Похожие презентации:
Neurology
1.
NeurologyINTRACRANIAL TUMOURS & DEMENTIA
2.
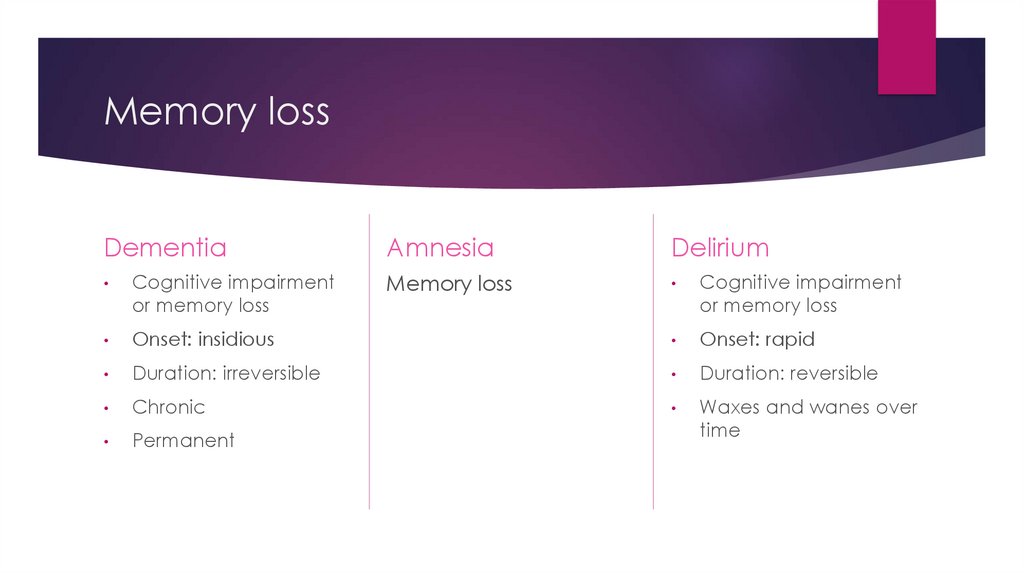
Memory lossDementia
Amnesia
Delirium
Memory loss
Cognitive impairment
or memory loss
Cognitive impairment
or memory loss
Onset: insidious
Onset: rapid
Duration: irreversible
Duration: reversible
Chronic
Permanent
Waxes and wanes over
time
3.
4.
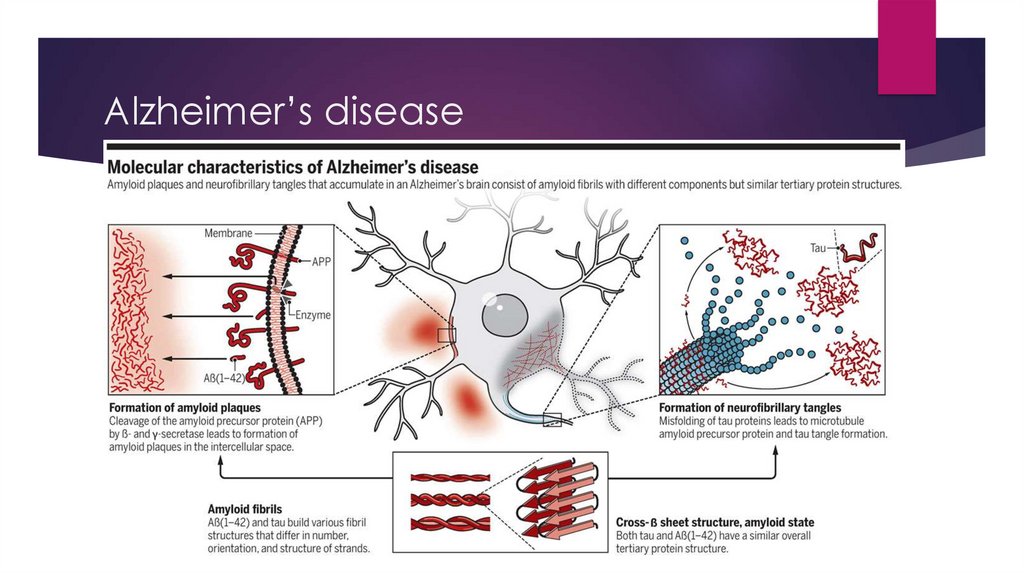
Alzheimer’sdisease
5.
