Похожие презентации:
Congenital dislocation of the hip
1. CDH CONGENITAL DISLOCATION OF THE HIP
2. Nomenclature
CDH : Congenital Dislocation of the HipDDH : Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip
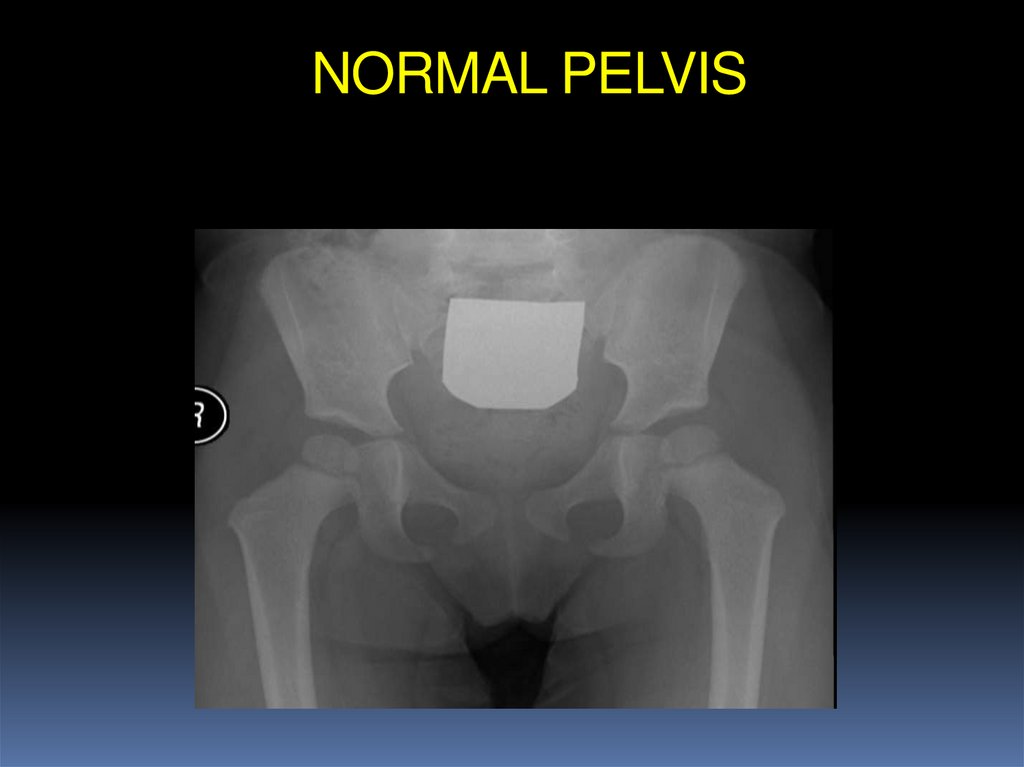
3. NORMAL PELVIS
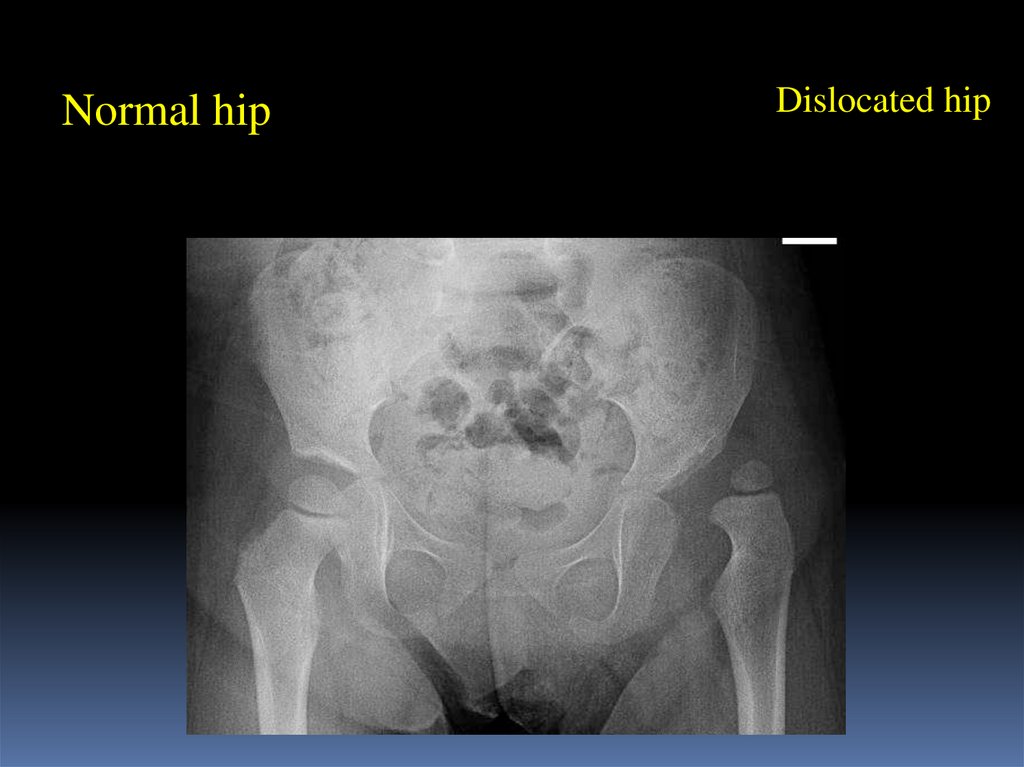
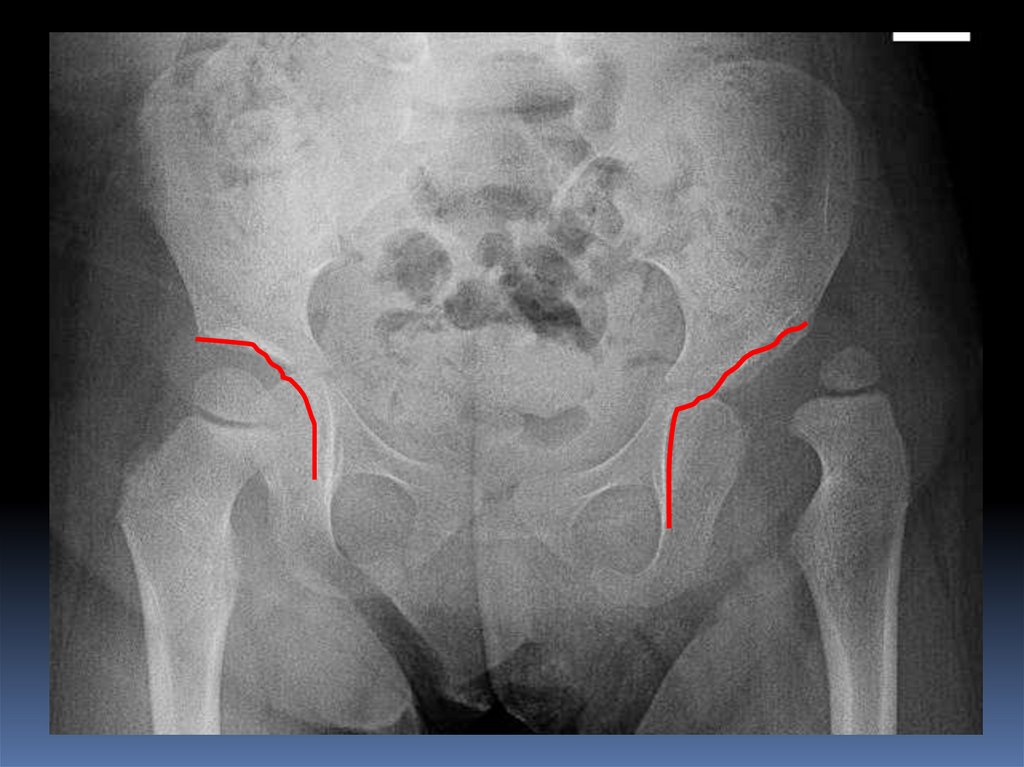
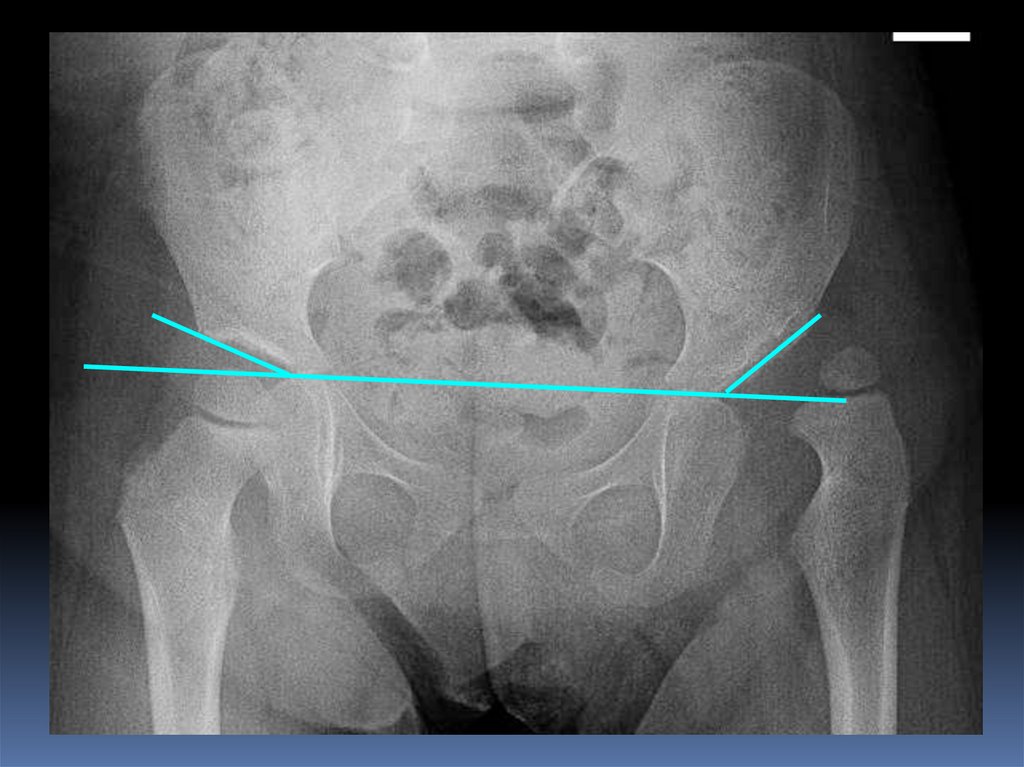
4.
