Похожие презентации:
What is acute coronary syndrome?
1.
- RAJA KUMAR PREMJITH RAJA2.
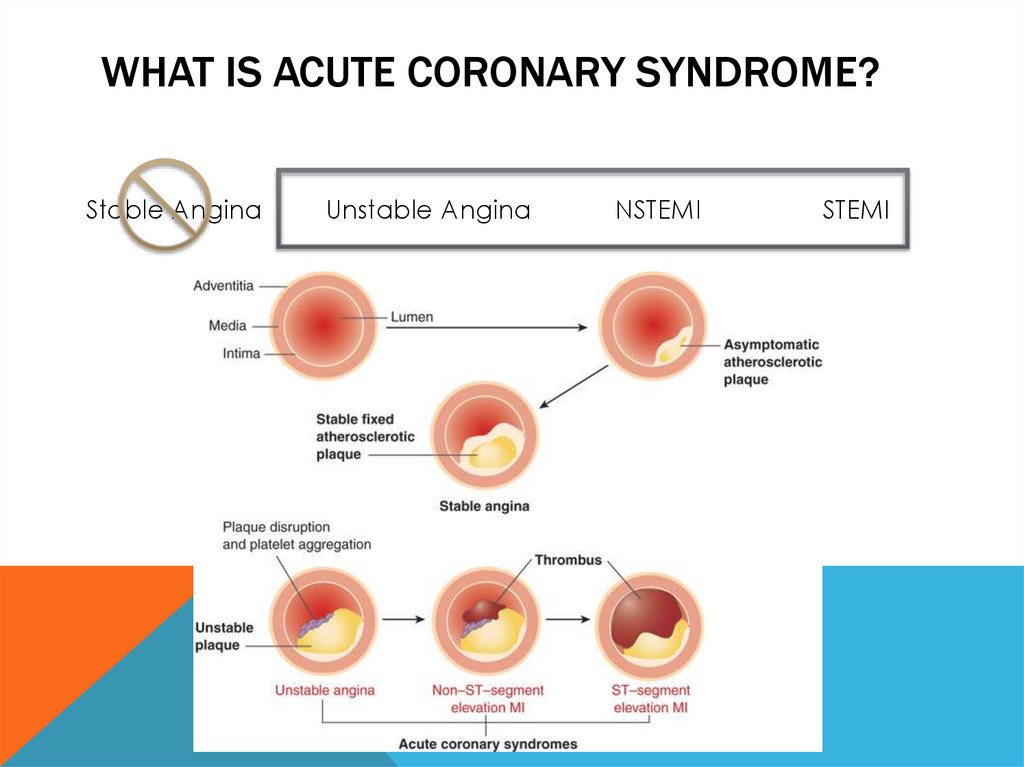
WHAT IS ACUTE CORONARY SYNDROME?Stable Angina
Unstable Angina
NSTEMI
STEMI
3.
DEFINITIONSUnstable angina:
An unprovoked or prolonged episode of chest pain raising suspicion of
acute myocardial infarction (AMI)
Without definite ECG or laboratory evidence
NSTEMI:
Chest pain suggestive of AMI
Non-specific ECG changes (ST depression/T inversion/normal)
Laboratory tests showing release of troponins
STEMI:
Sustained chest pain suggestive of AMI
Acute ST elevation or new LBBB
4.
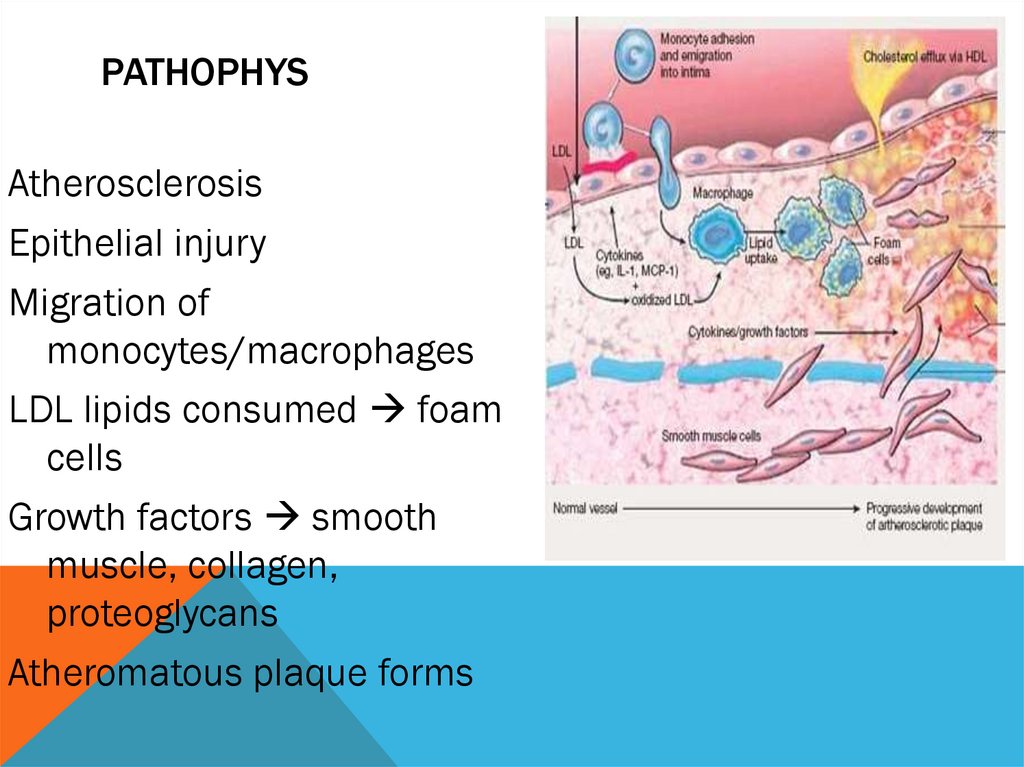
PATHOPHYSAtherosclerosis
Epithelial injury
Migration of
monocytes/macrophages
LDL lipids consumed foam
cells
Growth factors smooth
muscle, collagen,
proteoglycans
Atheromatous plaque forms
5.
