Похожие презентации:
Pattern. Planning Assistance Through Technical Evaluation of Relevance Numbers
1. PATTERN
Planning Assistance ThroughTechnical Evaluation of
Relevance Numbers
2. PATTERN
Normative forecastingRelevance tree method
Goal-oriented forecasting method where one
establishes a future need and recedes
backwards to the present and to the
technologies needed to achieve the objective
of the future.
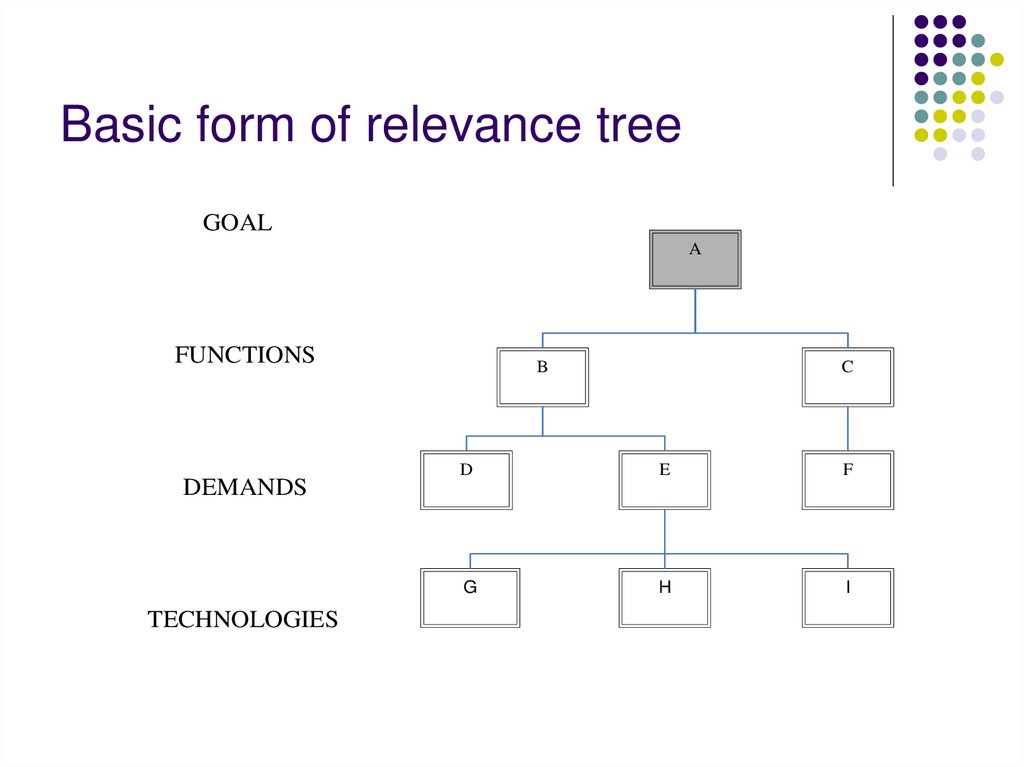
3. Basic form of relevance tree
GOALA
FUNCTIONS
DEMANDS
TECHNOLOGIES
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
4. Characteristics for forming the relevance tree:
There is hierarchy in the relevance treeBranches represent goals and subgoals
All relevant subgoals for each goal have to
be identified
Each branch must be well defined so that
there are no overlaps
5. PATTERN
PATTERN has been used by the HoneywellCorporation for military, space and medical
purposes.
6. PATTERN is based on:
Goal identificationRecognizing the relevance of set goals in
relation to criteria (means ranking, e.g.
setting goals priority)
Recognizing technological alternatives
necessary for achieving the goal
7. Steps for PATTERN
Model description, recognizing the goals andhierarchy of the relevance tree
Recognize criteria
Determine relevance numbers – with
participation of experts; selected exploratory,
intuitive methods can be used
Data processing and final results –
calculating relevance numbers, goals priority,
ranking of technological alternatives
8. Basic terms
Goals A, B,C...j...NCriteria α, β, …, x, …, v.
Levels 1, 2, 3...i...n
Criteria weights
Wα, Wβ, …, Wx, …, Wv.
Contribution marks of the goal j to criteria x element weights
Sjα, Sjβ, …, Sjx, …, Sjv.
