Похожие презентации:
Anatomy of the human body
1.
Perm State Medical University named after academician E.A. VagnerDepartment of Foreign Languages
ANATOMY OF THE HUMAN BODY
The report was prepared by: Belolugova Anastasia, Maria Rusinova,
Tuneva Polina, Alina Dmitrieva, Andrey Snegirev.
Students of Group 3 of the Dental Faculty
Scientific Adviser: ass.prof. Lyamova O.O.
Perm 2020
2.
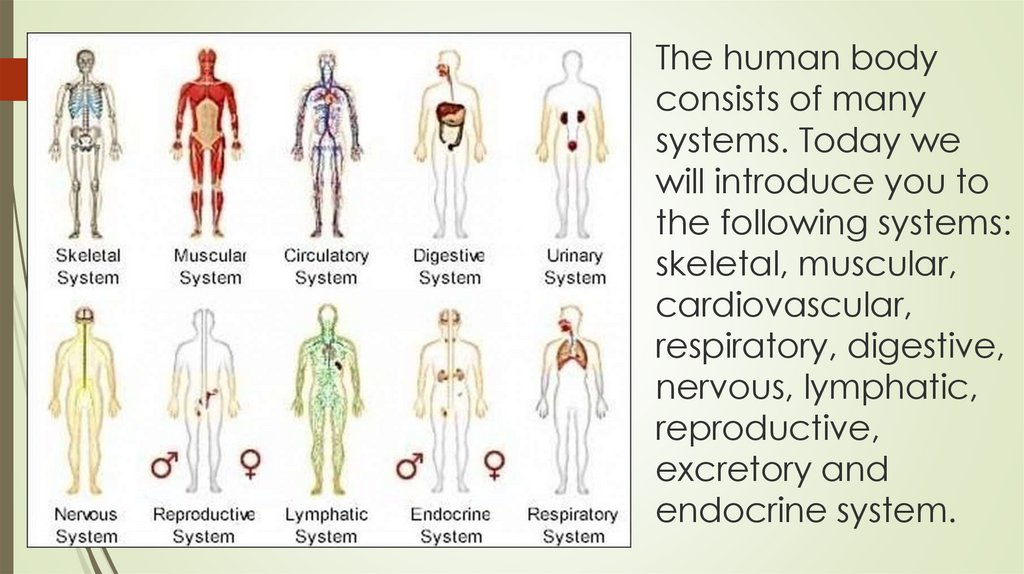
The human bodyconsists of many
systems. Today we
will introduce you to
the following systems:
skeletal, muscular,
cardiovascular,
respiratory, digestive,
nervous, lymphatic,
reproductive,
excretory and
endocrine system.
3.
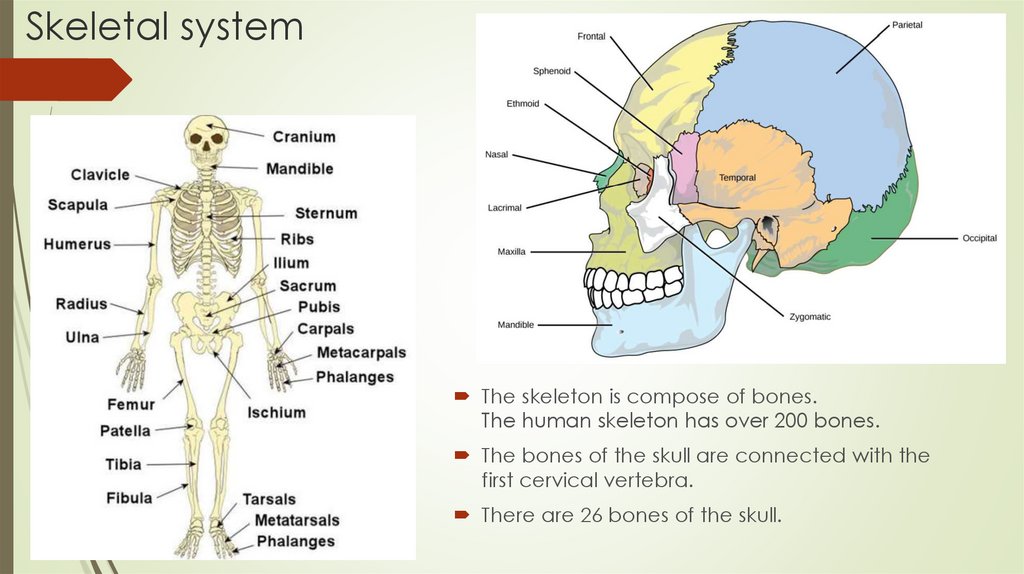
Skeletal systemThe skeleton is compose of bones.