RISK FACTORSSmoking
Increasing age
Obesity
Gender (male)
Diet
Family History
Lack of exercise
Hypertension
High serum cholesterol
Diabetes
6.
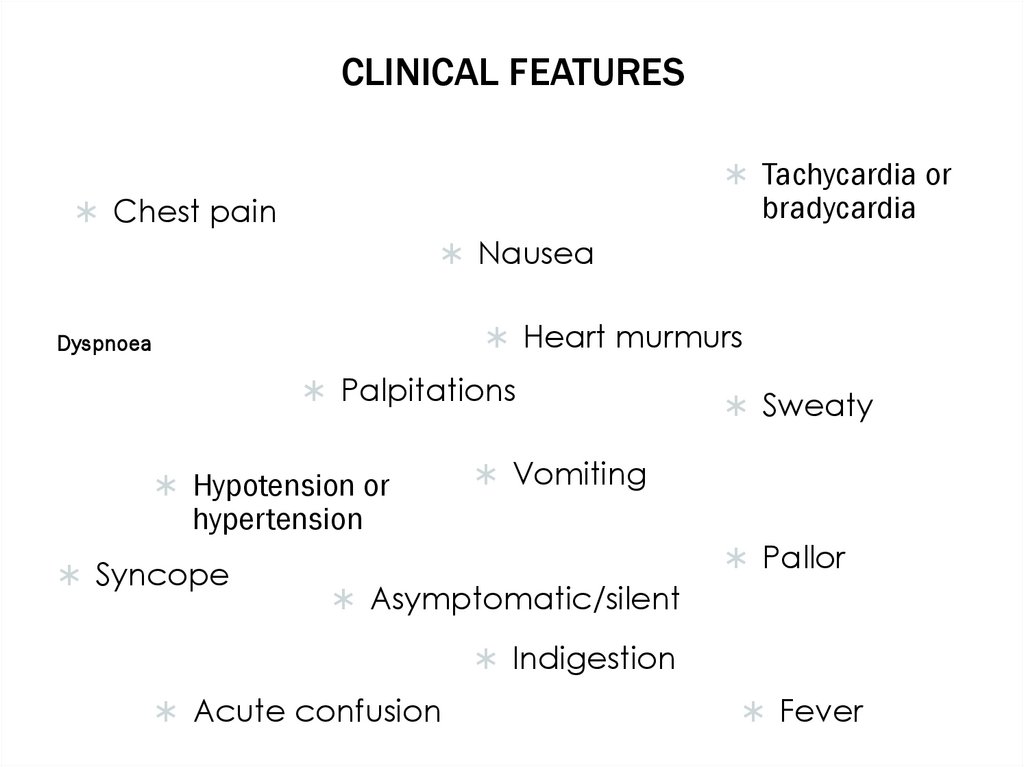
CLINICAL FEATURESTachycardia or
bradycardia
Chest pain
Nausea
Heart murmurs
Dyspnoea
Palpitations
Hypotension or
Sweaty
Vomiting
hypertension
Syncope
Pallor
Asymptomatic/silent
Indigestion
Acute confusion
Fever
7.