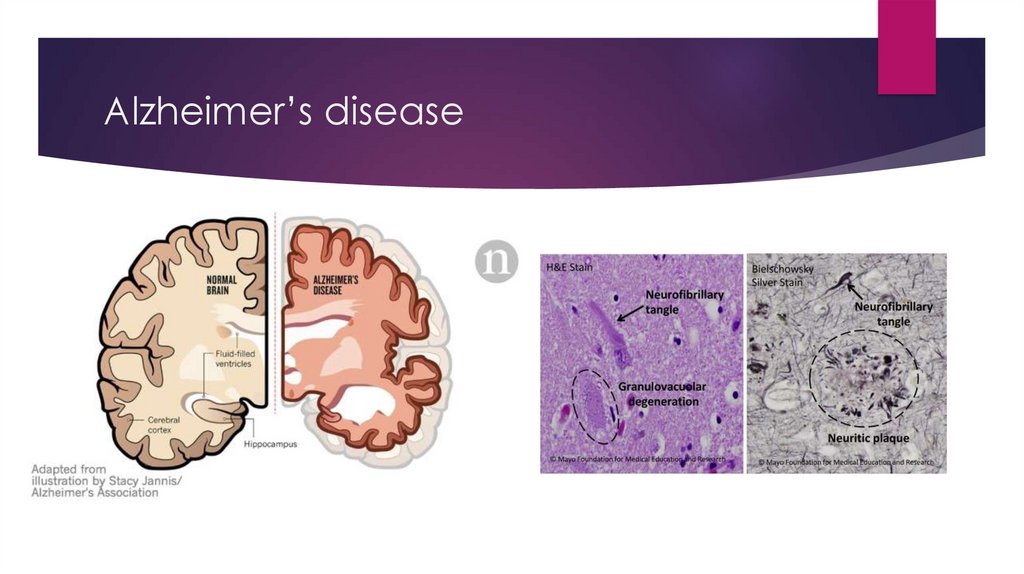
Alzheimer’s disease6.
Alzheimer’s disease7.
Alzheimer’s diseaseSporadic and Familial (PSEN-1 or PSEN2 mutation and trisomy 21)
Symptoms: short-term memory loss->
loss of motor skills and language->
long-term memory loss-> more
disoriented-> bedridden->death
Diagnosis: clinical, brain biopsy,
CT (cortical atrophy)
Treatment: no cure, supportive care,
family education.
Cholinesterase inhibitors: Tacrine,
Donepezil, Rivastigmine, Galantamine
8.
Pick’s disease9.
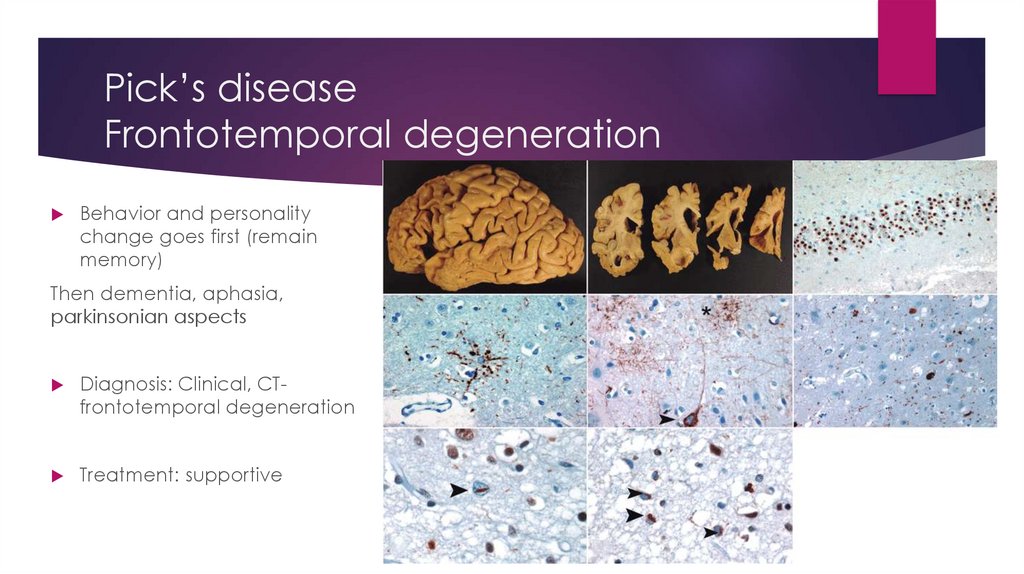
Pick’s diseaseFrontotemporal degeneration
Behavior and personality
change goes first (remain
memory)
Then dementia, aphasia,
parkinsonian aspects
Diagnosis: Clinical, CTfrontotemporal degeneration
Treatment: supportive
10.
Lewy-bodydementia
11.
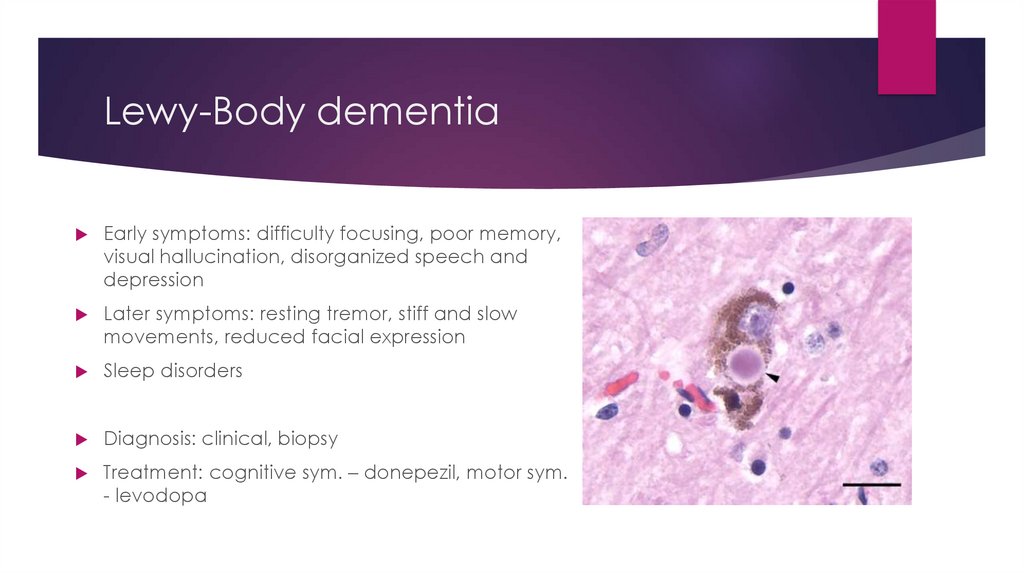
Lewy-Body dementiaEarly symptoms: difficulty focusing, poor memory,
visual hallucination, disorganized speech and
depression
Later symptoms: resting tremor, stiff and slow
movements, reduced facial expression
Sleep disorders
Diagnosis: clinical, biopsy
Treatment: cognitive sym. – donepezil, motor sym.