The human skeleton has over 200 bones.
The bones of the skull are connected with the
first cervical vertebra.
There are 26 bones of the skull.
4.
Skeletal systemVertebra form the
vertebral column.
The vertebral
column consist of
cervical, thoracic,
lumbar and sacral
vertebrae and the
coccyx.
In the spine there
are 32 or 34
vertebrae.
7 cervical, 12
thoracic, 5
lumbar, 5 sacral
vertebrae and the
coccyx.
The breastbone is a
long bone in the
middle of the chest.
Ribs connect with
the breastbone with
the help of
cartilages and
ligaments.
The breastbone
connects with 7 ribs
on each side of the
chest
The upper
extremity is
formed by arm,
forearm and
hand.
The lower
extremity is
formed by thigh,
leg and foot
5.
The muscle systemThe human body has 640 muscles
There are three main types of muscle tissue:
1) smooth muscles,
2) striated muscles,
3) heart muscle.
Muscles are important for the
functioning of the body.
6.
The cardiovascular systemThe heart
The heart consists of
two separate
chambers divided by
the septum. Each of
the chambers has two
connected parts: the
atrium and the
ventricle.
The heart is an inner
hollow muscular organ
placed within the chest
and included in the
pericardium.
Arteries: carry blood away
from heart
Arterioles: small arteries
Veins: Carry blood toward
heart
Venules: small veins
Capillaries: microscopic
blood vessels that
carry blood from arterioles to
venules
7.
The cardiovascular systemBlood is composed of plasma and the corpuscular elements which are called red
corpuscles or erythrocytes, white corpuscles or leucocytes and blood platelets or
thrombocytes.
Leucocytes (4,500 to 9,500 per cu mm)
Erythrocytes (4,000,000 to 5,000,000 per cu mm)
Thrombocytes (200 000- 400 000 per cu mm)
8.
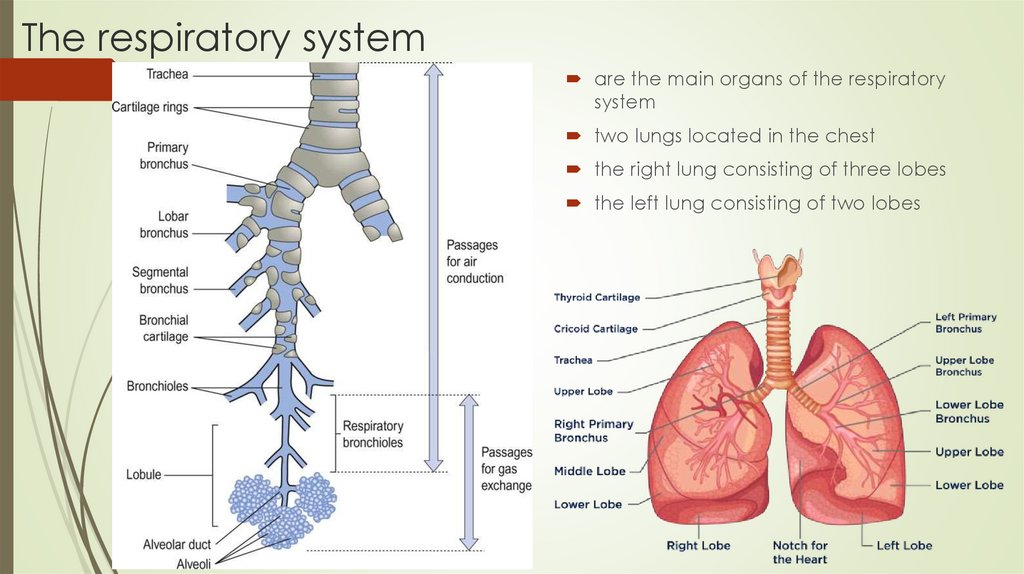
The respiratory systemare the main organs of the respiratory
system
two lungs located in the chest
the right lung consisting of three lobes
the left lung consisting of two lobes
9.