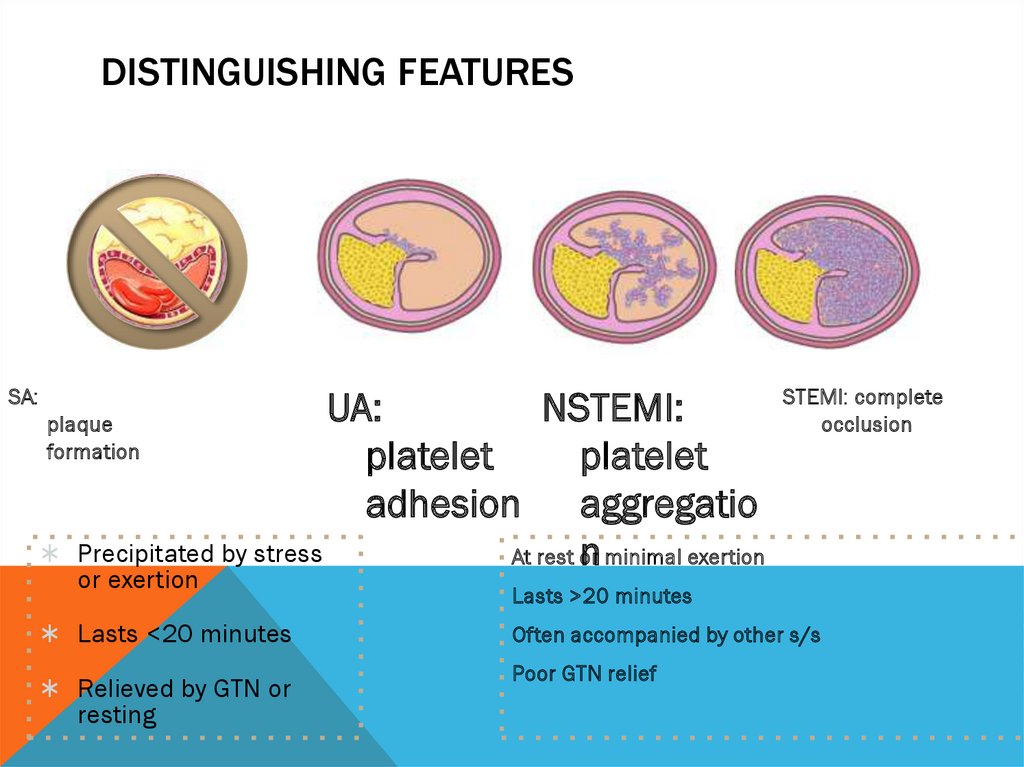
DISTINGUISHING FEATURESSA:
UA:
NSTEMI:
plaque
formation
platelet
platelet
adhesion aggregatio
Precipitated by stress
At rest or
n minimal exertion
or exertion
Lasts <20 minutes
Relieved by GTN or
resting
STEMI: complete
occlusion
Lasts >20 minutes
Often accompanied by other s/s
Poor GTN relief
8.
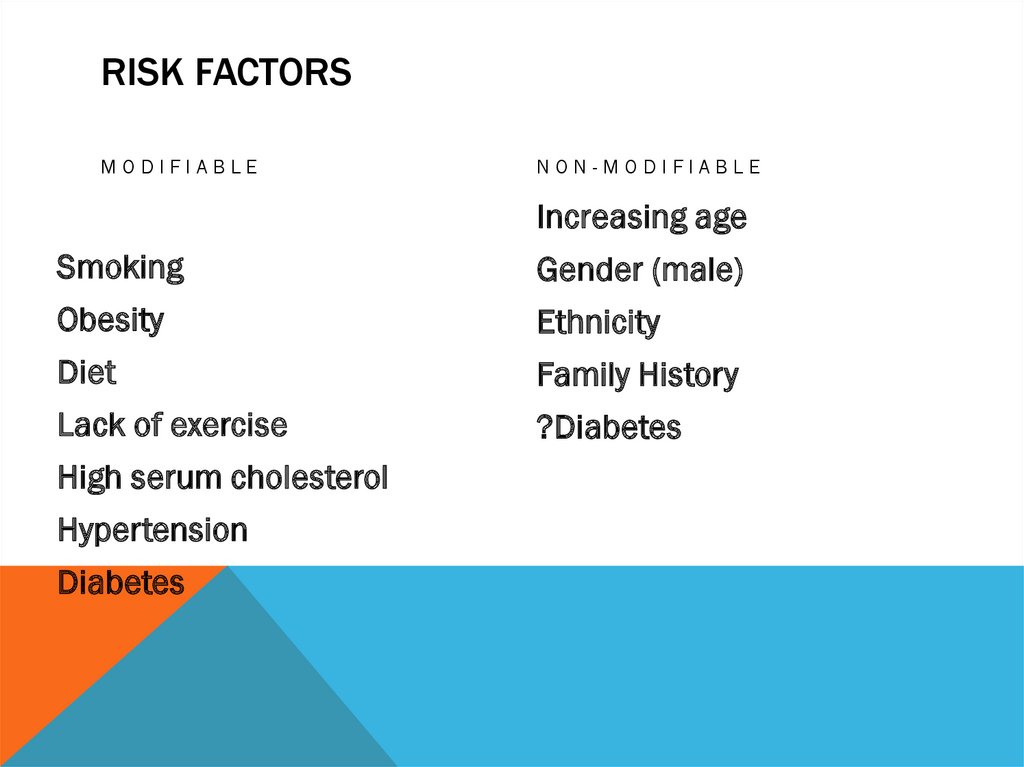
RISK FACTORSMODIFIABLE
NON-MODIFIABLE
Increasing age
Smoking
Gender (male)
Obesity
Ethnicity
Diet
Family History
Lack of exercise
?Diabetes
High serum cholesterol
Hypertension
Diabetes
9.