- levodopa
12.
Vasculardementia
13.
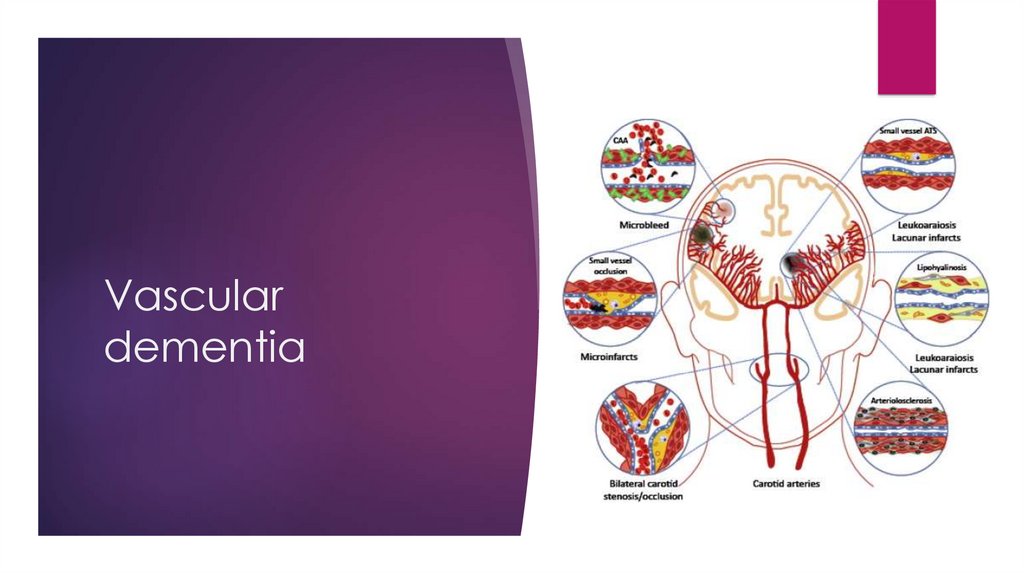
Vascular dementiaMulti-infarct dementia
Symptoms:
Very depend on which region of the
brain is damage
Stepwise decline
Diagnosis: Clinical, neuropsychological
test, CT or MRI
Treatment: reducing rick of repeated
strokes
14.
CJD15.
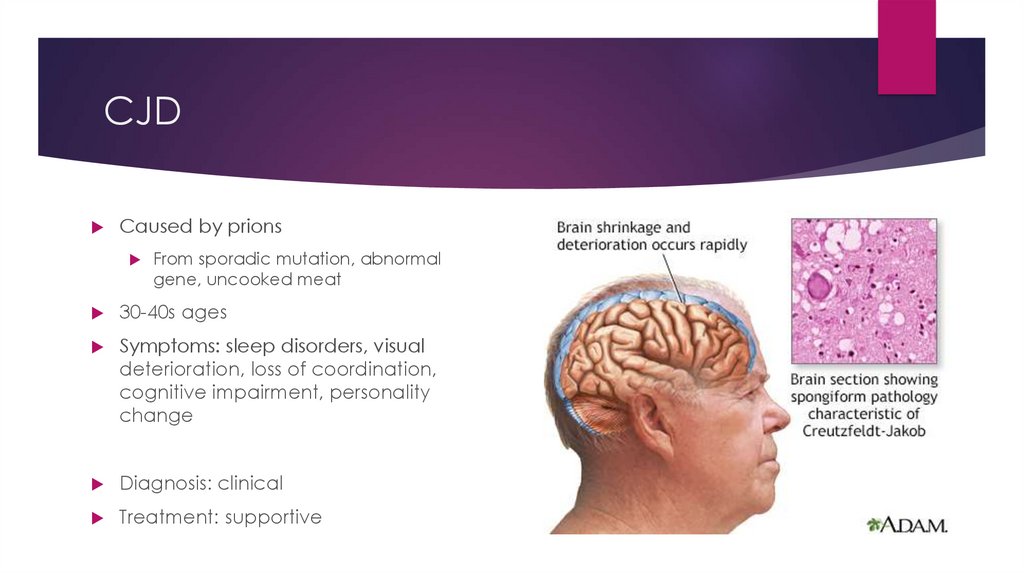
CJDCaused by prions
From sporadic mutation, abnormal
gene, uncooked meat
30-40s ages
Symptoms: sleep disorders, visual
deterioration, loss of coordination,
cognitive impairment, personality
change
Diagnosis: clinical
Treatment: supportive
16.
Normal PressureHydrocephalus
17.