Normal hipDislocated hip
5. Patterns of disease
DislocatedDislocatable
Sublaxated
Acetabular dysplasia
6. Radiology
After 6 months: reliable7.
8. Causes (multi factorial)
HormonalRelaxin, oxytocin
Familial
Lig.laxity diseases
Genetics
Female 4 X male --- twins 40%
Mechanical
Pre natal
Post natal
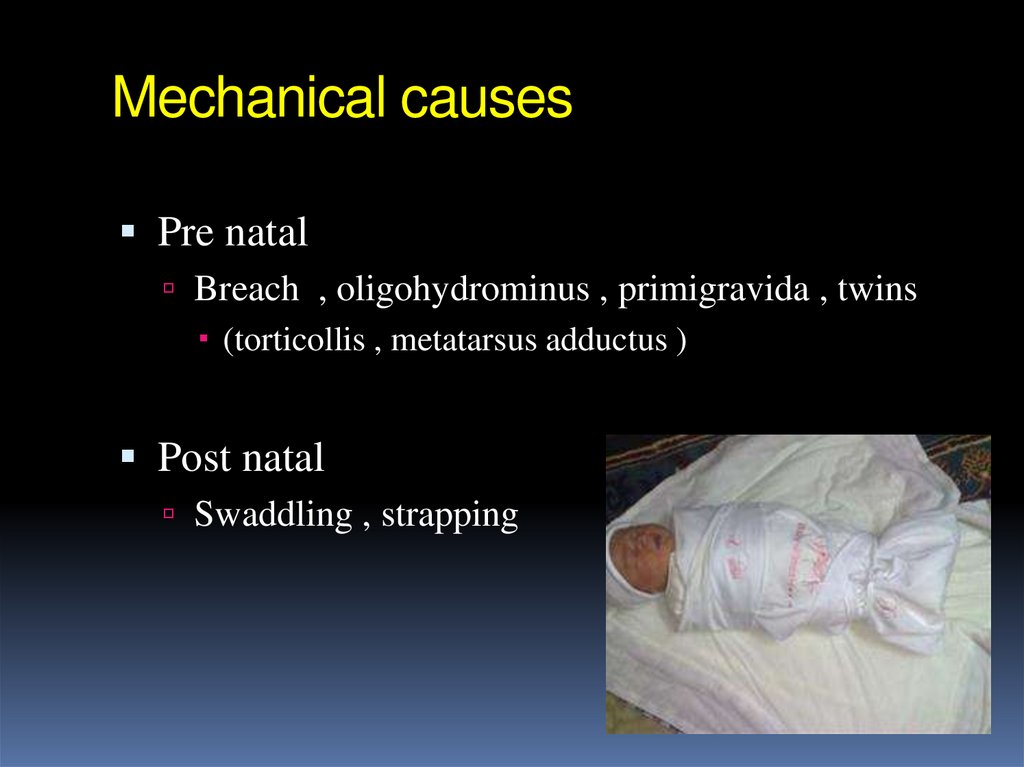
9. Mechanical causes
Pre natalBreach , oligohydrominus , primigravida , twins
(torticollis , metatarsus adductus )
Post natal
Swaddling , strapping
10. Infants at risk
Positive family history: 10XA baby girl:
4-6 X
Breach presentation: 5-10 X
Torticollis: CDH in 10-20% of cases
Foot deformities:
Calcaneo-valgus and metatarsus adductus
Knee deformities:
hyperextension and dislocation
11. Infants at risk
When risk factors are presentThe infant should be reviewed
Clinically
radiologically
12. Clinical examination
The infant should bequiet
comfortable
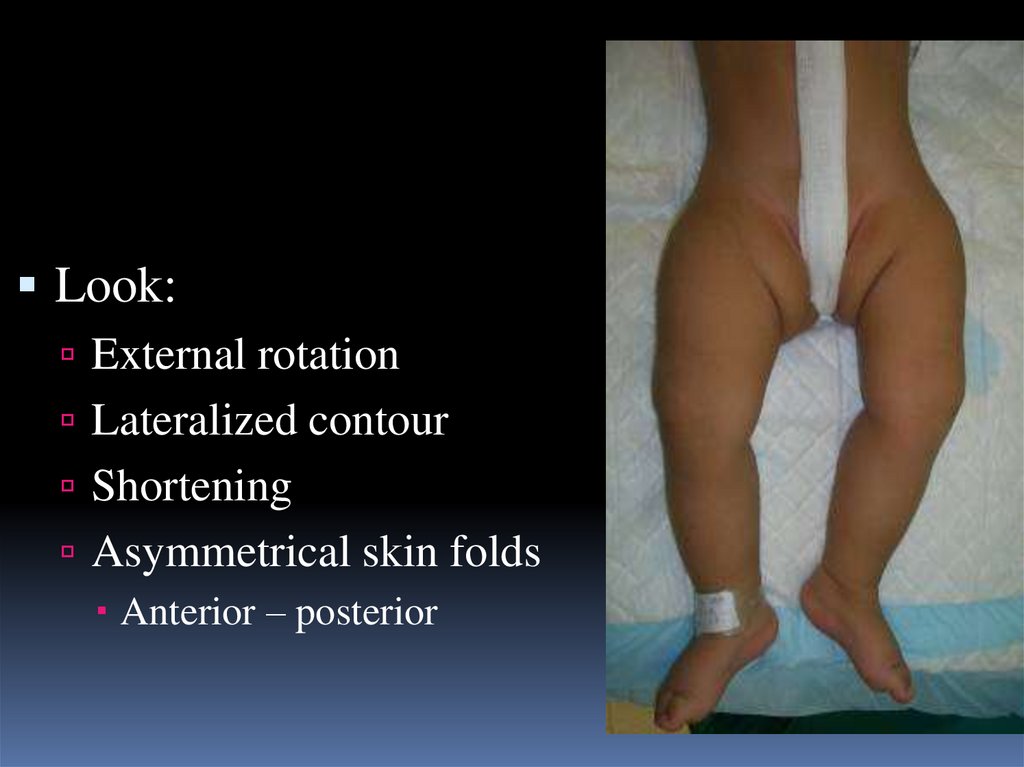
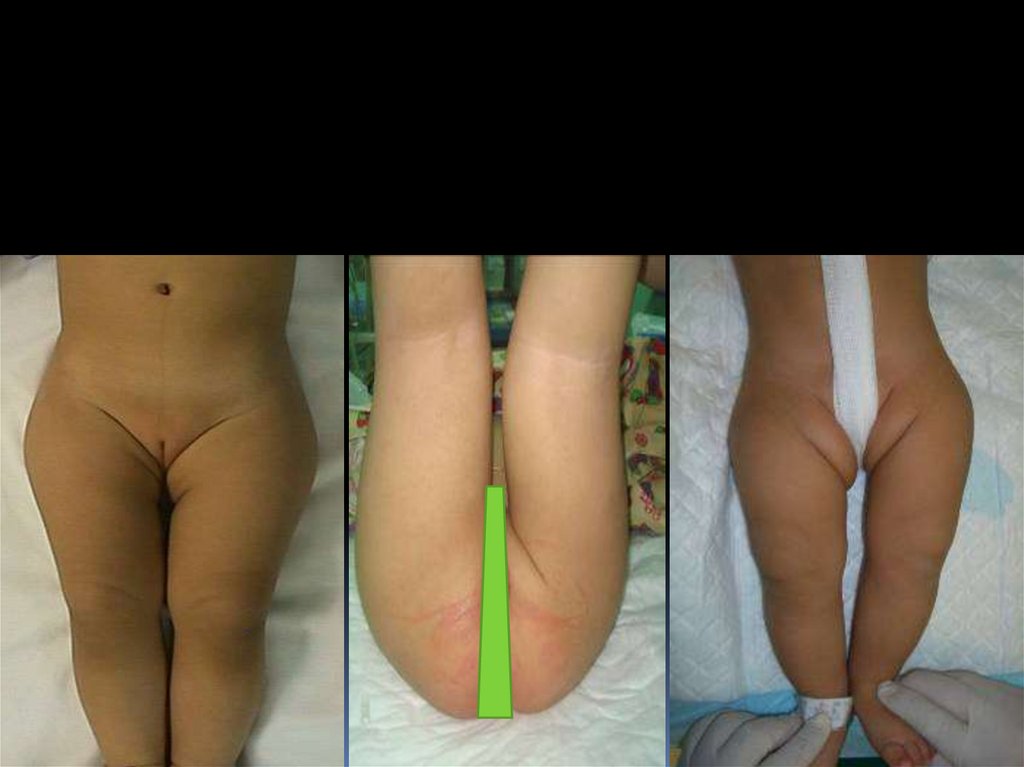
13.
Look:External rotation
Lateralized contour
Shortening
Asymmetrical skin folds
Anterior – posterior
14.