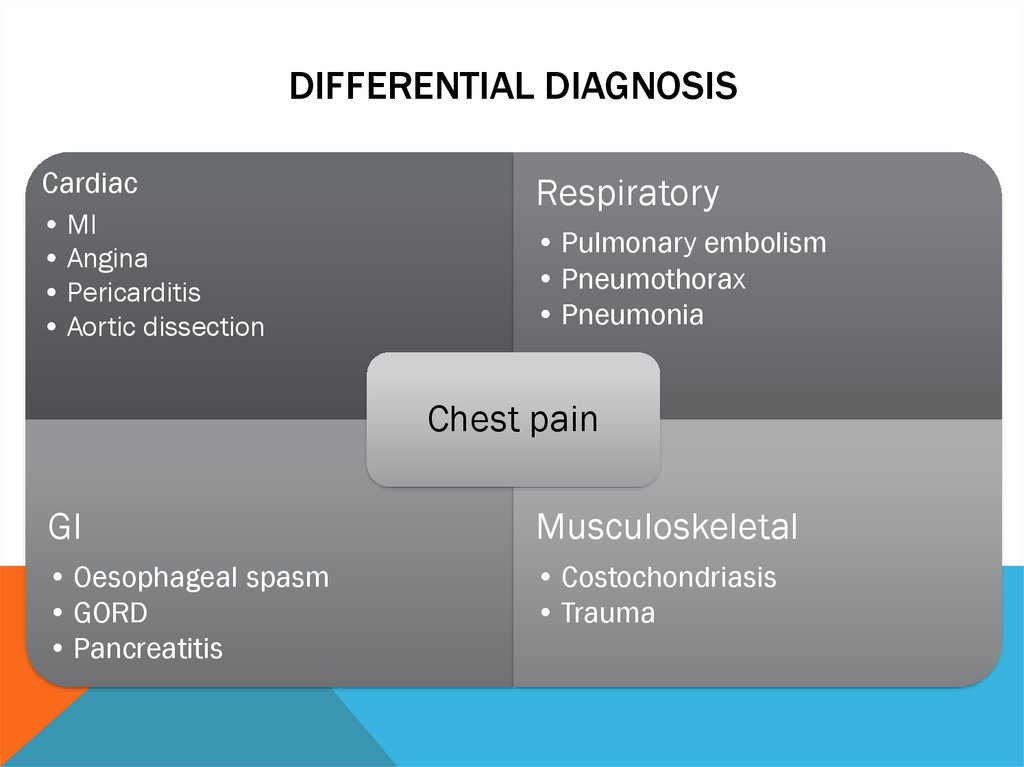
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSISCardiac
• MI
• Angina
• Pericarditis
• Aortic dissection
Respiratory
• Pulmonary embolism
• Pneumothorax
• Pneumonia
Chest pain
GI
Musculoskeletal
• Oesophageal spasm
• GORD
• Pancreatitis
• Costochondriasis
• Trauma
10.
WHAT DO YOU WANT TO ASK HIM/HER?30minute history of central ‘crushing’ chest pain radiating to his jaw and left arm,
10/10
He is SOB, looks very pale, clammy and sweaty, and has vomited twice
PMHx of hypertension and hypercholesterolaemia
Takes metformin, salbutamol inhalers and citalopram
FHx includes father dying of MI aged 50
Smoked 40 cigarettes a day for the past 35 years and drinks a bottle of whiskey a
week
Cant exercise “because of my asthma”
11.
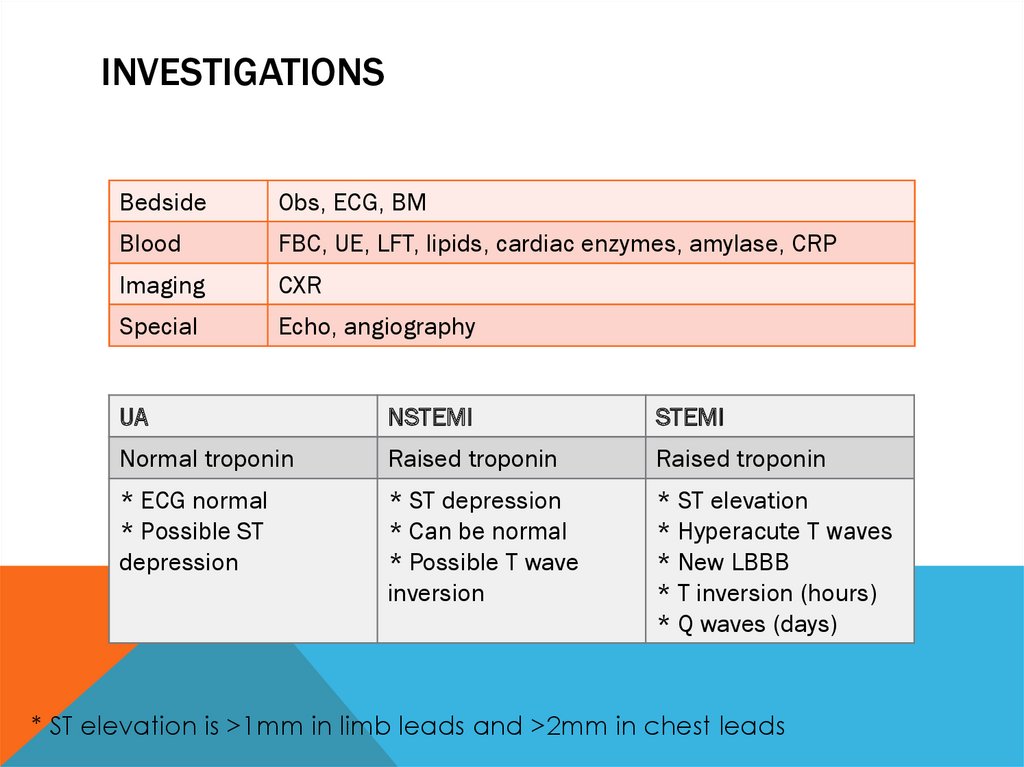
INVESTIGATIONSBedside
Obs, ECG, BM
Blood
FBC, UE, LFT, lipids, cardiac enzymes, amylase, CRP