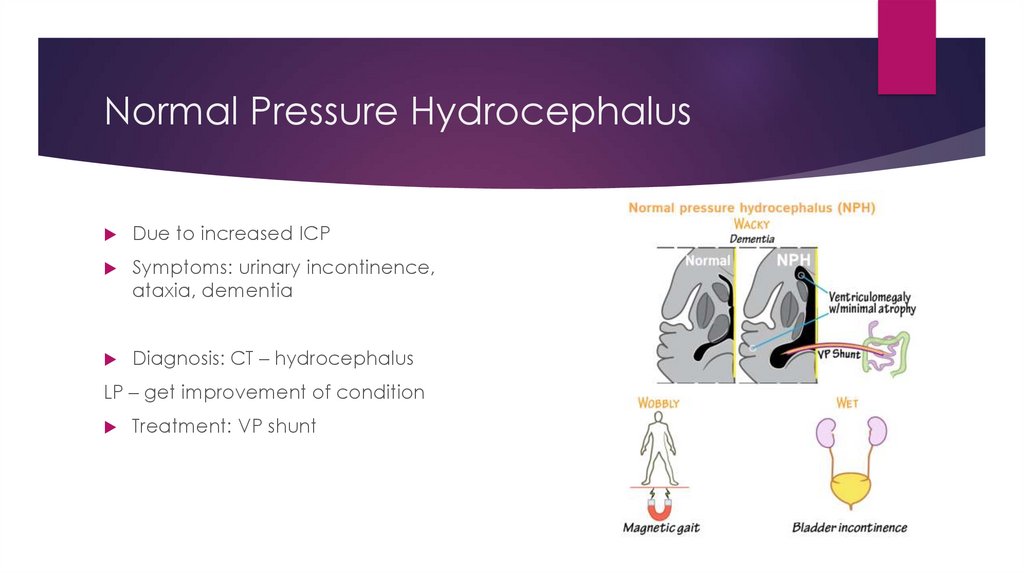
Normal Pressure HydrocephalusDue to increased ICP
Symptoms: urinary incontinence,
ataxia, dementia
Diagnosis: CT – hydrocephalus
LP – get improvement of condition
Treatment: VP shunt
18.
Huntington’sdisease
19.
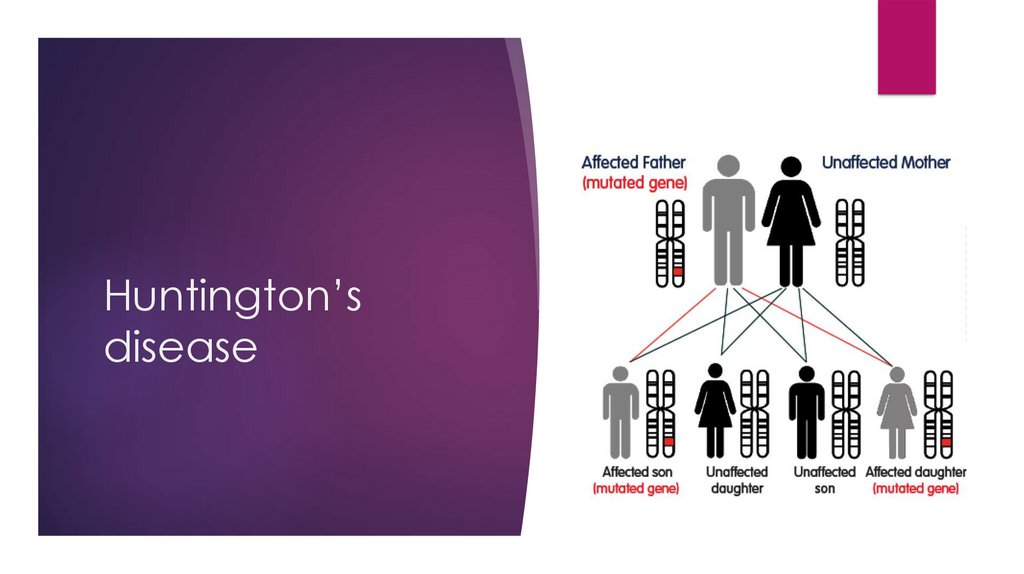
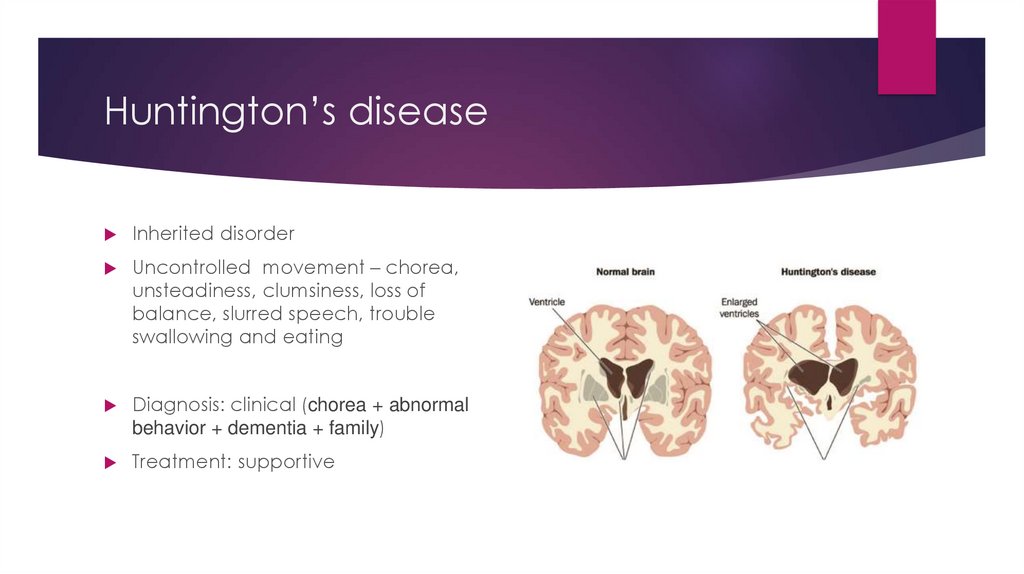
Huntington’s diseaseInherited disorder
Uncontrolled movement – chorea,
unsteadiness, clumsiness, loss of
balance, slurred speech, trouble
swallowing and eating
Diagnosis: clinical (chorea + abnormal
behavior + dementia + family)
Treatment: supportive
20.