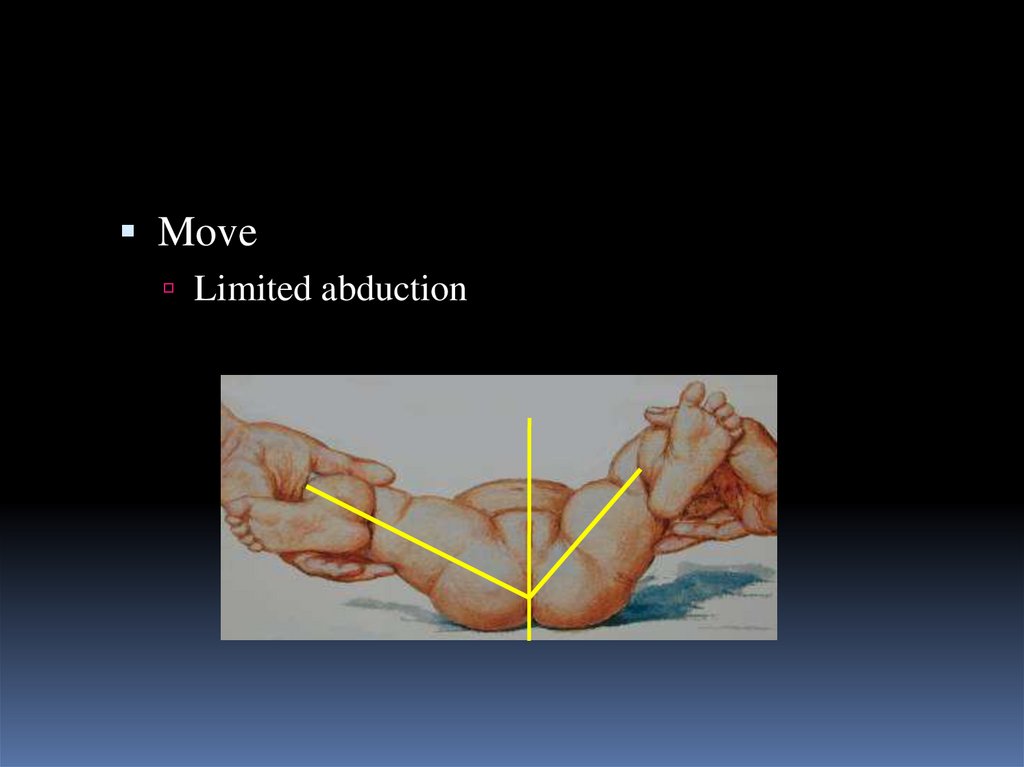
15.
MoveLimited abduction
16.
Special testGaliazzi
Ortolani , Barlow test
Trendelenburgh sign
Limping ( waddling gait if bilateral)
17. Special test
Galiazzi test18. Special test
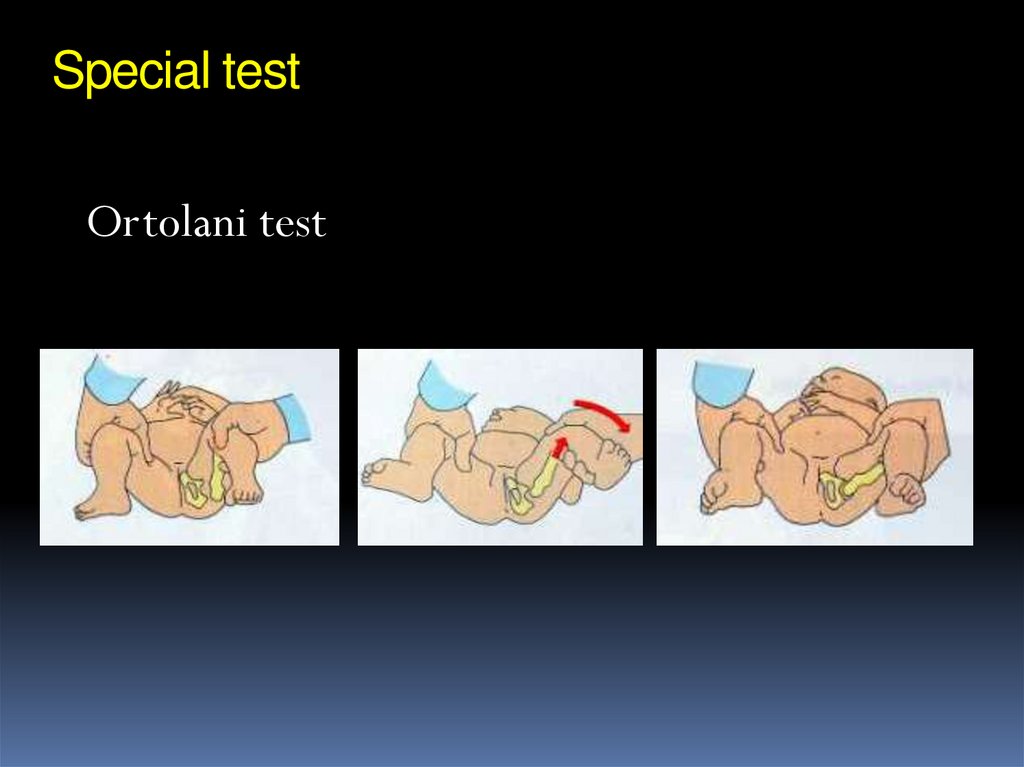
Ortolani test19. Special test
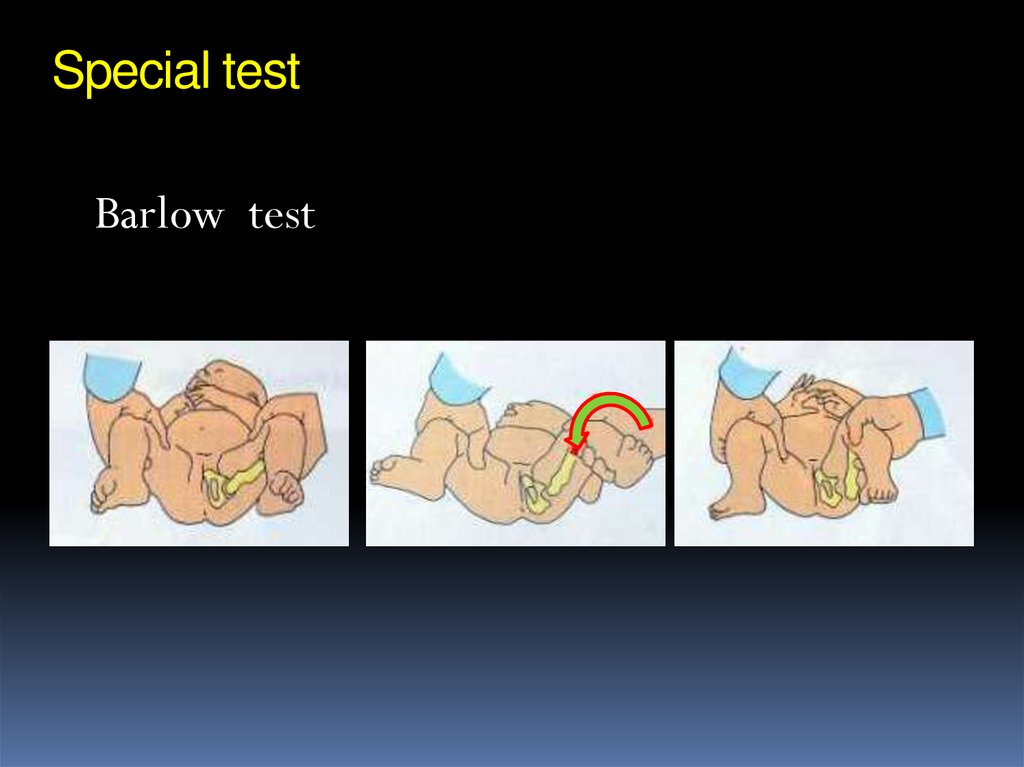
Barlow test20. Special test
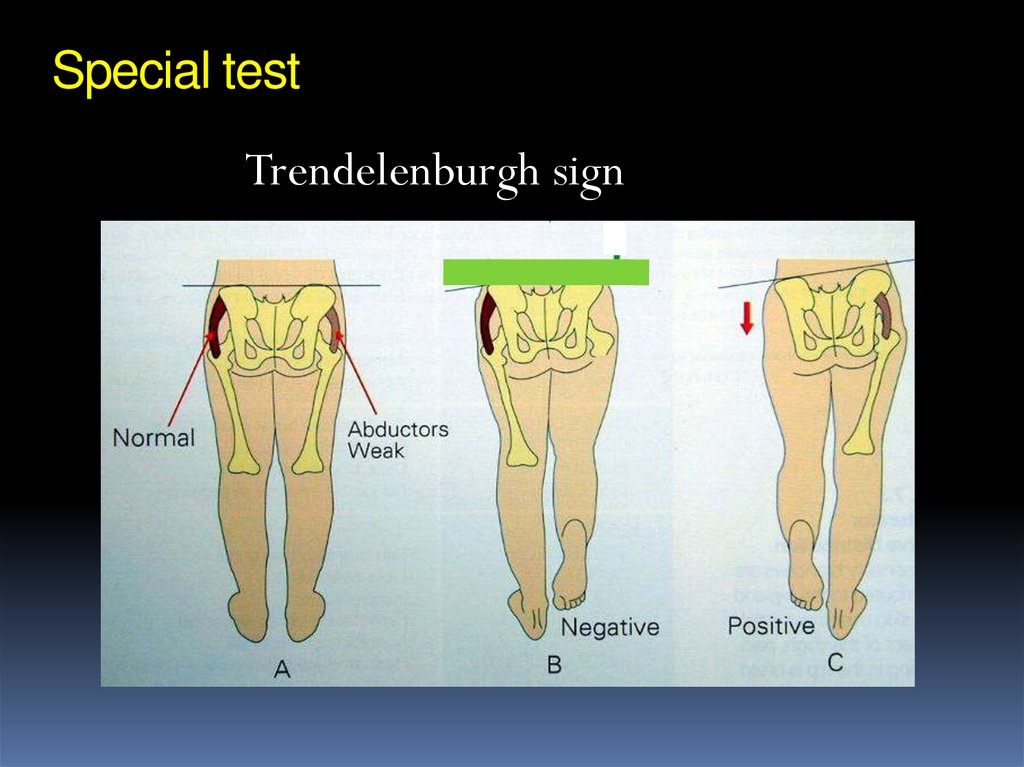
Trendelenburgh sign21. Screening programs
Clinical screening proven to be effectivePerformed by trained personnel
Must be dynamic
Repeated with periodic examination
U/S screening is controversial
22. Investigations
0-3 monthsU/S
> 3months X-ray pelvis AP + abduction
23. U/S Screening
Incidence of hip stability declines rapidly to50% within the first week of neonatal life.