Imaging
CXR
Special
Echo, angiography
UA
NSTEMI
STEMI
Normal troponin
Raised troponin
Raised troponin
* ECG normal
* Possible ST
depression
* ST depression
* Can be normal
* Possible T wave
inversion
* ST elevation
* Hyperacute T waves
* New LBBB
* T inversion (hours)
* Q waves (days)
* ST elevation is >1mm in limb leads and >2mm in chest leads
12.
IMPORTANT ECG FINDINGS13.
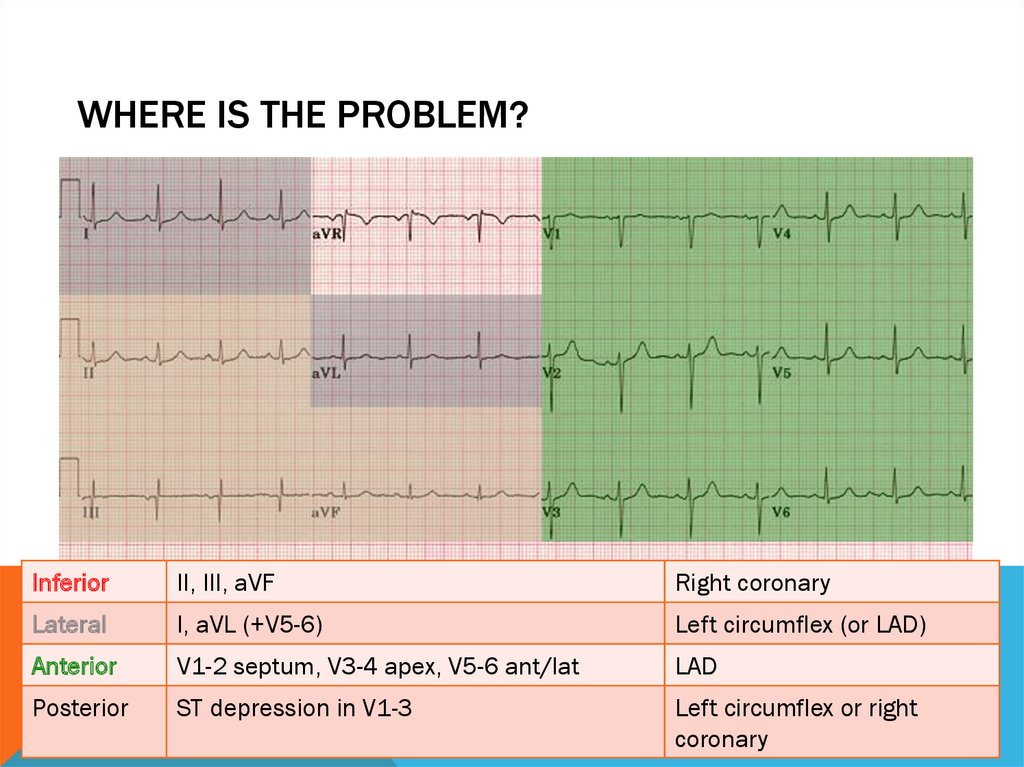
WHERE IS THE PROBLEM?Inferior
II, III, aVF
Right coronary
Lateral
I, aVL (+V5-6)
Left circumflex (or LAD)
Anterior
V1-2 septum, V3-4 apex, V5-6 ant/lat
LAD
Posterior
ST depression in V1-3
Left circumflex or right
coronary
14.
COMMON ACS MANAGEMENTMorphine (5-10mg slow IV injection)
Oxygen (titrate sats to need)
Nitrates - GTN spray (400mcg = 1 spray) or tablet (1mg)
Aspirin (300mg chewed)
Plus an antiemetic i.e.
Metoclopramide 10mg IV
15.