The respiratory systemnose
oral cavity
trachea
bronchi
bronchioles
alveoli
10.
The digestive systemthe digestive
tract
digestive
glands
11.
The nervous systemthe most complicated
mechanism
weight is from one to two
kg
volume of about 3.21
litres
about 12 billion cells
12.
The nervous systemthe nervous cells of the
cortex are the most
delicate
the nerve cells in the
brain can be «put to
sleep»
stimuli comes into the
brain through the spinal
cord
sleep is of a great
protective
13.
The lymphatic systemThe tonsils, spleen, and thymus
are all part of the lymphatic
system.
14.
The reproductive systemThe female system consist of ovaries, uterus,
cervix, vagina, fallopian tubes and external
genitals.
Female germ cell is called ova.
Female sex hormones are called estrogens.
The male system consist of the testicles,
penis, prostate, seminal vesicles, urethra,
typewriter and epididymis.
Male germ cell is called sperm.
Male sex hormones are called androgens.
The main androgen is testosterone
15.
The excretory systemHarmful
substances
entering the
blood are
removed from
the body by the
excretory
organs, namely
the kidneys, skin
and lungs
16.
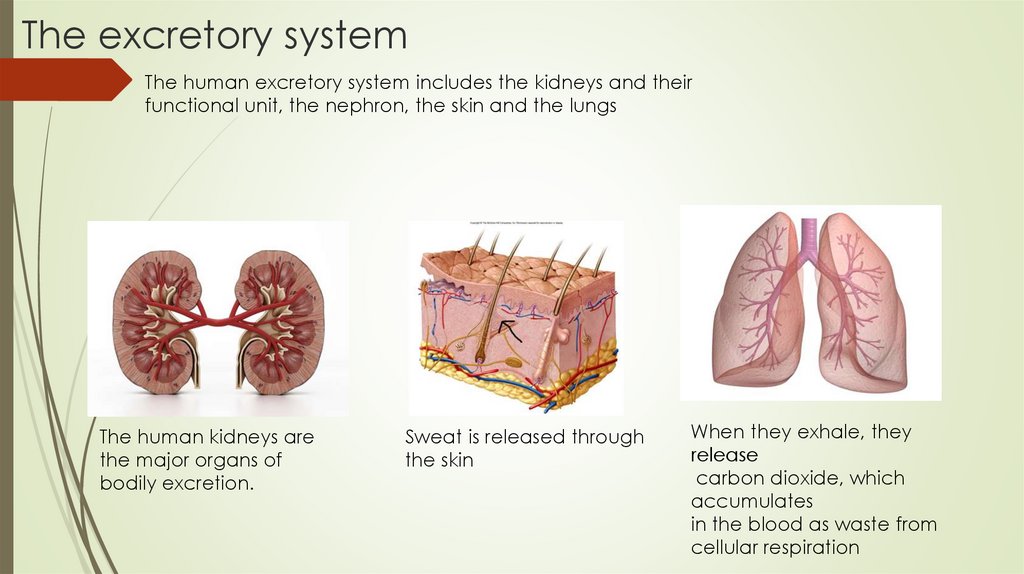
The excretory systemThe human excretory system includes the kidneys and their
functional unit, the nephron, the skin and the lungs
The human kidneys are
the major organs of
bodily excretion.
Sweat is released through
the skin
When they exhale, they
release
carbon dioxide, which
accumulates
in the blood as waste from
cellular respiration
17.
The endocrine systemThe endocrine system is a chemical messenger system comprising feedback loops of the
hormones released by internal glands organism directly into the circulatory system, regulating
distant target organs.
The key
mechanism of the endocrine s
ystem is the hormone.
18.
In the brain the hypothalamus,pituitary and pineal gland are involved
in the regulation of other endocrine
organs
The neck contains the thyroid and
parathyroid glands.
Endocrine system in the body consists
of a number of glands, which produce
regulatory substances















 Медицина
Медицина Английский язык
Английский язык