Better to delay U/S screening
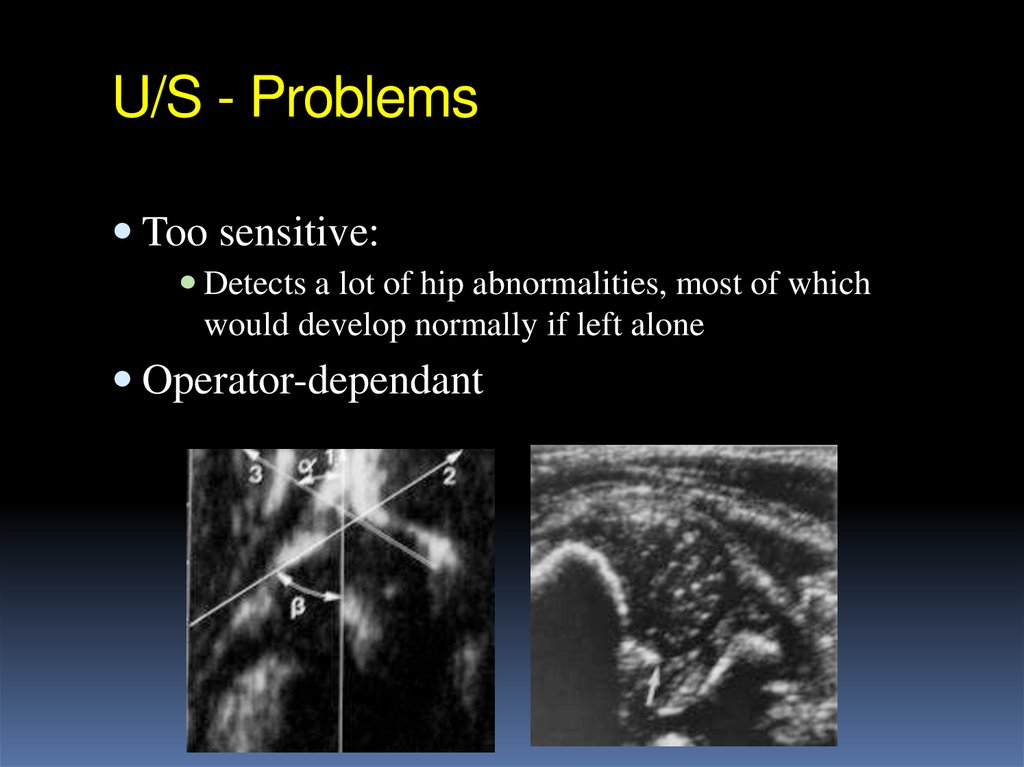
24. U/S - Problems
Too sensitive:Detects a lot of hip abnormalities, most of which
would develop normally if left alone
Operator-dependant
25. Radiology
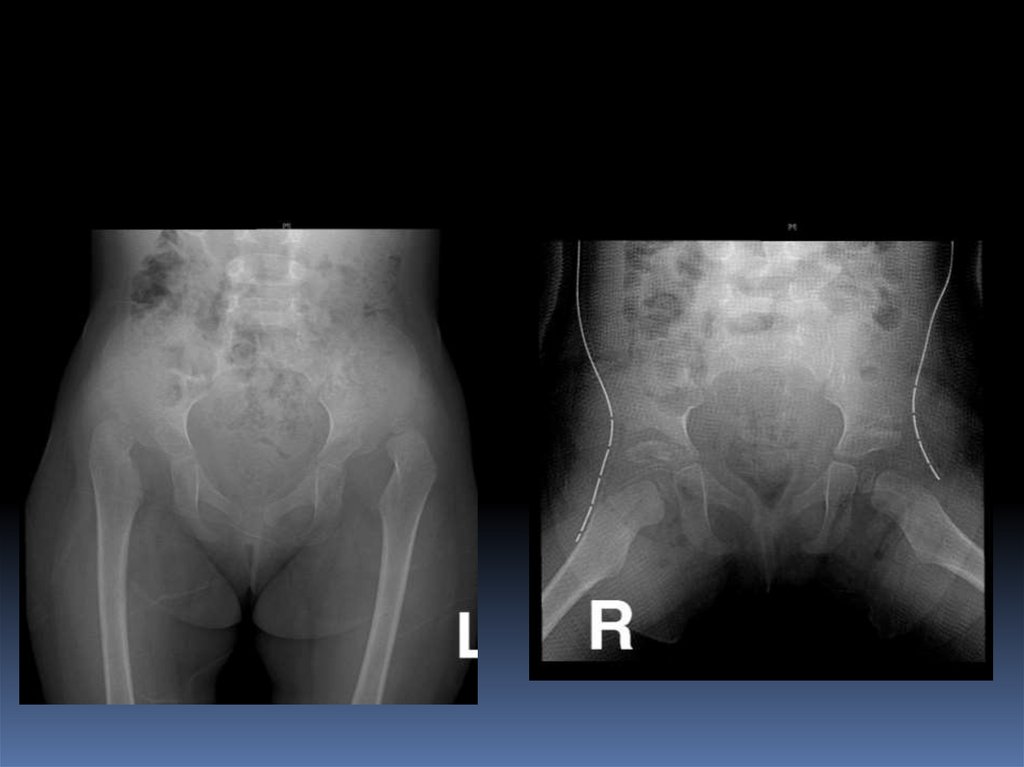
Early infancy: not reliable26. Radiology
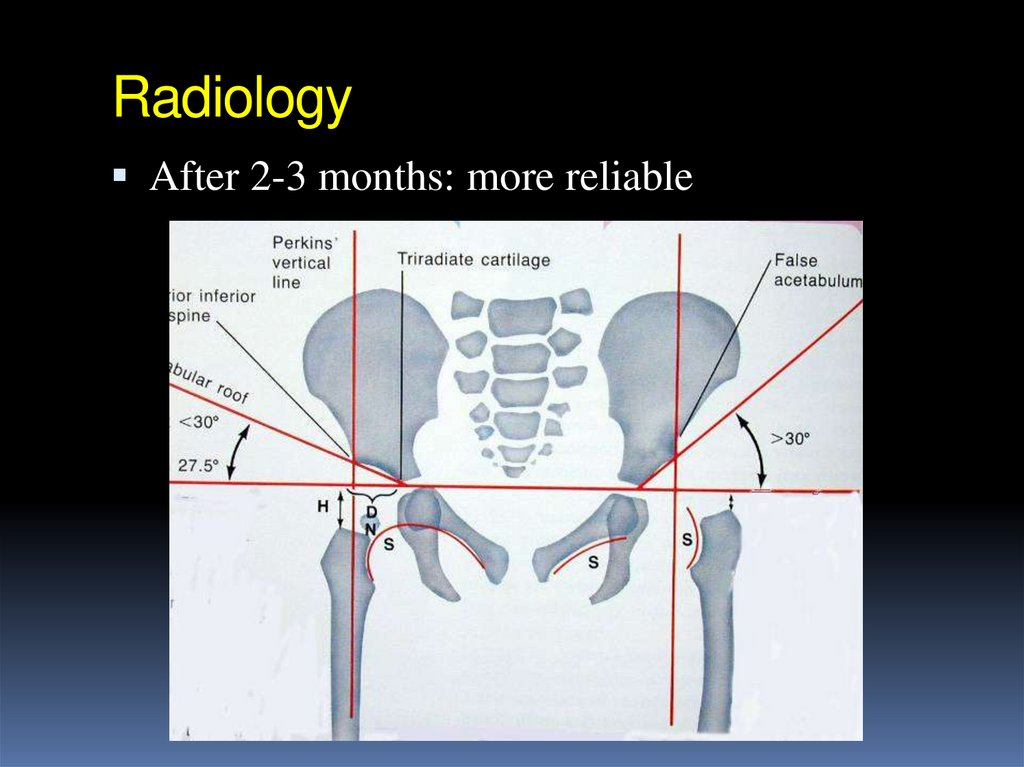
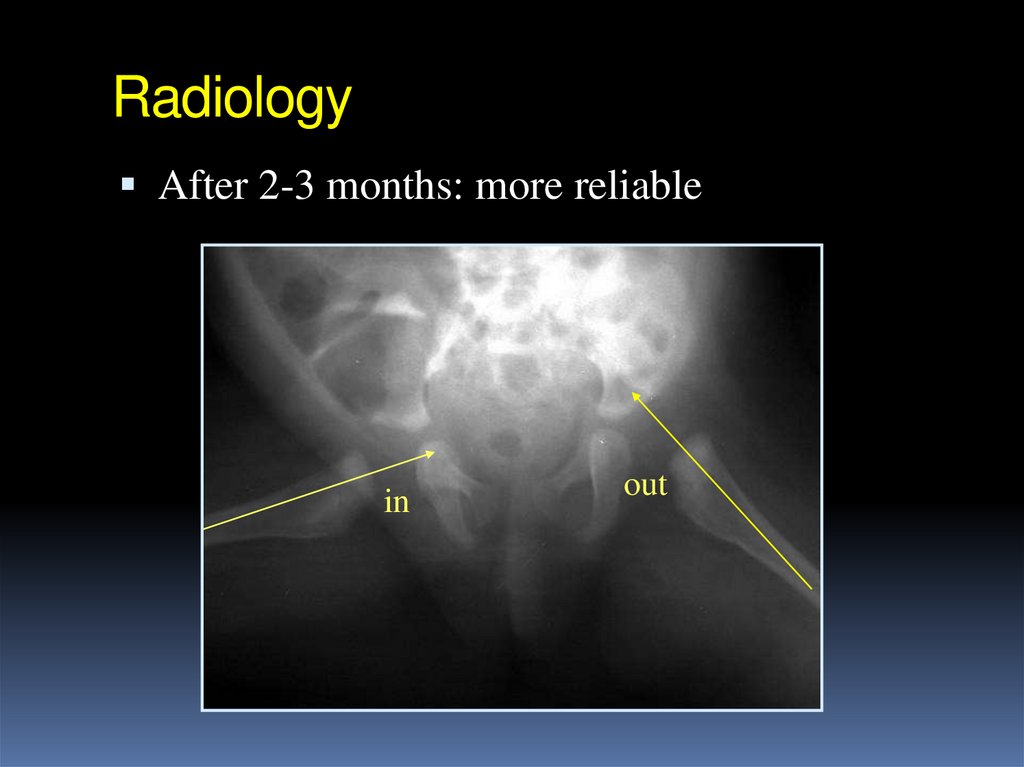
After 2-3 months: more reliable27. Radiology
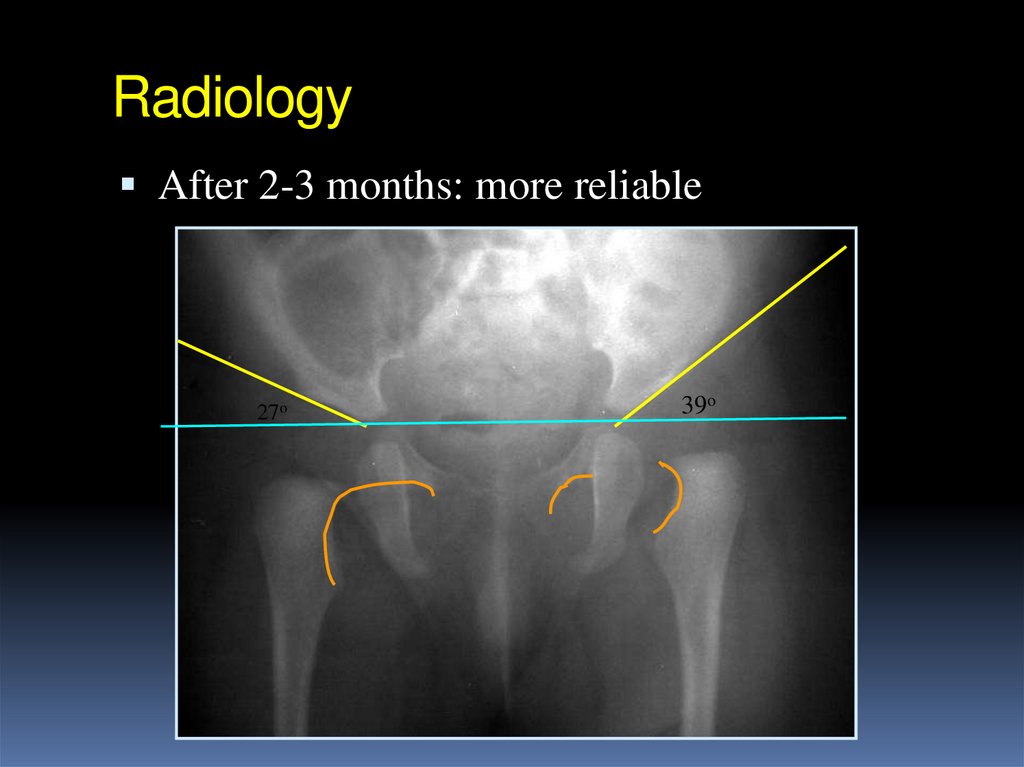
After 2-3 months: more reliable27o
39o
28. Radiology
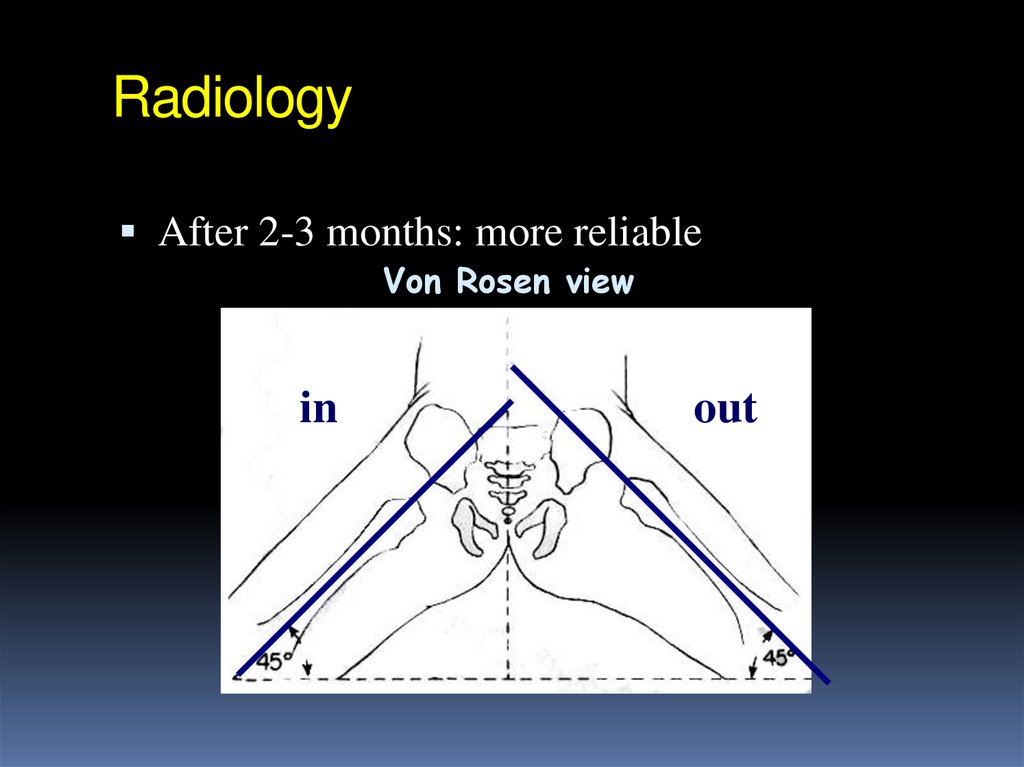