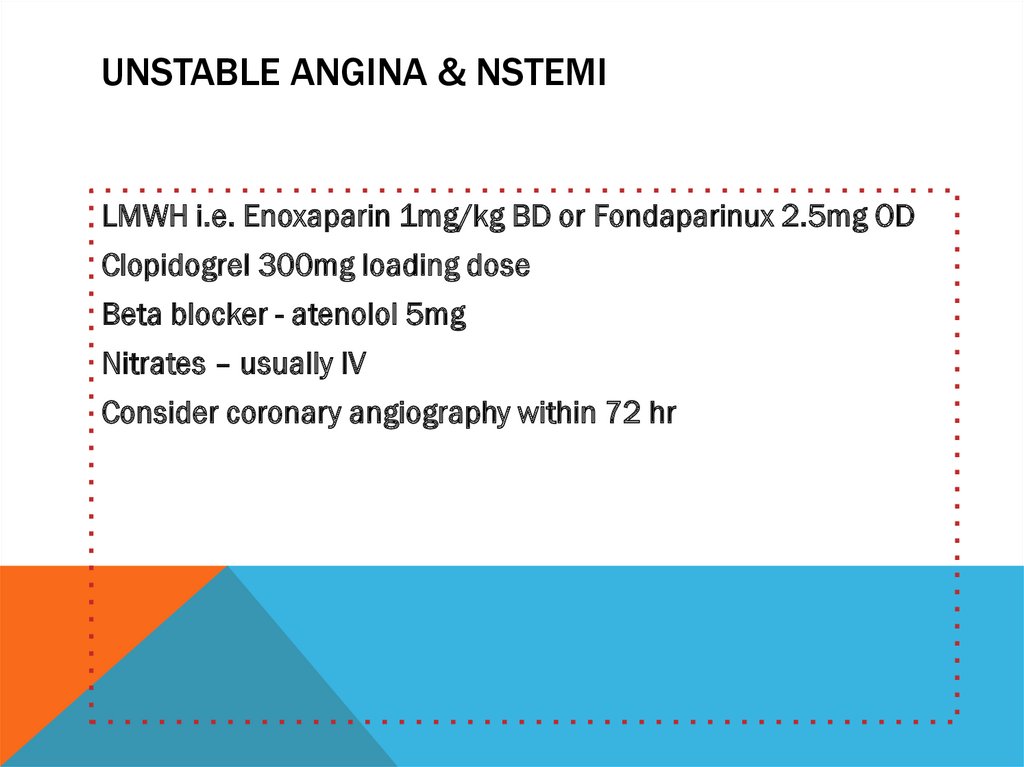
UNSTABLE ANGINA & NSTEMILMWH i.e. Enoxaparin 1mg/kg BD or Fondaparinux 2.5mg OD
Clopidogrel 300mg loading dose
Beta blocker - atenolol 5mg
Nitrates – usually IV
Consider coronary angiography within 72 hr
16.
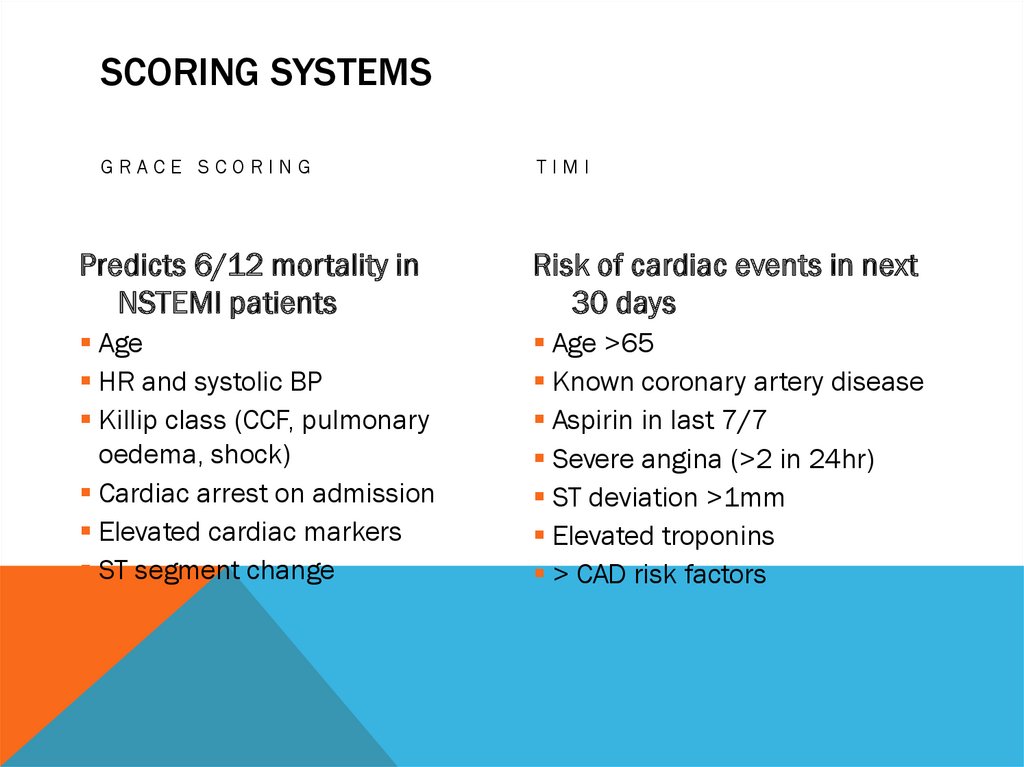
SCORING SYSTEMSGRACE SCORING
TIMI
Predicts 6/12 mortality in
NSTEMI patients
Risk of cardiac events in next
30 days
Age
HR and systolic BP
Killip class (CCF, pulmonary
oedema, shock)
Cardiac arrest on admission
Elevated cardiac markers
ST segment change
Age >65
Known coronary artery disease
Aspirin in last 7/7
Severe angina (>2 in 24hr)
ST deviation >1mm
Elevated troponins
> CAD risk factors
17.
