Похожие презентации:
First aid in different situations
1.
Ministry of science and education of the Russian FederationFederal state budgetary educational institution of higher education
«Yaroslav Mudryi Novgorod state University»
MEDICAL COLLEGE
FIRST AID IN VARIOUS SITUATIONS
Discipline «English»
Specialty 31.02.01 Medical care (in-depth training)
Performed by:
Student group 7871 to Konstantinova Emilia
Pavlovna
Teacher:
Limicheva Olga Sergeevna
2.
First aid is a complex of simple medicalmeasures performed at the site of injury, mainly
in the order of self-help and mutual assistance,
as well as by participants in rescue operations.
First aid consists of:
• timely and accurate assessment of the
victim's condition
• in providing the victim with an optimal
position
• implementation of the necessary priority
measures to ensure the patency of the
respiratory tract, respiration and blood
circulation
3.
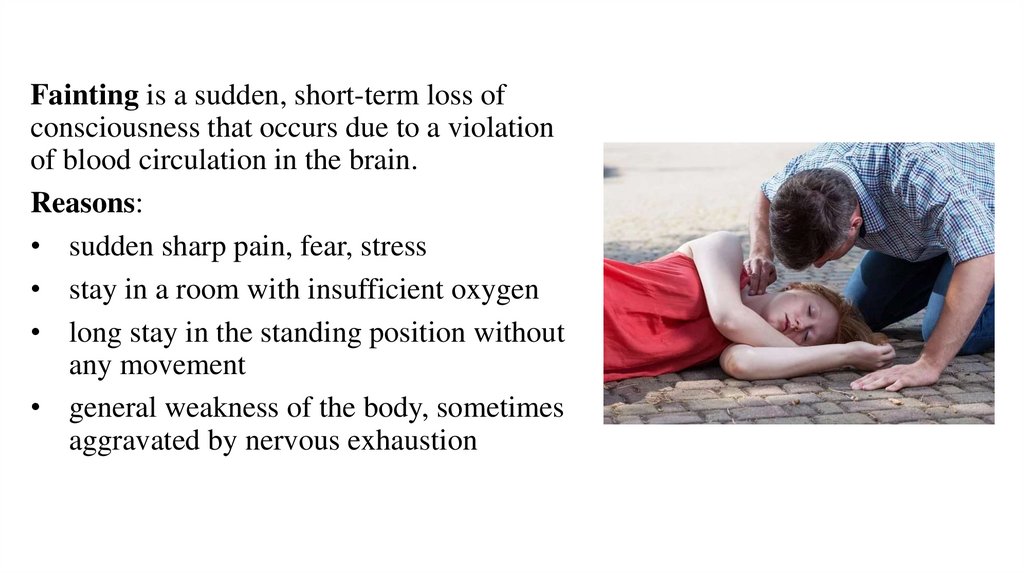
Fainting is a sudden, short-term loss ofconsciousness that occurs due to a violation
of blood circulation in the brain.
Reasons:
• sudden sharp pain, fear, stress
• stay in a room with insufficient oxygen
• long stay in the standing position without
any movement
• general weakness of the body, sometimes
aggravated by nervous exhaustion
4.
Symptoms and signs of fainting:• short-term loss of consciousness,
the victim falls
• airway clear
• pulse is weak and rare
• breathing is rare and shallow
• dizziness, tinnitus, sudden
weakness, blurred vision, cold
sweat, nausea, numbness of the
limbs
5.
First aid for fainting:• put the patient on his back
• provide fresh air supply
• raise the patient's legs above head level or bend their knees
6.
IMPORTANT!• Fainting can be a manifestation of a serious, including acute illness that
requires emergency medical care.
• You should not rush to lift the victim after he regained consciousness. If
the conditions allow, the victim can be given a drink of hot tea, then
help to rise and sit down. If the victim again feels fainting, it is
necessary to lay him on his back and lift his legs.
• If the victim is unconscious for several minutes, then immediately
call an ambulance!
7.
Shock is a condition that threatens the life of the victim and ischaracterized by insufficient blood supply to tissues and internal organs.
Reasons:
• heart problems
• reducing the volume of fluid circulating in the body (severe bleeding,
vomiting, diarhea, etc.)
8.
Symptoms and signs of shock:• The victim is usually conscious, but the condition can worsen very
quickly, up to loss of consciousness
• Airways are clear, breathing is frequent and shallow
• Pulse is weak and rapid
• There may be nausea, vomiting, chills
• The skin is pale, cool and sticky
• The victim may feel a sense of thirst, due to the fact that the brain feels a
lack of fluid
9.
First aid for shock:• Any first aid includes shockproof measures
• Calm the victim
• Cover the victim with a blanket to keep them warm
• Lay the victim on his back and lift his legs (if he is conscious and does
not have injuries to the head, neck and spine)
• Give a warm sweet drink
• Monitor the status
In any case, do not leave the victim alone!
10.
• If the shock is caused by a violation of heart activity, the victim shouldbe given a semi-sitting position, placing pillows or rolled clothes under
the head, shoulders and knees
• It is not advisable to lay the victim on his back, since in this case it will
be more difficult for him to breathe
• Allow the victim to chew an Aspirin tablet
In all these cases, it is necessary to call an ambulance and monitor the
condition of the victim before its arrival, being ready to start
cardiopulmonary resuscitation!