Intracranialtumors
21.
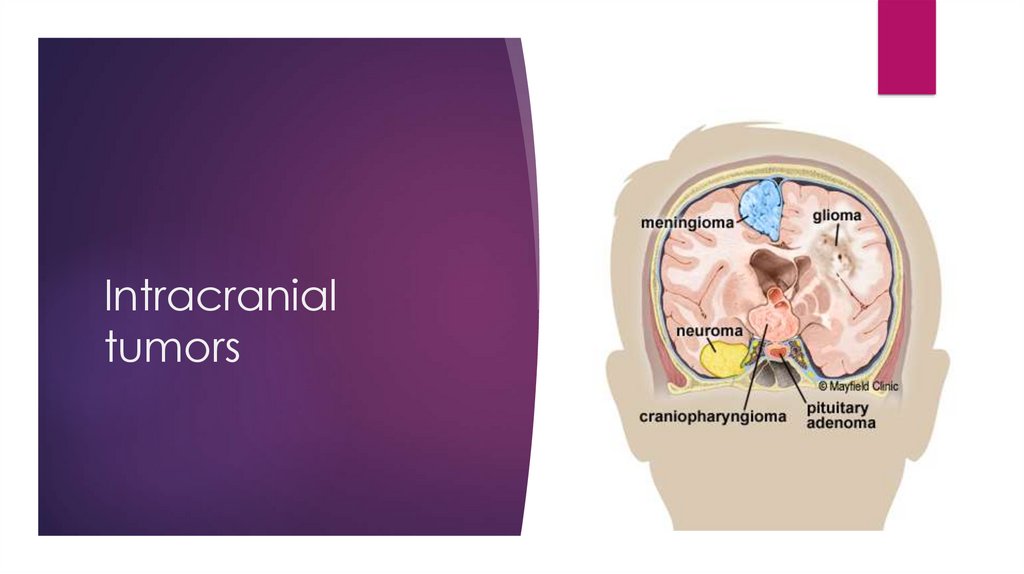
Brain cancerPrimary 30%(singular) and secondary 70%(multiple lesions)
Symptoms: focal neurologic deficit, seizure, headache worse in the
morning
Diagnosis: MRI with contrast, CT, biopsy
Treatment: resection, radiation or/and chemo, steroids, seizure profilaxis
22.
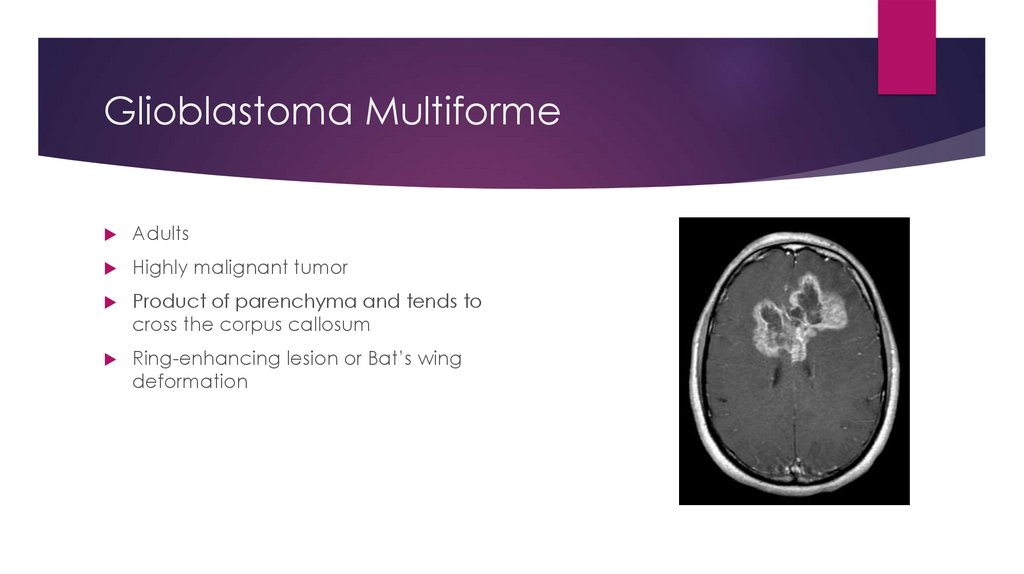
Glioblastoma MultiformeAdults
Highly malignant tumor
Product of parenchyma and tends to
cross the corpus callosum
Ring-enhancing lesion or Bat’s wing
deformation
23.