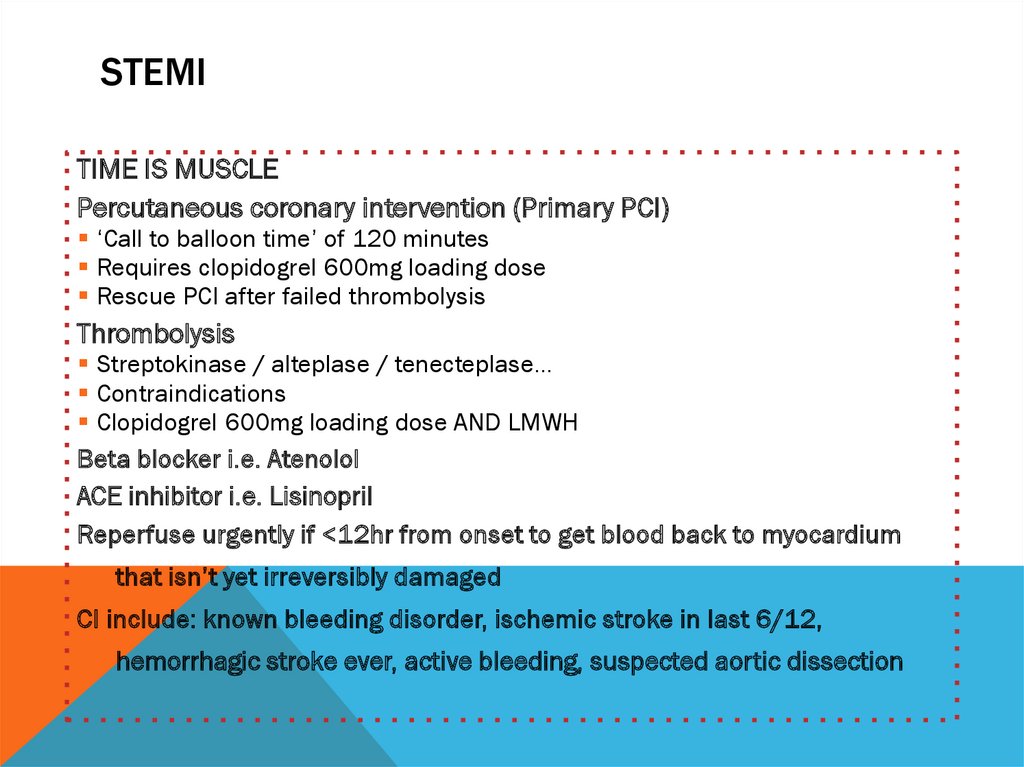
STEMITIME IS MUSCLE
Percutaneous coronary intervention (Primary PCI)
‘Call to balloon time’ of 120 minutes
Requires clopidogrel 600mg loading dose
Rescue PCI after failed thrombolysis
Thrombolysis
Streptokinase / alteplase / tenecteplase…
Contraindications
Clopidogrel 600mg loading dose AND LMWH
Beta blocker i.e. Atenolol
ACE inhibitor i.e. Lisinopril
Reperfuse urgently if <12hr from onset to get blood back to myocardium
that isn’t yet irreversibly damaged
CI include: known bleeding disorder, ischemic stroke in last 6/12,
hemorrhagic stroke ever, active bleeding, suspected aortic dissection
18.