Based on the relevance tree primary matrix has to
be made for each expert
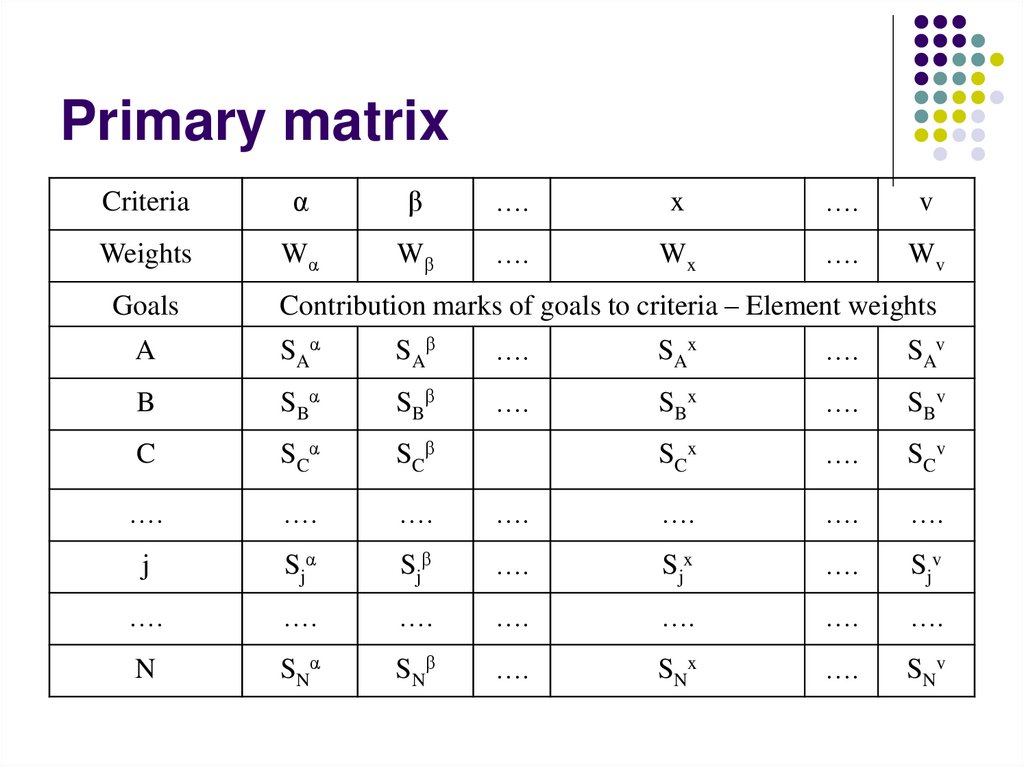
9. Primary matrix
Criteriaα
β
….
x
….
v
Weights
Wα
Wβ
….
Wx
….
Wv
Goals
Contribution marks of goals to criteria – Element weights
A
SAα
SAβ
….
SAx
….
SAv
B
SBα
SBβ
….
SBx
….
SBv
C
SCα
SCβ
SCx
….
SCv
….
….
….
….
….
….
….
j
S jα
Sjβ
….
Sjx
….
Sjv
….
….
….
….
….
….
….
N
SNα
SNβ
….
SNx
….
SNv
10. Basic terms
Based on the primary matrix the final primarymatrix has to be calculated
The elements of final primary matrix are
average values of responding elements in
primary matrixes
11. Basic terms
A panel of experts can be asked to weight theimportance of each criterium in relation to the
others
The panel could be asked to weight the
contribution of each element/goal to criteria –
element weights
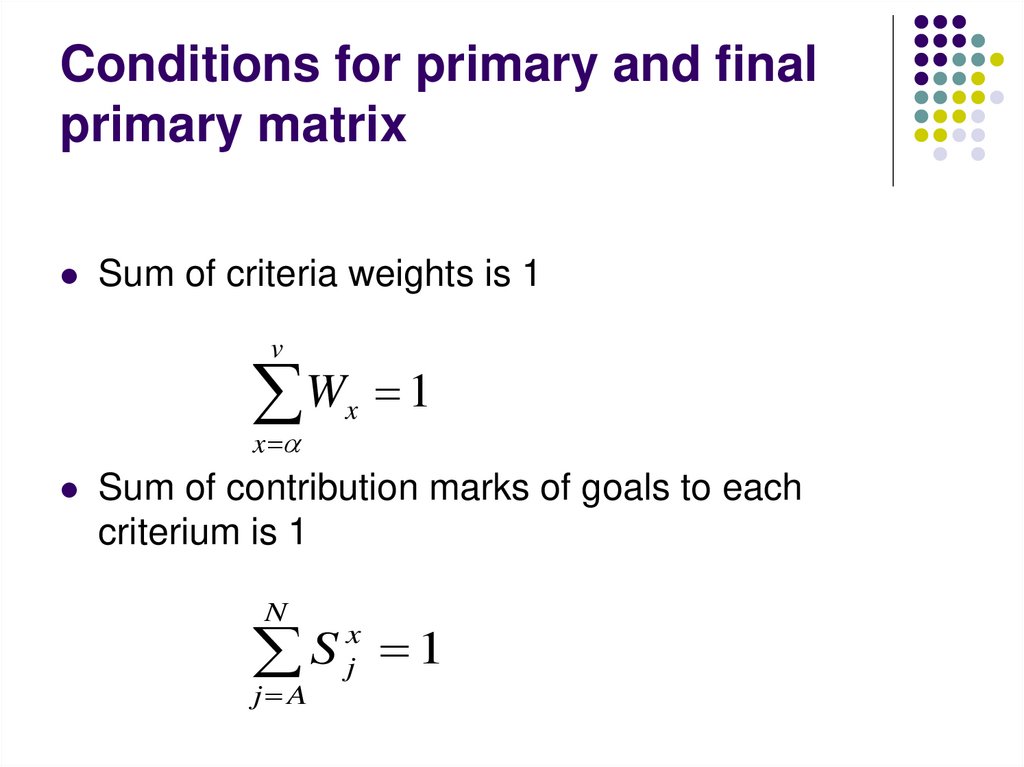
12. Conditions for primary and final primary matrix
Sum of criteria weights is 1v
W 1
x
x
Sum of contribution marks of goals to each
criterium is 1
N
S 1
j A
x
j
13.
