Похожие презентации:
General approach to drug administration
1. General Approach To Drug Administration
2. QUESTIONS
What are indications to injections?
What kinds of syringes do you know?
What solution do they use for intracutaneous, subcutaneous and
intramuscular introduction?
What are necessary characteristics of syringe for different types of
injections (both lengths and diameter of a needle, syringe
capacity)?
What is permissible dosage schedule to different kinds of
injections and ways of the usage of medicines?
What is a technique of taking a drug from an ampoule?
What is a technique of intracutaneous allergic test?
What is a technique of subcutaneous injections?
Instruction for nurses about insulinization.
What is a technique of intramuscular injections?
What rules of making an injections in treatment room and ward do
you know?
What complications of injections do you know?
3. Drug Administration
oral intramuscular subcutanous topical intravenousAbsorbtion
Tissue
Plasma water
Metabolism
Excretion
Site of Action
4.
Pharmacokinetics: Relationship between the dose of a drug& the subsequent concentration of the drug in body fluids &
tissues over time
drug absorption, passage of drug from site of administration
to circulation
drug distribution, to where does the drug finally pass and
become therapeutic
drug metabolism, breakdown of drug to an inactive form
usually within the liver
drug elimination, final excretion either in urine, feces, or even
exhalation
5.
Routes of AdministrationOral, drug is delivered by mouth and absorbed in the
gastrointestinal (GI) tract
Parenteral, delivery with a needle or syringe
Transdermal, absorption of drug through the skin
Inhalation, administration through the respiratory tract
Nasal, absorption of drug by olfactory epithelia
Rectal, absorption through colon epithelium
6.
Systemic vs. Local EffectsSystemic effects mean that the delivered drugs circulate
through the entire body
Example: Orally delivered pain reliever for a sore toe
Local effects are restricted to region of delivery
Example: nasal spray for stuffy nose
7. Parenteral Injection Sites
Used for drugs poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal (GI)tract or those that are unstable in the GI.
Also used in unconscious patients or when rapid onset of action is
required
subcutanously
intramuscularly
intravenously
8. Subcutaneous Route
Subcutaneous (SC) Requires absorption of the drug throughtissue which minimizes some of the risks associated with IV
injection
Can be self administered
Can be painful, irritant drugs can cause local tissue damage
Maximum of 2 ml injection thus often small doses limit use.
Absorption depending on blood flow
Constant & slow absorption
Prolonged effect
(Ex.of drugs: Insulin, Heparin)
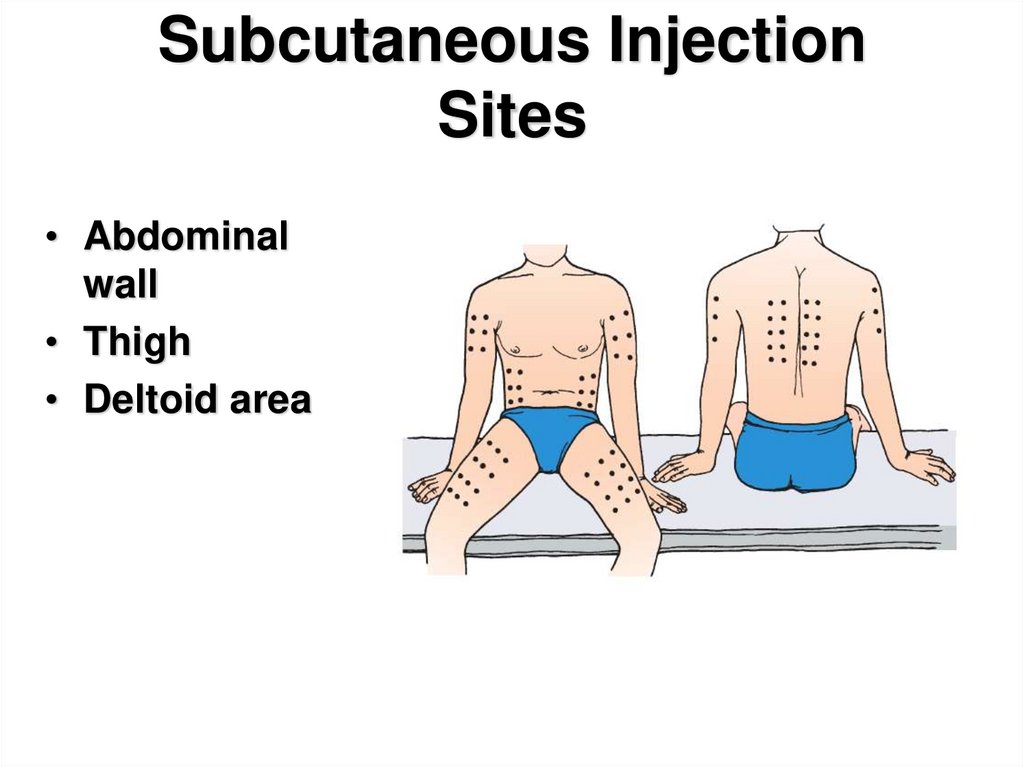
9. Subcutaneous Injection Sites
• Abdominalwall
• Thigh
• Deltoid area
10.
Intramuscular (IM) rapid absorption of aqueous drugs, largervolume, than SC, can be given by IM
Trained personnel required for injections. The site of injection will
influence the absorption.
Absorption depending on blood flow
Rapid onset & shorter duration
Use at least a one inch needle to assure that the drug is placed
deep in the muscle for proper absorption.