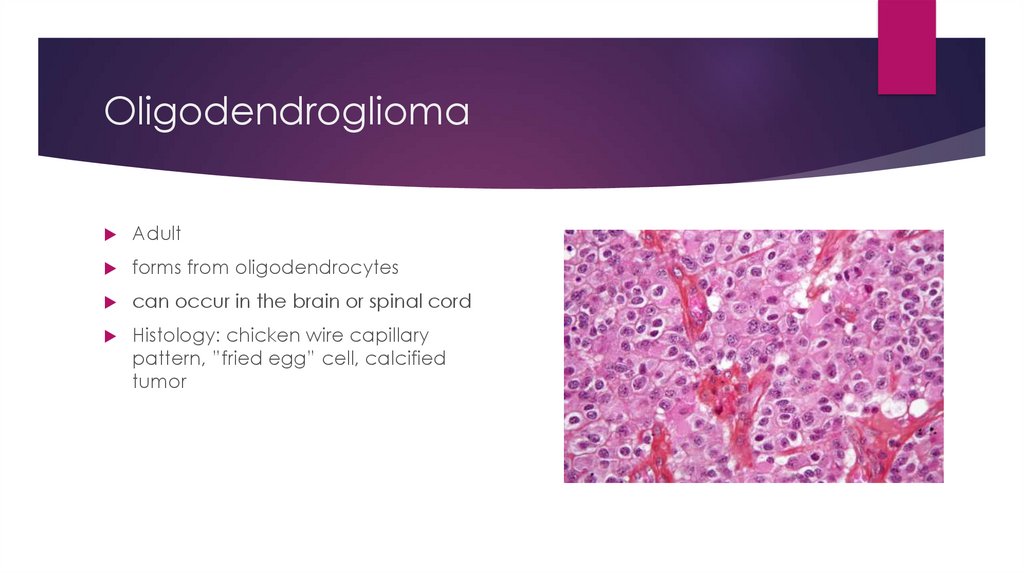
OligodendrogliomaAdult
forms from oligodendrocytes
can occur in the brain or spinal cord
Histology: chicken wire capillary
pattern, ”fried egg” cell, calcified
tumor
24.
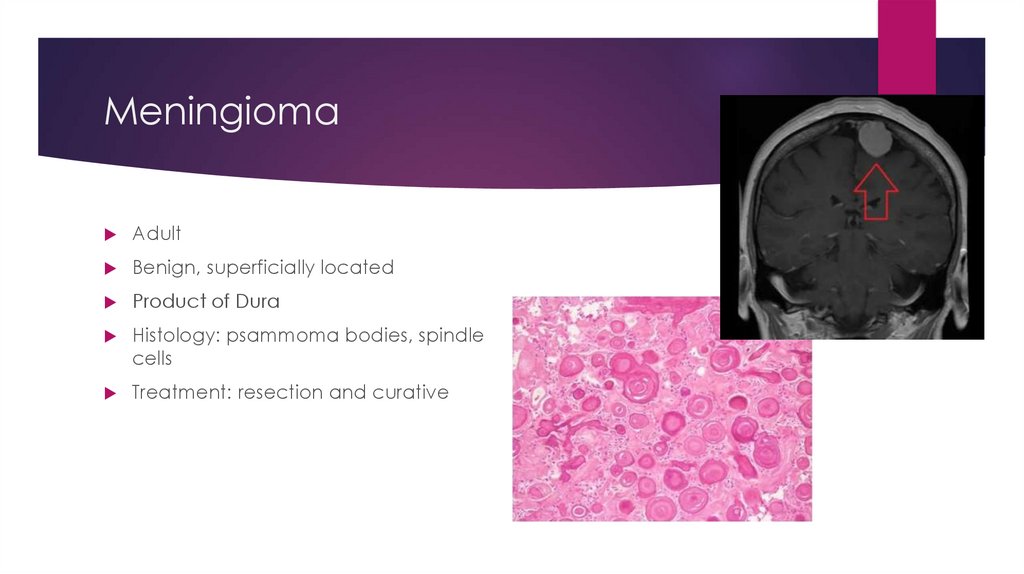
MeningiomaAdult
Benign, superficially located
Product of Dura
Histology: psammoma bodies, spindle
cells
Treatment: resection and curative
25.