Partial relevance numbers(relevance of goal j for
criterium x)
Local relevance numbers
(relevance of goal j at
level i)
PRN Wx S
x
j
v
ri Wx S
j
x
x
j
x
j
14.
Condition – Sum oflocal relevance numbers
at one level has to be 1
N
ri 1
j A
j
15.
Cumulative directrelevance number –
Relevance of goal j for
main goal, whole
relevance tree
n
R ri
i 1
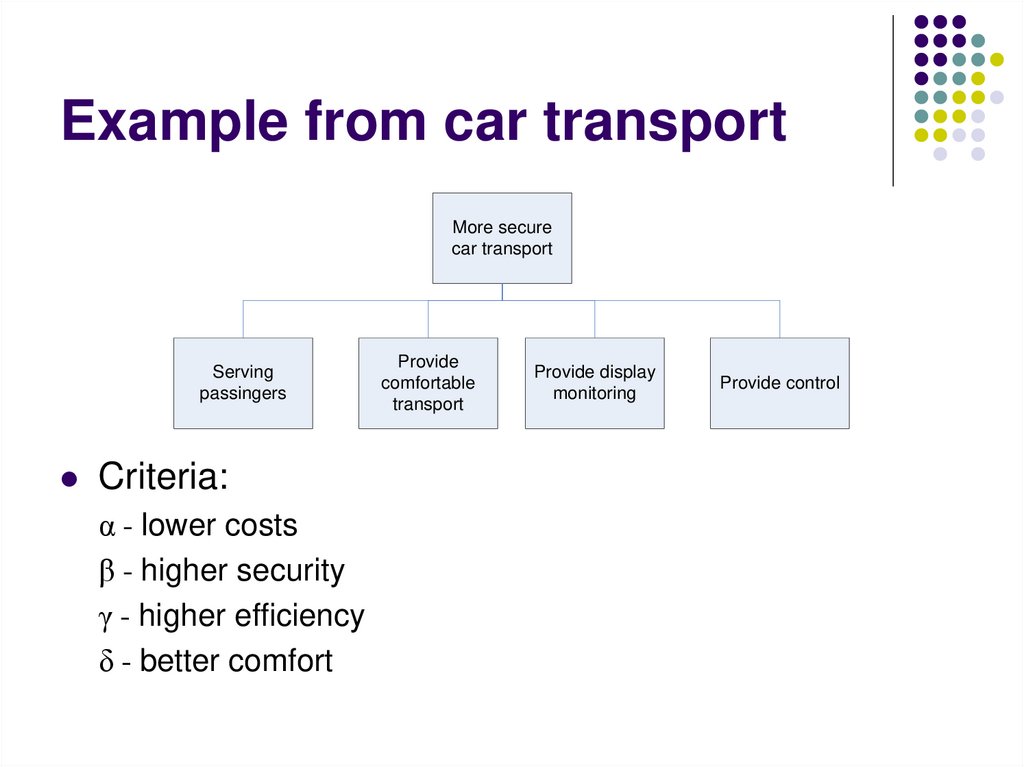
16. Example from car transport
More securecar transport
Serving
passingers
Criteria:
α - lower costs
β - higher security
γ - higher efficiency
δ - better comfort
Provide
comfortable
transport
Provide display
monitoring
Provide control











 Математика
Математика Информатика
Информатика