After 2-3 months: more reliableVon Rosen view
in
out
in
out
in
out
29. Radiology
After 2-3 months: more reliablein
out
30. Radiology
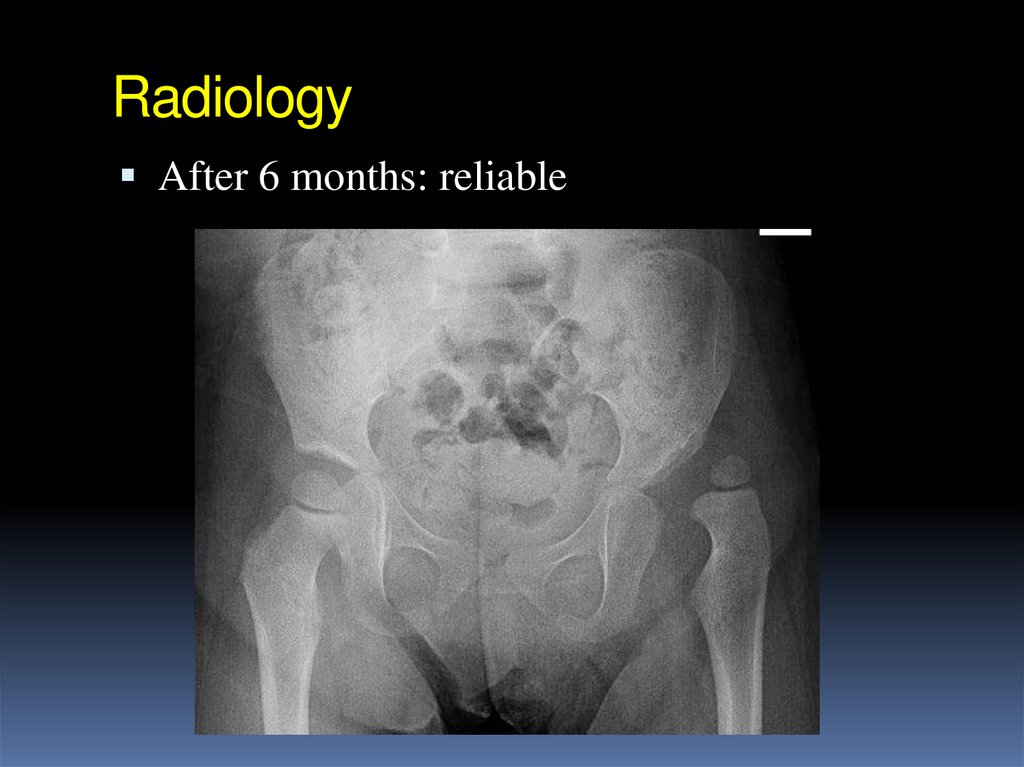
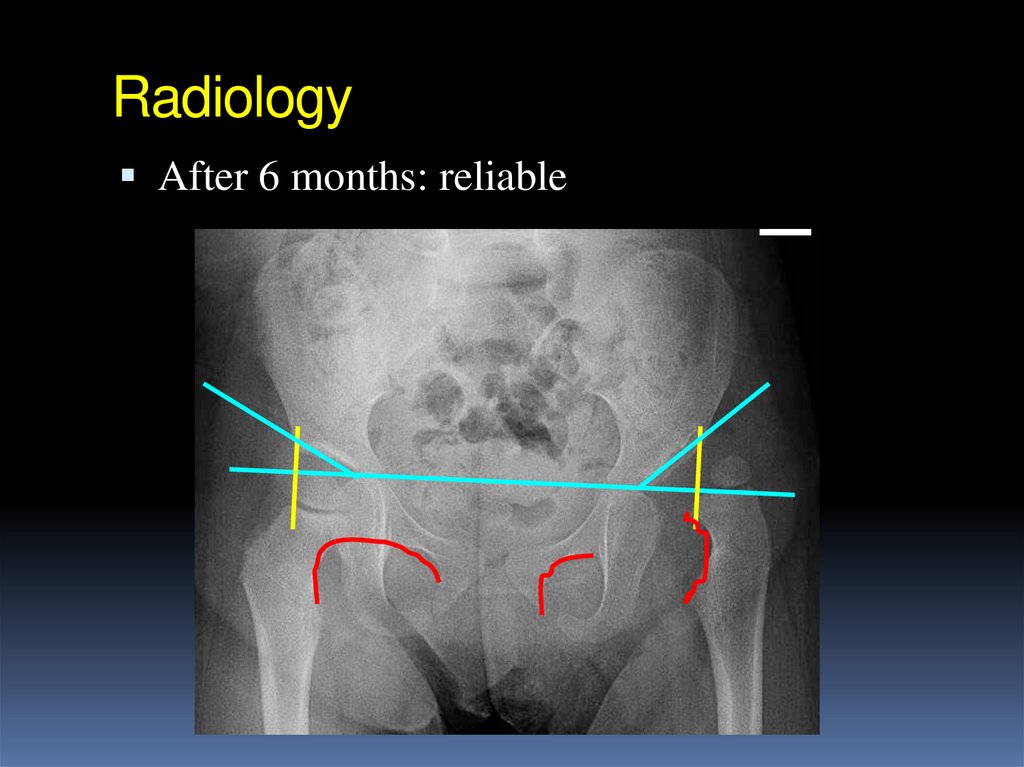
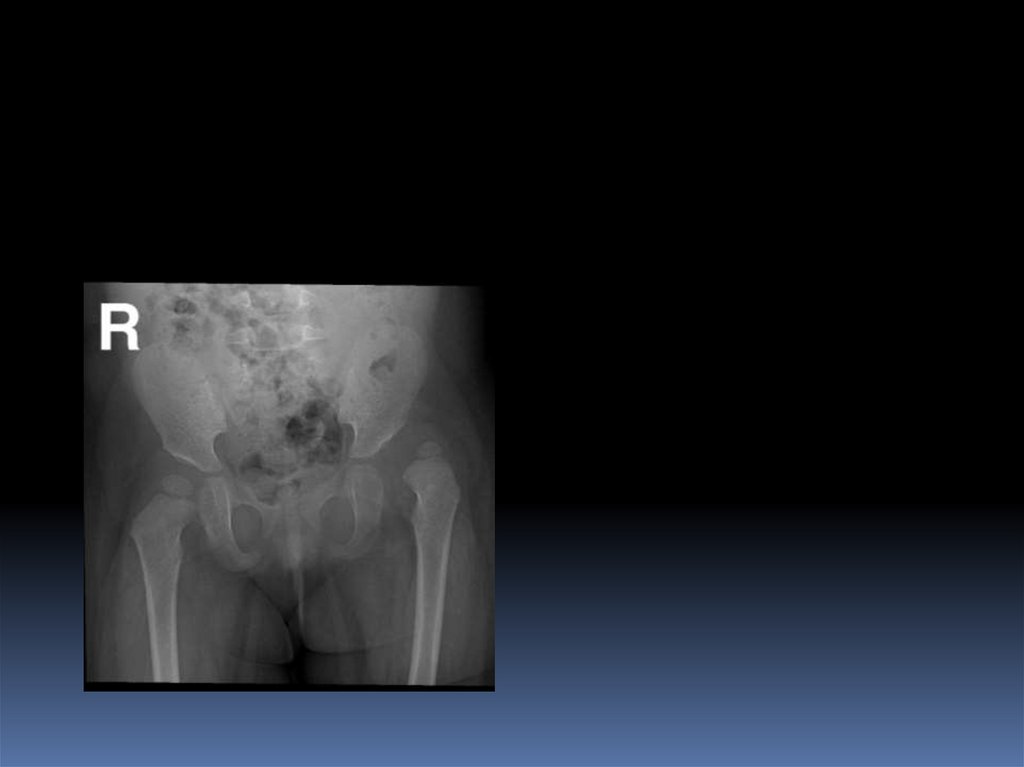
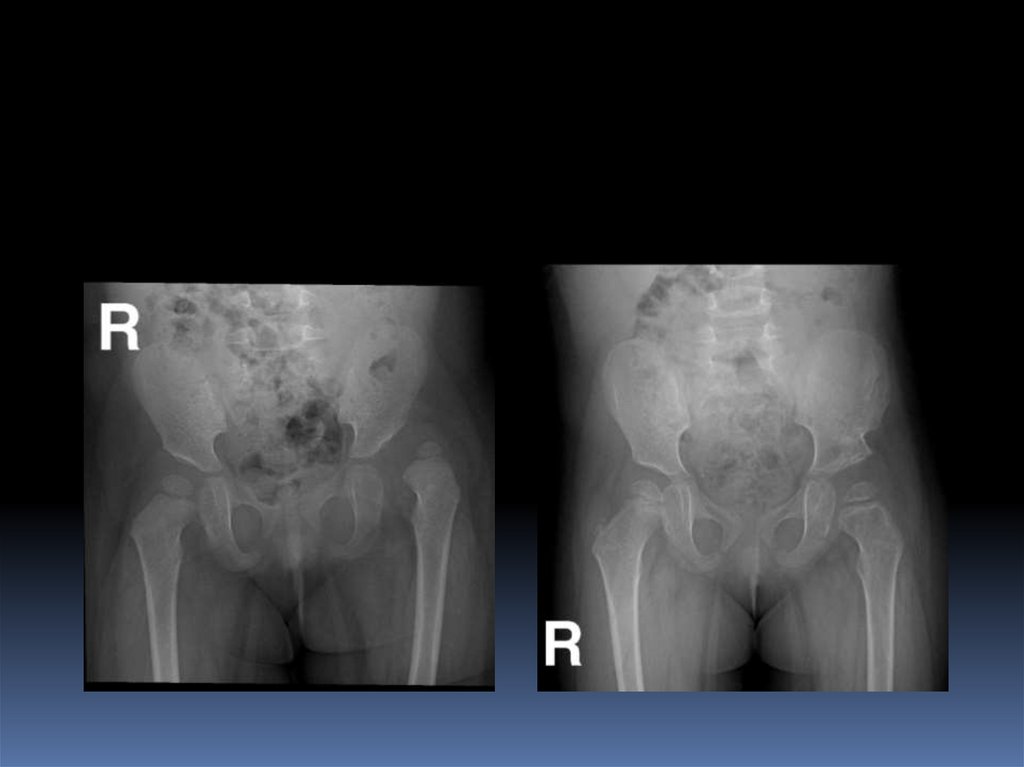
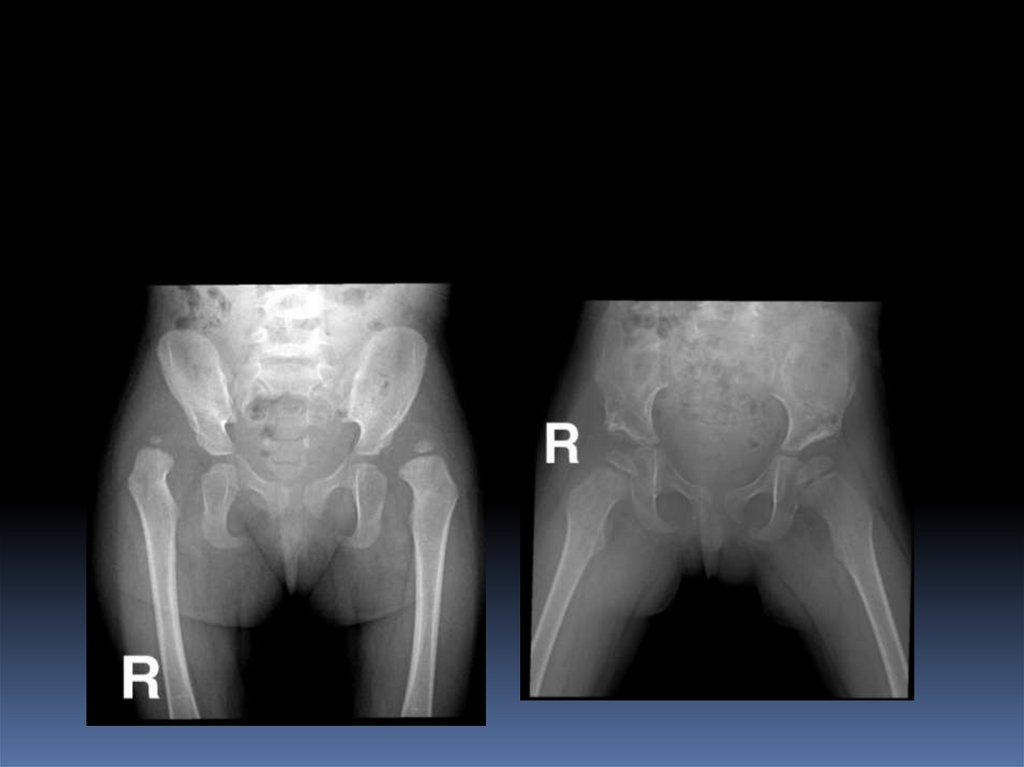
After 6 months: reliable31. Radiology
After 6 months: reliable32. Treatment - Aims
Obtain concentric reductionMaintain concentric reduction
In a non-traumatic fashion
Without disrupting the blood supply to
femoral head
33. Treatment
Method depends on ageThe earlier started, the easier it is
The earlier started, the better the results are
Should be detected EARLY
34. Treatment
Birth – 6mPavlik harness or hip spica
6-12 m:
Closed reduction under GA and hip spica
12 - 18 m:
Open reduction
18 – 24 m:
Open reduction and Acetabuloplasty
2-8 years:
Open reduction, Acetabuloplasty, and femoral shortening
Above 8 years:
Open reduction, Acetabuloplasty cutting all three pelvic bones, and
femoral shortening
35. Treatment: Neonatal hip instability
Most resolve spontaneouslyCan initially wait
Avoid adduction swaddle
Apply double diapers – to bring back!!
