Похожие презентации:
Согласование времён Sequence of Tenses
1. Sequence of Tenses
Согласование времён1
Tregubenko N.V.
2. Основное правило:
Еслив главном предложении
используется одно из
прошедших времён (Past), то в
придаточном тоже должно
быть использовано
прошедшее (Past) время или
будущее в прошедшем (Futurein-the-Past).
2
Tregubenko N.V.
3. FUTURE IN THE PAST
Используется, чтобы выразитьдействие, которое было будущим
с точки зрения прошлого.
I thought Jack would come in time.
3
Tregubenko N.V.
4. Future Simple in the Past
“He said he would beready in a moment.”
4
“He hoped he would do
it.”
Tregubenko N.V.
5. Future Simple in the Past
“Did you think youwould return home
today?”
5
“I hoped I would help
you.”
Tregubenko N.V.
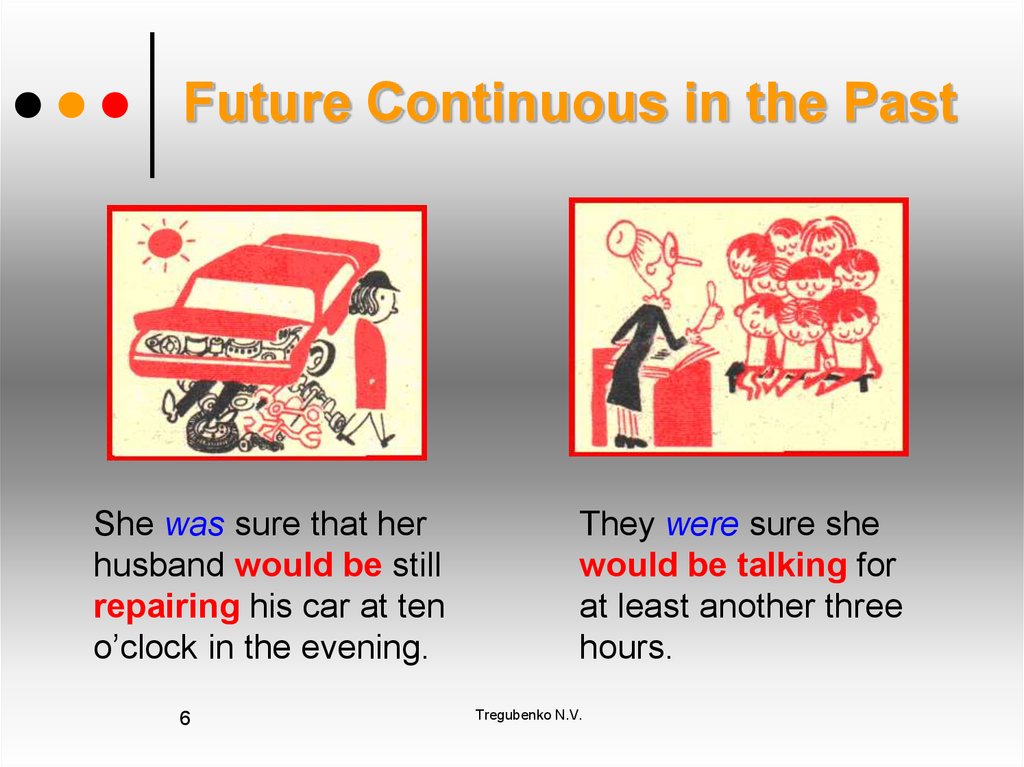
6. Future Continuous in the Past
She was sure that herhusband would be still
repairing his car at ten
o’clock in the evening.
6
They were sure she
would be talking for
at least another three
hours.
Tregubenko N.V.
7. Future Perfect in the Past
I hoped you wouldn’thave forgotten
everything by today.
7
“I thought I would have
finished the work
before your arrival.”
Tregubenko N.V.
8. Действие в придаточном предложении может быть :
одновременным с действиемглавного предложения
предшествовать действию
главного предложения
относиться к будущему
8
Tregubenko N.V.
9.
I knew (that) –(Я знал, что)
He said (that) –
(Он сказал, что)
Одновременное
действие
he lived in Kiev.
он живёт в Киеве.
Предшествующее
действие
he had lived in Kiev.
он жил в Киеве.
Будущее действие
he would live in Kiev.
он будет жить в Киеве.
9
Tregubenko N.V.
10. В придаточном предложении мы отступаем «на одно время назад»:
“Present”becomes “Past”
“Past” becomes “Past Perfect”
“will” becomes “would”
10
Tregubenko N.V.
11.
Present IndefiniteI do …
Past Indefinite
I did …
Present Continuous
Past Continuous
He is doing …
He was doing …
Present Perfect
I have done …
I had done …
Past Indefinite
I did …
Past Continuous
Past Perfect Continuous
I had been doing …
Past Perfect
I had gone …
11
Past Perfect
I had done …
I was doing …
Past Perfect
does not change
I had gone …
Tregubenko N.V.
12.
will (future)would
can
could
may
might
must
must or had to
12
Tregubenko N.V.
13. Time and Place Changes
13here
this
these
now
today
yesterday
a year ago
last night
tonight
Tregubenko N.V.
there
that
those
then / at the moment
that day
the day before
the previous day
a year before
the previous night
that night
14. Past Indefinite / Continuous can stay the same if we use:
in 19452 years ago
yesterday
last week
when he came
(after) since
14
He said that he left Moscow
5 years ago.
He knew that Peter was at home
yesterday.
She said she was working
when I rang her up.
She said I had been writing
since she came.
Tregubenko N.V.
15.
15Tregubenko N.V.
16. Раскройте скобки, поставив глаголы в такую форму, чтобы действия в придаточных предложениях были по отношению к главному: a)
одновременными;b) предшествующими;
c) будущими.
Переведите на русский язык.
I was happy you (to know) my name.
a)
b)
c)
I was happy you knew my name.
I was happy you had known my name.
I was happy you would know my name.
16
Tregubenko N.V.
(знаешь)
(знала)
(узнаешь)
17. Раскройте скобки, поставив глаголы в такую форму, чтобы действия в придаточных предложениях были по отношению к главному: a)
одновременными;b) предшествующими;
c) будущими.
Переведите на русский язык.
He thought she (to feel) lonely in London.
a)
b)
c)
He thought she felt lonely in London.
(чувствует)
He thought she had felt lonely in London.
(чувствовала)
He thought she would feel lonely in London. (будет чувствовать)
17
Tregubenko N.V.
18. Раскройте скобки, поставив глаголы в такую форму, чтобы действия в придаточных предложениях были по отношению к главному: a)
одновременными;b) предшествующими;
c) будущими.
Переведите на русский язык.
I hoped that he (to have) breakfast at home.
I hoped that he had breakfast at home.
I hoped that he had had breakfast at home.
I hoped that he would have breakfast at home.
18
Tregubenko N.V.
(завтракает)
(позавтракал)
(позавтракает)
19.
Сегодня мы познакомились с тем,как изменяется видо-временная
форма глагола в придаточном
предложении, если в главном
глагол употреблён в одном из
прошедших времён.
Другими словами, мы
познакомились с правилом
согласования времён:
Sequence of Tenses
19
Tregubenko N.V.


















 Английский язык
Английский язык