11.
Anaphylactic shock is an extensive immediate allergic reaction thatoccurs when an allergen is ingested (insect bites, medicinal or food
allergens). Usually develops in a few seconds.
Immediate hospitalization is required!
12.
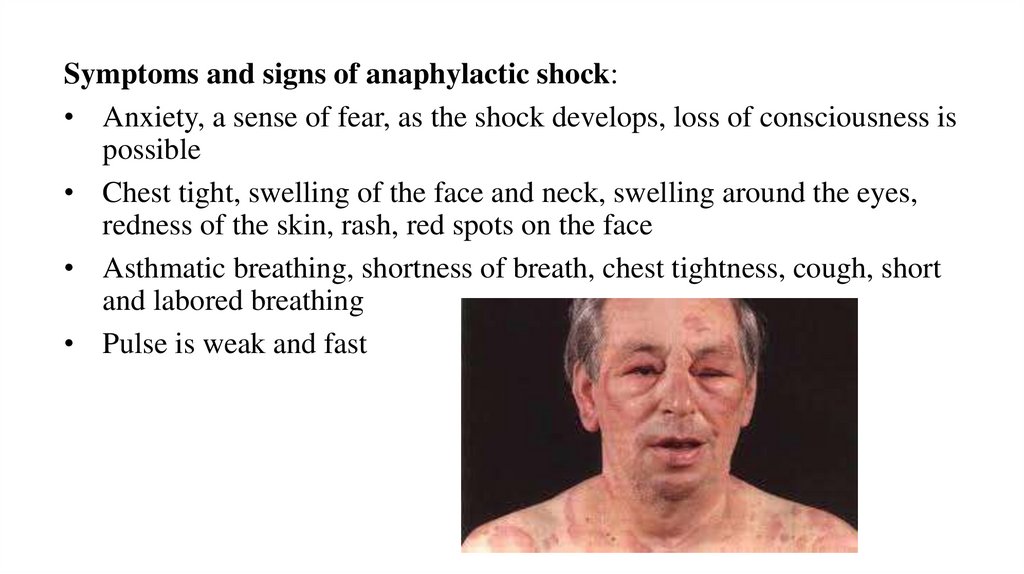
Symptoms and signs of anaphylactic shock:• Anxiety, a sense of fear, as the shock develops, loss of consciousness is
possible
• Chest tight, swelling of the face and neck, swelling around the eyes,
redness of the skin, rash, red spots on the face
• Asthmatic breathing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, cough, short
and labored breathing
• Pulse is weak and fast
13.
First aid for anaphylactic shock:1. If the victim is conscious, give him a semi-sitting position to facilitate
breathing. It is better to put the victim on the floor, unbutton his
clothes
2. Call an ambulance
3. If the victim is unconscious, move him to a safe position, control his
breathing and blood circulation, and be ready to start cardiopulmonary
resuscitation
14.
Bronchial asthma is an allergic disease, the main manifestation of which isan attack of suffocation caused by a violation of the patency of the
bronchi. It is caused by various allergens (pollen of plants and other
substances of plant and animal origin, industrial products, etc.).
Symptoms and signs of bronchial asthma:
• Shortness of breath
• Rale
• Cough (including night cough)
• Dyspnea
• Chest pain
15.
First aid for an attack of bronchial asthma:• Calm the victim
• Unbutton the victim's clothing to make it easier for her to breathe
• Open the window
• The use of a pocket inhaler available to the victim (salbutamol, fenoterol) can be
repeated 3 times with an interval of 20 minutes.
• Help the victim to use their medicine: take it out, remove it from the package, put
on the nozzle, turn the aerosol over and make 1-2 clicks so that the drug gets into
the area of the back wall of the pharynx during spraying. At this time, the victim
will take a few breaths, and the active substance will enter the respiratory tract.
• Give the victim a comfortable sitting position (the patient's hands should lie on
the table or handrails of the chair, elbows apart).
• If there is no effect or the patient's condition becomes more severe (there is a
threat of asthmatic status), you should immediately call an ambulance.
16.
Hypoglycemia is a low level of glucose in the blood. This may be in a patientwith diabetes.
Diabetes mellitus is a disease in which the body does not produce enough of
the hormone insulin, which regulates the amount of sugar in the blood.
Hypoglycemia in a patient with diabetes can occur for three reasons:
• The victim gave himself an injection of insulin, but did not have time to
eat in time
• In case of an insulin overdose
• With excessive physical activity
17.
Symptoms and signs of hypoglycemia:• Drowsiness
• Sweat
• Pallor
• Dizziness
• Irritability
• Hunger
18.
First aid for hypoglycemia:1. If the victim is conscious, give him a
relaxed position (lying or sitting).
2. Give the victim a sugar drink (two
tablespoons of sugar per glass of water), a
piece of sugar, chocolate or candy, you
can caramel or cookies.
3. Provide rest until the condition is fully
normalized.
4. If the victim has lost consciousness, move
him to a safe position, call an ambulance,
and monitor the condition.















 Медицина
Медицина