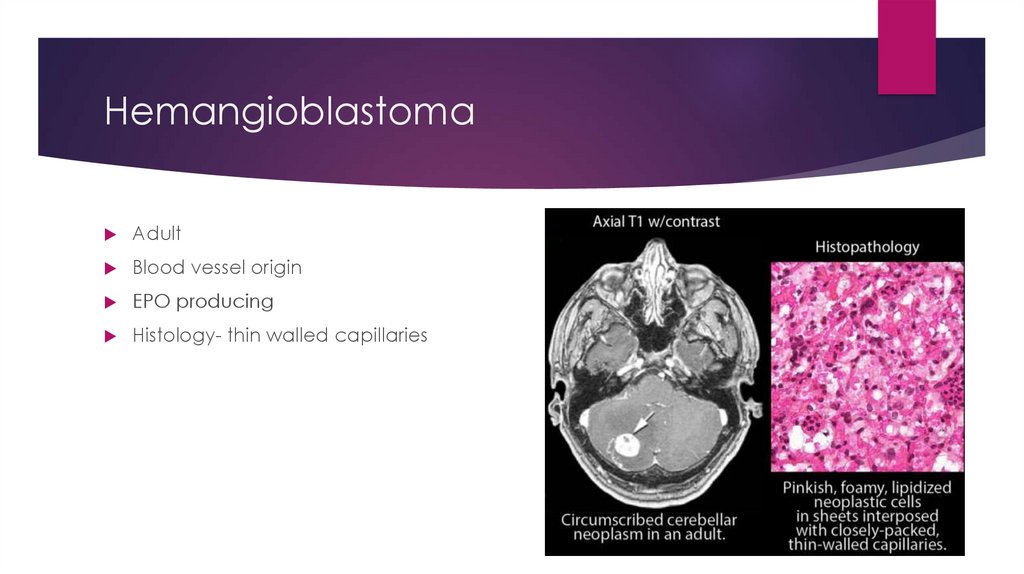
HemangioblastomaAdult
Blood vessel origin
EPO producing
Histology- thin walled capillaries
26.
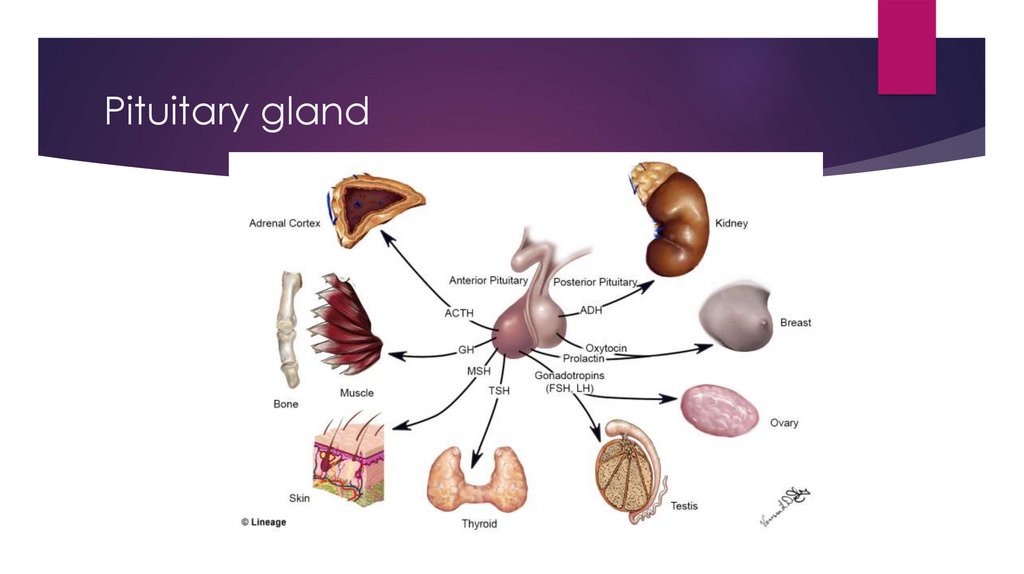
Pituitary gland27.
Pituitary AdenomaProlactinoma
Acromegaly
Cushing disease
Premenopausal females:
Hypogonadism,
oligomenorrhea or
amenorrhea, galactorrhea
Kids: gigantism
Mood face, buffalo hump, truncal
obesity
Males:
Decrease libido, impotence,
infertility
Dx: prolactin, MRI
Tx: Cabergoline
Adults: acromegaly hands,
feet, face and visceral
organs, diabetes and
diastolic heart failure
Dx: IGF1 glucose suppression
test
Tx: surgery, Octreotide,
Debulking or radiotherapy
Dx: ACTH
Tx: surgery, radiation therapy,
Metyrapone
28.
Acromegaly29.
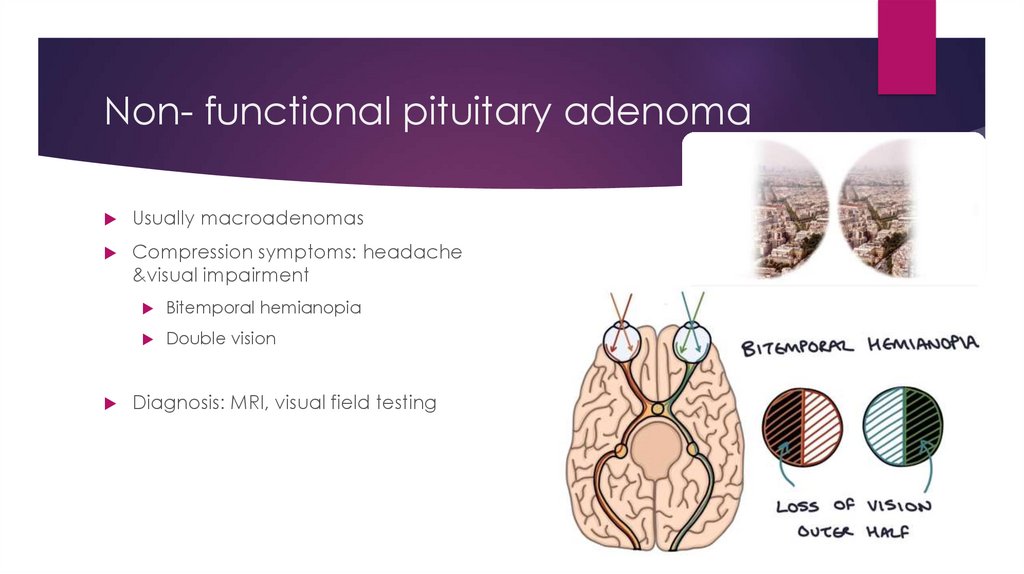
Non- functional pituitary adenomaUsually macroadenomas
Compression symptoms: headache
&visual impairment
Bitemporal hemianopia
Double vision
Diagnosis: MRI, visual field testing
30.