This route allows for the second fastest rate of absorption
(Ex.of drugs: Glucagon, Adrenaline)
11. Intramuscular injection sites Deltoid muscle
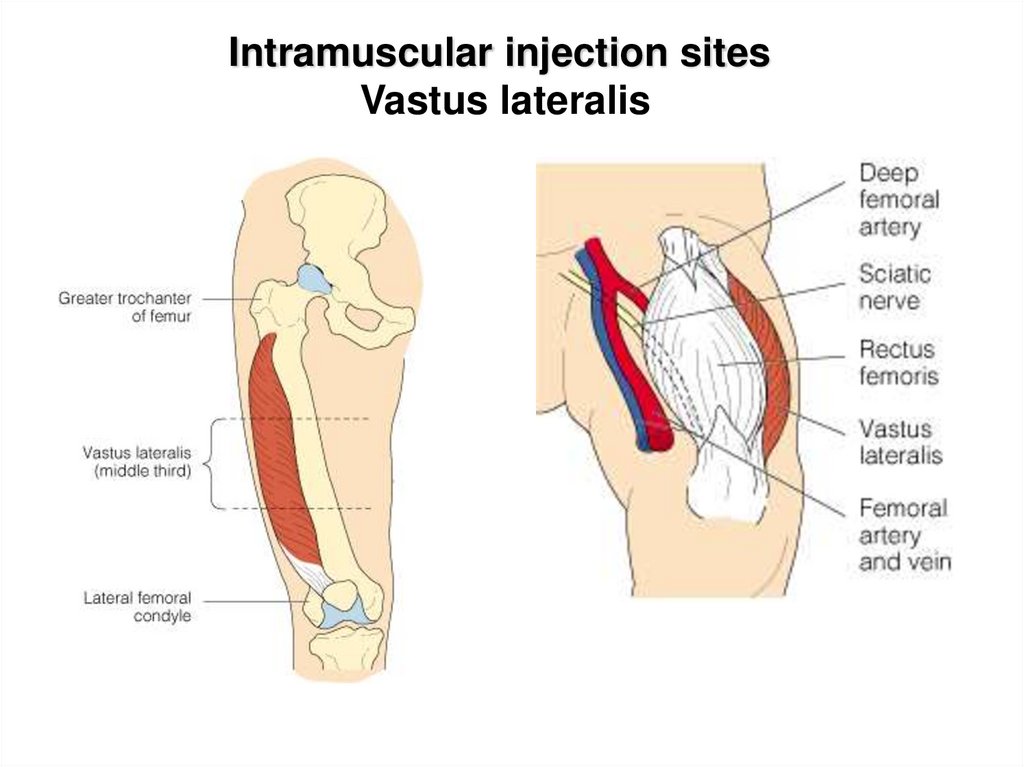
12. Intramuscular injection sites Vastus lateralis
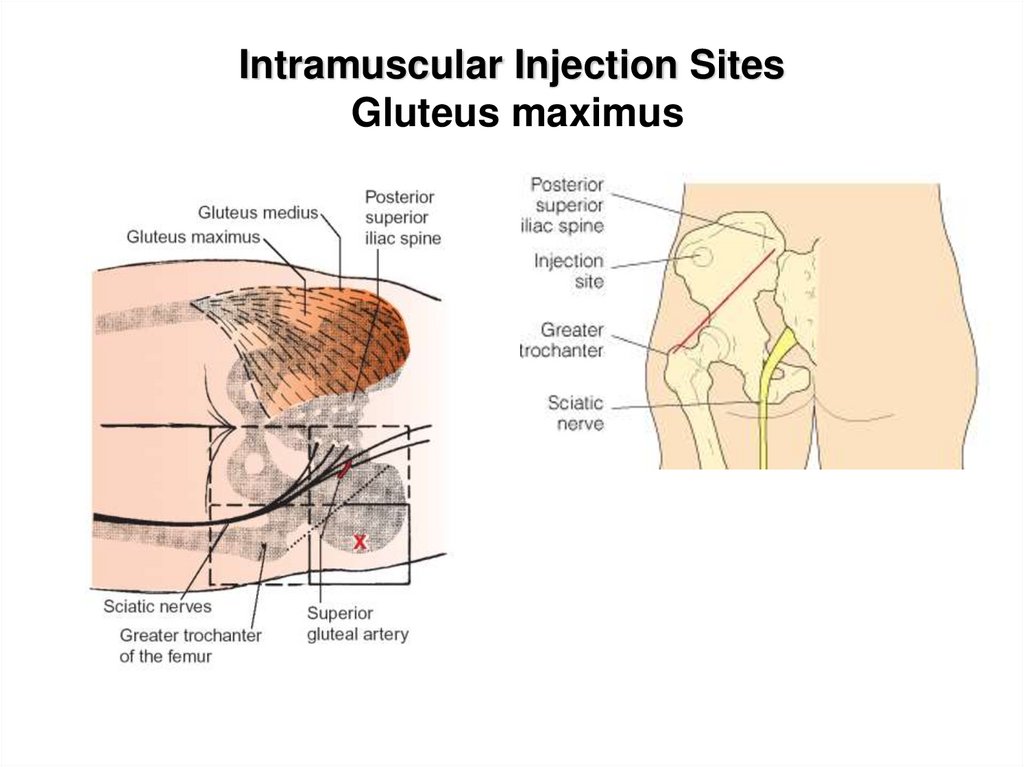
13. Intramuscular Injection Sites Gluteus maximus
14. Intramuscular Route
• Limitations– Neurovascular damage
– Bleeding (eg anticoagulant therapy)
– Pain
– Infection
– Delayed absorption in shock










 Медицина
Медицина








