into the balance
chamber
Pressure on the membrane forces the same
amount of fresh dialysate to the patient
The fluid is pushed through DDE to create a
back pressure of 400 mbar
Back
107. Folie 107
StartBalance Chamber
Phase 2
Patient
From FPA to patient to FPA
The FPE pumps used dialysate into the balance
chamber
Pressure on the membrane forces the same
amount of fresh dialysate to the patient
The fluid is pushed through DDE to create a
back pressure of 400 mbar
Back
108. Folie 108
StartBalance Chamber
Phase 2
Patient
From FPA to patient to FPA
The FPE pumps used dialysate into the balance
chamber
Pressure on the membrane forces the same
amount of fresh dialysate to the patient
The fluid is pushed through DDE to create a
back pressure of 400 mbar
Back
109. Folie 109
StartBalance Chamber
Phase 2
Patient
From FPA to patient to FPA
The FPE pumps used dialysate into the balance
chamber
Pressure on the membrane forces the same
amount of fresh dialysate to the patient
The fluid is pushed through DDE to create a
back pressure of 400 mbar
Back
110. Folie 110
StartBalance Chamber
Phase 2
Patient
From FPA to patient to FPA
The FPE pumps used dialysate into the balance
chamber
Pressure on the membrane forces the same
amount of fresh dialysate to the patient
The fluid is pushed through DDE to create a
back pressure of 400 mbar
Back
111. Folie 111
StartBalance Chamber
Phase 2
Patient
From FPA to patient to FPA
The FPE pumps used dialysate into the balance
chamber
Pressure on the membrane forces the same
amount of fresh dialysate to the patient
The fluid is pushed through DDE to create a
back pressure of 400 mbar
Back
112. Folie 112
StartBalance Chamber
Phase 2
Patient
From FPA to patient to FPA
The FPE pumps used dialysate into the balance
chamber
Pressure on the membrane forces the same
amount of fresh dialysate to the patient
The fluid is pushed through DDE to create a
back pressure of 400 mbar
Back
113. Folie 113
StartBalance Chamber
Phase 2
Patient
From FPA to patient to FPA
The FPE pumps used dialysate into the balance
chamber
Pressure on the membrane forces the same
amount of fresh dialysate to the patient
The fluid is pushed through DDE to create a
back pressure of 400 mbar
Phase 1 and 2
Repeat
Back
114. Folie 114
StartBalance Chamber
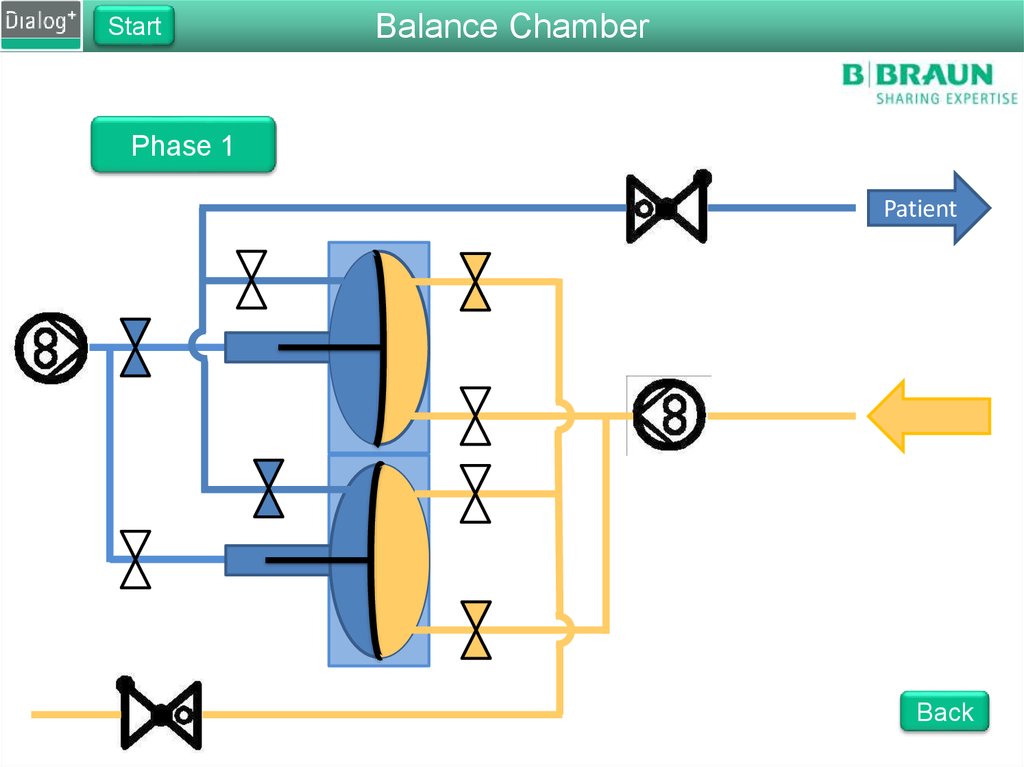
Phase 1
Patient
Back
115. Folie 115
StartBalance Chamber
Phase 1
Patient
Back
116. Folie 116
StartBalance Chamber
Phase 1
Patient
Back
117. Folie 117
StartBalance Chamber
Phase 1
Patient
Back
118. Folie 118
StartBalance Chamber
Phase 1
Patient
Back
119. Folie 119
StartBalance Chamber
Phase 1
Patient
Back
120. Folie 120
StartBalance Chamber
Phase 1
Patient
Back
121. Folie 121
StartBalance Chamber
Phase 1
Patient
Back
122. Folie 122
StartBalance Chamber
Phase 1
Patient
Back
123. Folie 123
StartBalance Chamber
Phase 1
Patient
Back
124. Folie 124
StartBalance Chamber
Phase 1
Patient
Back
125. Folie 125
StartBalance Chamber
Phase 1
Patient
Back
126. Folie 126
StartBalance Chamber
Phase 1
Patient
Back
127. Folie 127
StartBalance Chamber
Phase 1
Patient
Back
128. Folie 128
StartBalance Chamber
Phase 1
Patient
Back



































































 Промышленность
Промышленность