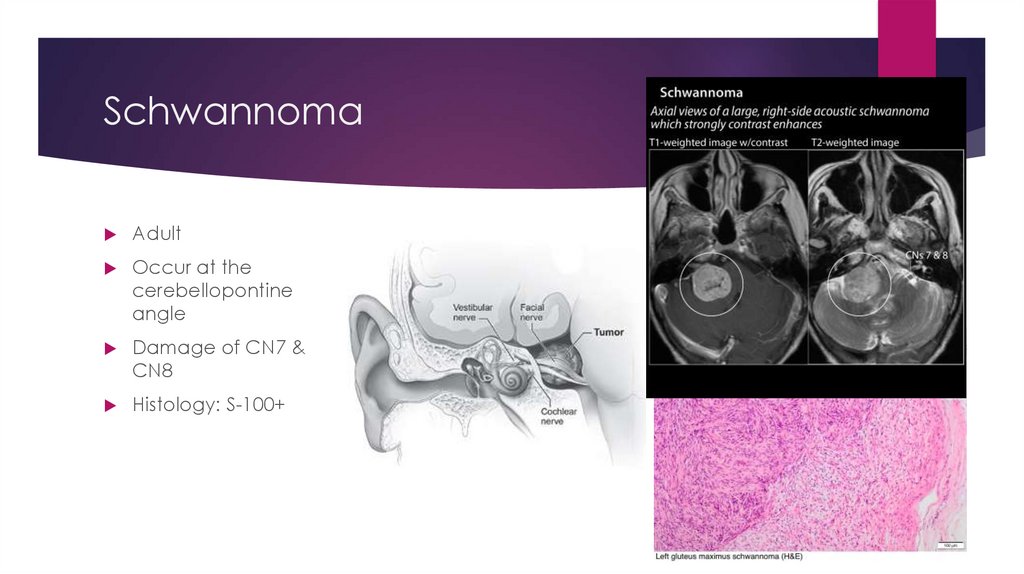
SchwannomaAdult
Occur at the
cerebellopontine
angle
Damage of CN7 &
CN8
Histology: S-100+
31.
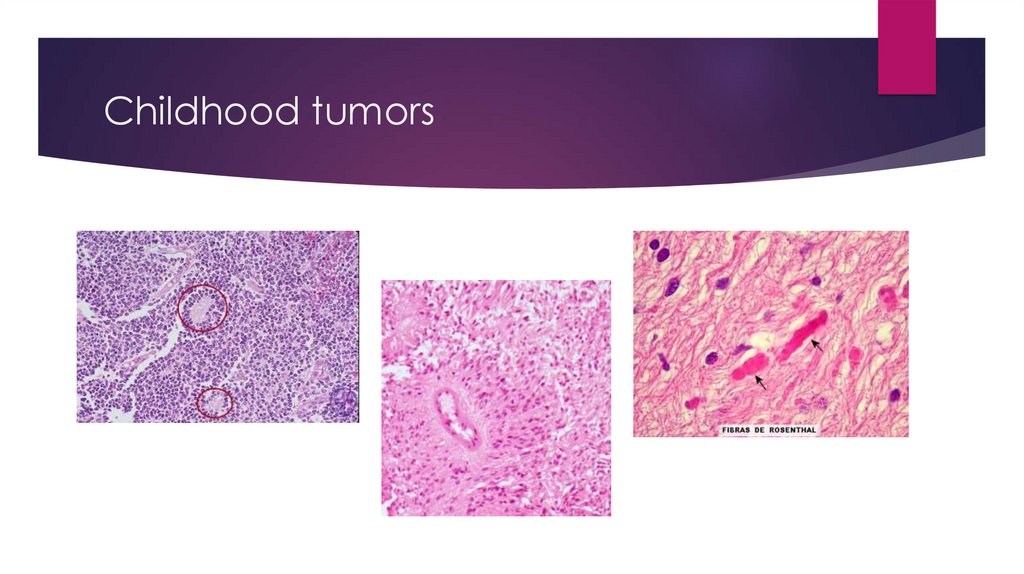
Childhood tumorsInfratentorial tumors
Pilocytic Astrocytoma
Craniopharyngioma
From Astrocytes
From remnants of Rathke’s pouch
Rosenthal Fibers
Above the sella turcica
pituitary gland
Medulloblastoma
Supratentorial tumors
From embryonic stem cells and primitive
neuroendocrine cells
Homer-Wright rosettes
Ependymoma
compress the
Pinealoma
From pinocytes or germ cells
Parinaud syndrome
From neuroglial cells
Paralysis of upward gaze
Perivascular pseudorosettes
Pupillary light-near dissociation
Convergent-retraction nystagmus












 Медицина
Медицина