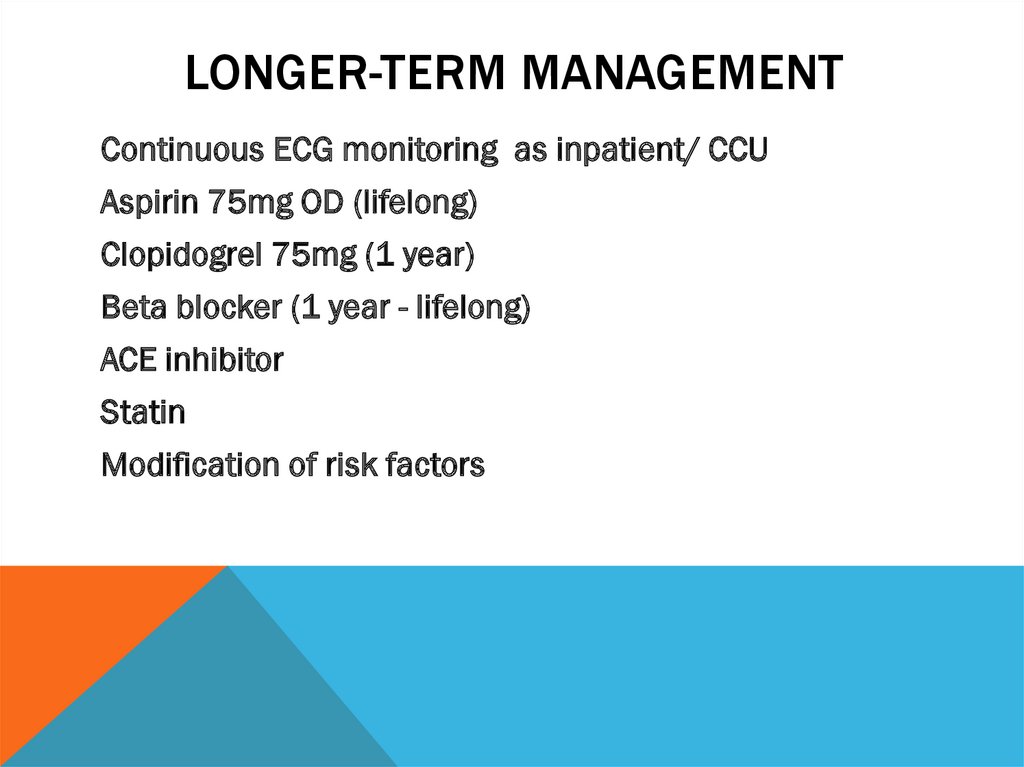
LONGER-TERM MANAGEMENTContinuous ECG monitoring as inpatient/ CCU
Aspirin 75mg OD (lifelong)
Clopidogrel 75mg (1 year)
Beta blocker (1 year - lifelong)
ACE inhibitor
Statin
Modification of risk factors
19.
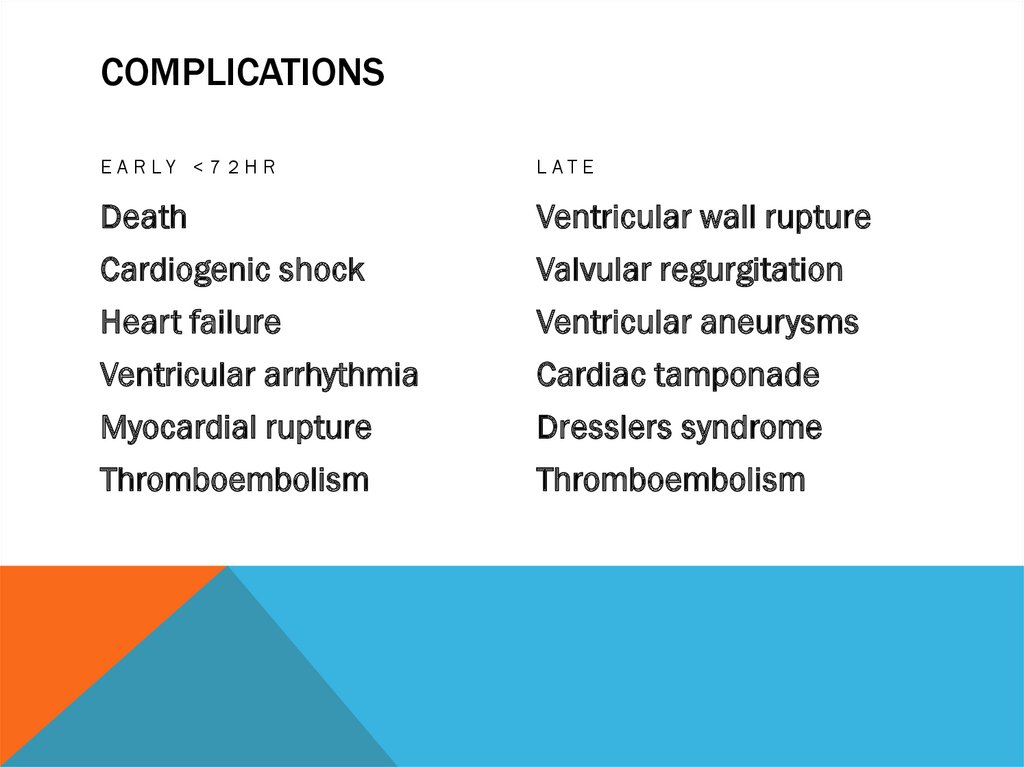
COMPLICATIONSE A R LY < 7 2 H R
LAT E
Death
Ventricular wall rupture
Cardiogenic shock
Valvular regurgitation
Heart failure
Ventricular aneurysms
Ventricular arrhythmia
Cardiac tamponade
Myocardial rupture
Dresslers syndrome
Thromboembolism
Thromboembolism





 Медицина
Медицина