See at 2weeks of age
36. Treatment: Neonatal hip instability
Unstable at 2 weeks:Double / Triple diapers: inadequate
Gives illusion that patient is “in treatment” while
wasting valuable time
37. Treatment: Neonatal hip instability
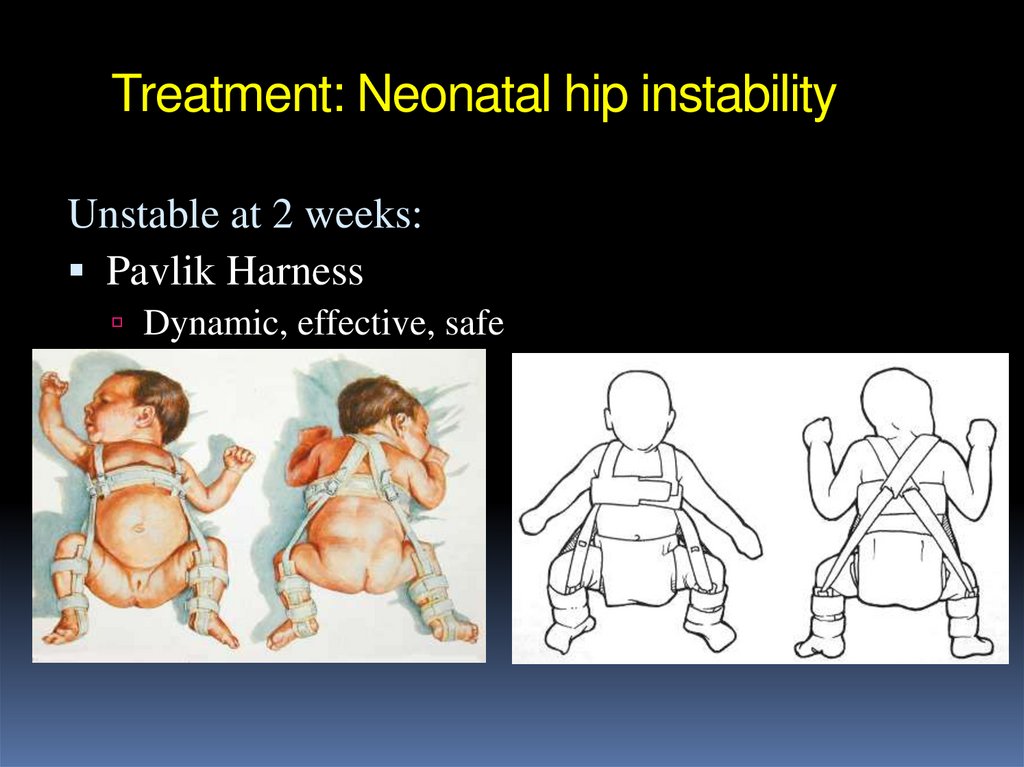
Unstable at 2 weeks:Pavlik Harness
Dynamic, effective, safe
38. Treatment: 6-12 m
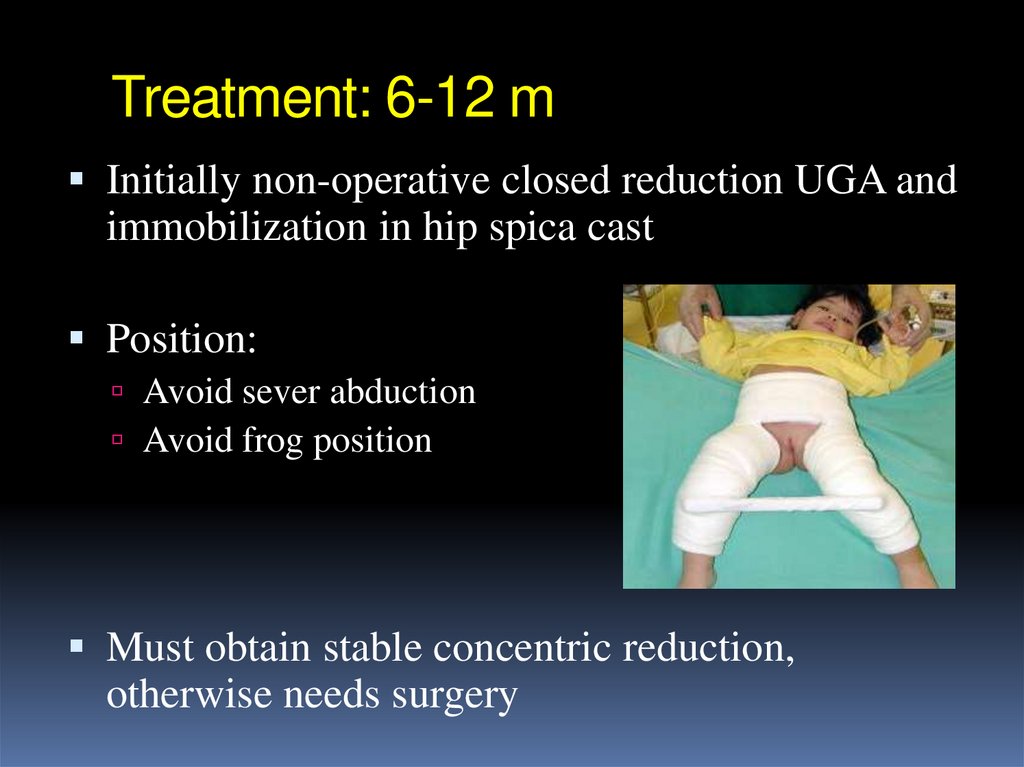
Initially non-operative closed reduction UGA andimmobilization in hip spica cast
Position:
Avoid sever abduction
Avoid frog position
Must obtain stable concentric reduction,
otherwise needs surgery
39. Treatment: 6-12 m
Possibly closed reductionStable and concentric reduction
Possibly open reduction
Unstable or un-concentric reduction
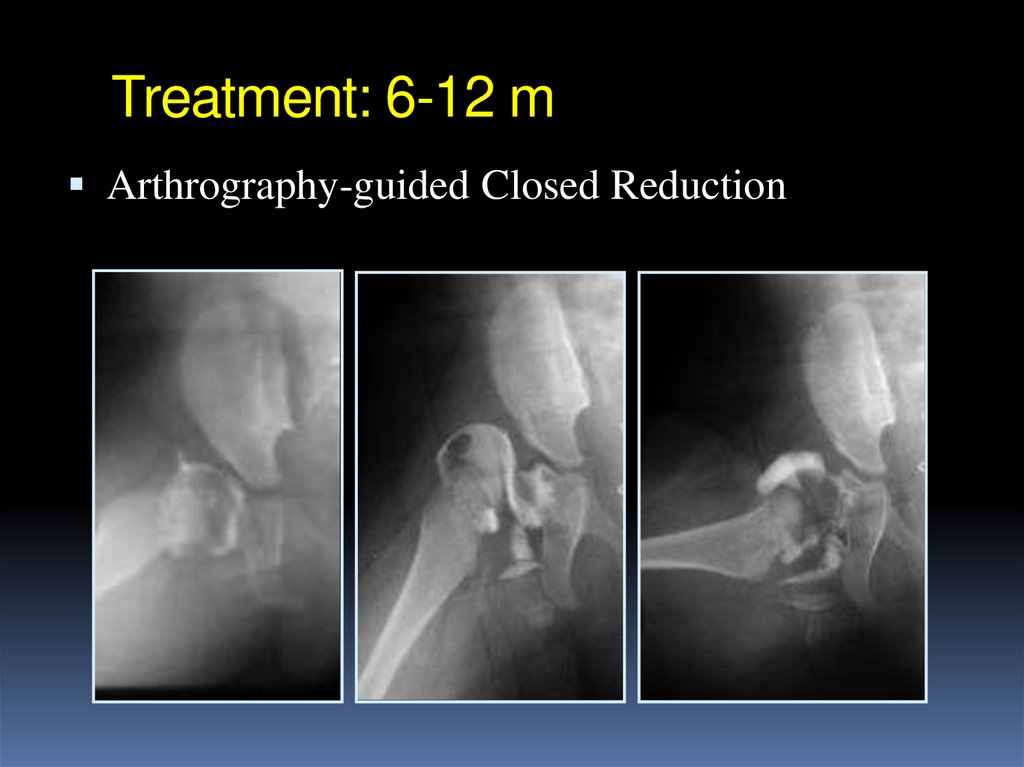
Arthrography-guided
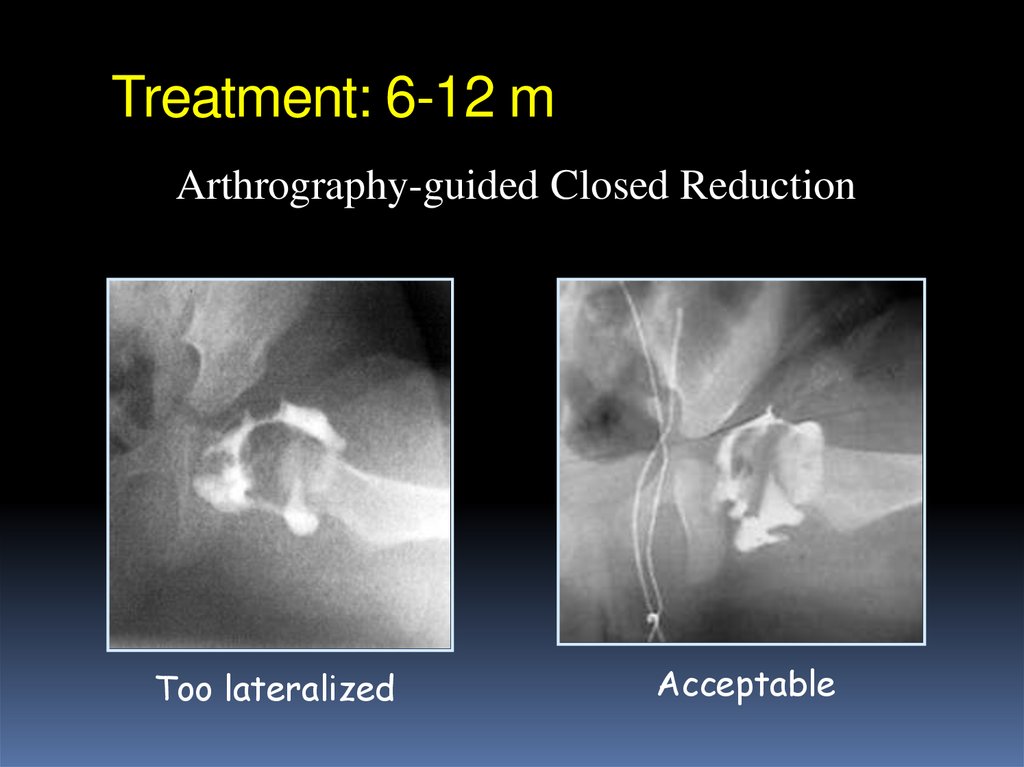
40. Treatment: 6-12 m
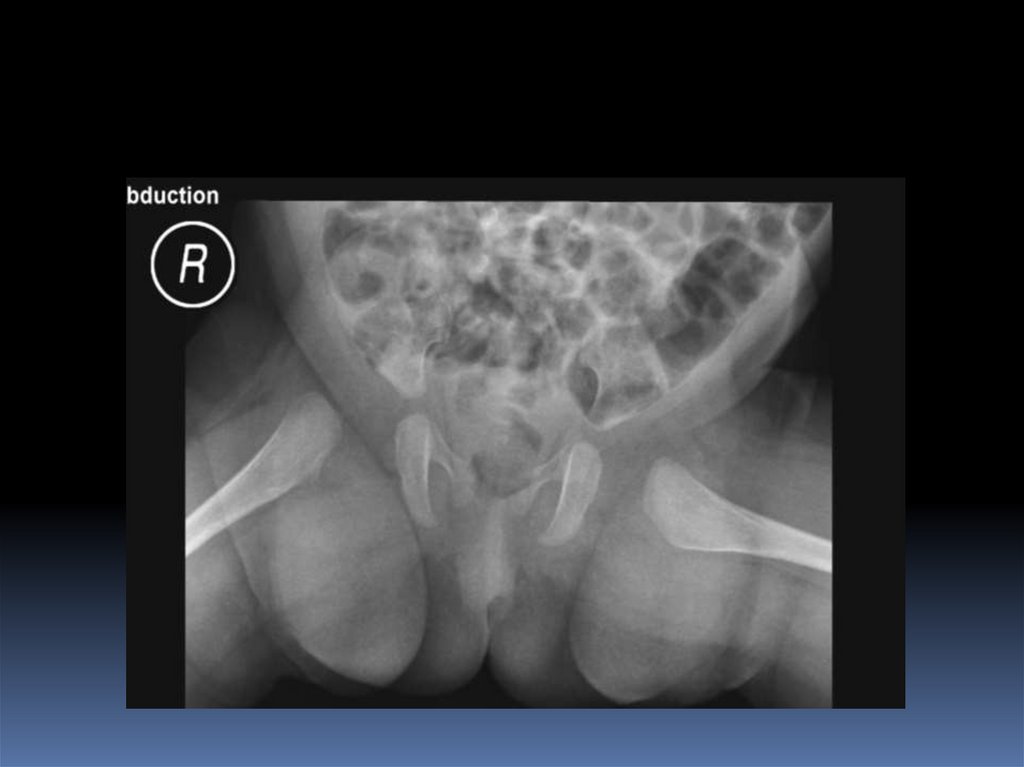
Arthrography-guided Closed Reduction41. Treatment: 6-12 m
Arthrography-guided Closed ReductionToo lateralized
Acceptable
42. Treatment: 6-12 m
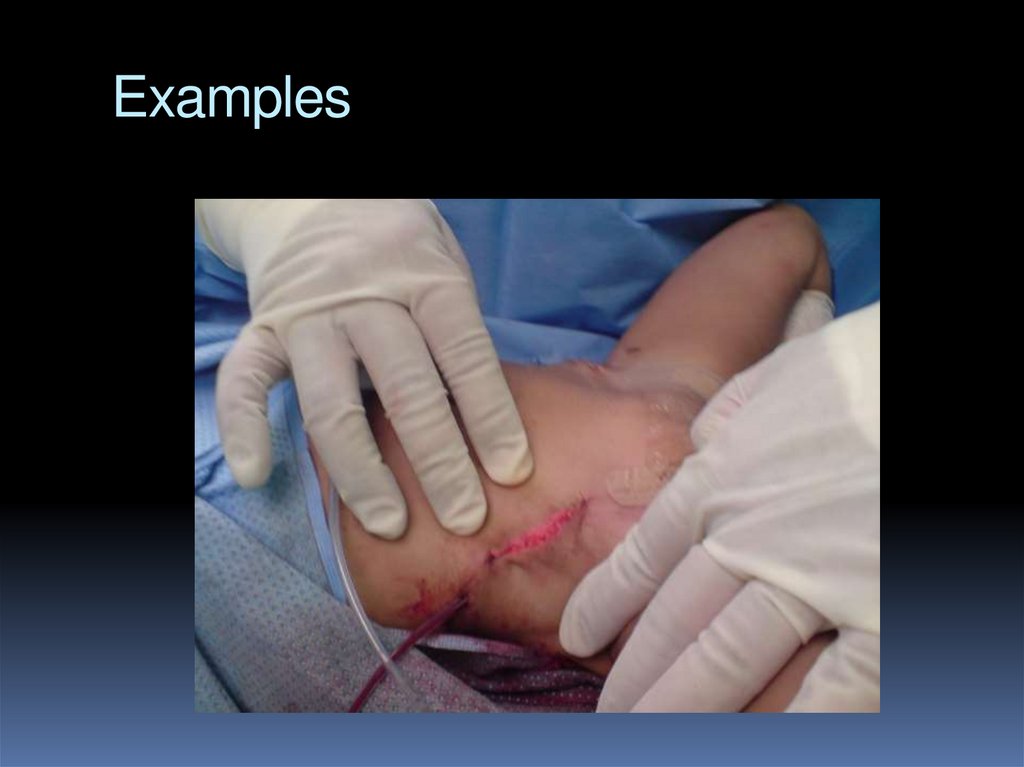
Treatment: 18-24 mOpen reduction – surgery
Possibly: Acetabuloplasty
43. Treatment: 18-24 m
Treatment: Above 2 yearsOpen reduction, and
Acetabuloplasty, and
Femoral shortening
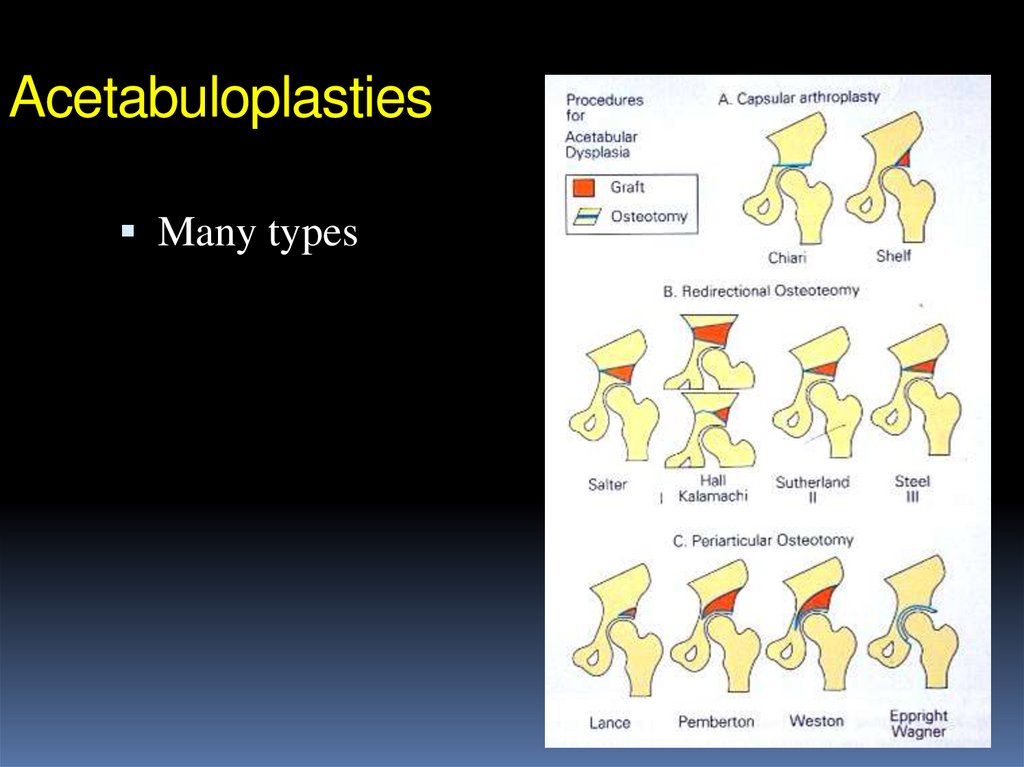
44. Treatment: Above 2 years
AcetabuloplastiesMany types
45. Acetabuloplasties
46.
TreatmentBirth – 6m
Pavlik harness or hip spica
6-12 m:
Closed reduction under GA and hip spica
12 - 18 m:
Open reduction
18 – 24 m:
Open reduction and Acetabuloplasty
2-8 years:
Open reduction, Acetabuloplasty, and femoral shortening
Above 8 years:
Open reduction, Acetabuloplasty cutting all three pelvic bones, and
femoral shortening
47. Treatment
CDH - SummaryComplex multi-factorial, endemic disease
Health education and Drs. awareness
Screening programs are needed
Learning proper examination methods
Identify at risk groups
Efficient referral system
Proper management by specialized Drs